Taxonomy
Prionailurus was first proposed by the Russian explorer and naturalist Nikolai Severtzov in 1858 as a generic name for a single felid occurring in tropical Asia, namely Felis pardachrous described by Brian Houghton Hodgson — the leopard cat. As varieties, Severtzov lists Felis nipalensis described by Thomas Horsfield and Nicholas Aylward Vigors, Leopardus Elliotti, Leopardus Horsfieldi and Leopardus chinensis described by John Edward Gray, and Felis bengalensis described by Anselme Gaëtan Desmarest. [5]
The British zoologist Reginald Innes Pocock recognized the taxonomic classification of Prionailurus in 1917. In 1939, he described the genus on the basis of skins and skulls, and compared these to body parts of Felis . Prionailurus species are marked with spots, which are frequently lanceolate, sometimes rosette-like, and occasionally tend to run into longitudinal chains, but never fuse to form vertical stripes as in Felis. Skulls of Prionailurus are lower and less vaulted than of Felis. The facial part is shorter than the cranial, and the bottom of the orbit longer. The nasal bones are not everted above the anterior nares, and the outer chamber of the bulla is much smaller than the inner. Pocock classified the leopard cat, rusty-spotted cat and fishing cat as belonging to the genus Prionailurus. [2]
Pocock's classification of Prionailurus has been widely accepted, with five species now recognised: [6]
Genus Prionailurus – Severtzov, 1858 – five species| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|
| Leopard cat  | Prionailurus bengalensis [7]
(Kerr, 1792)
- P. b. bengalensis (Kerr, 1792)
- P. b. euptilura (Elliott, 1871)
| continental South, Southeast and East Asia.
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
|
|---|
| Sunda leopard cat  | Prionailurus javanensis [8]
(Desmarest, 1816)
- P. j. javanensis (Desmarest, 1816)
- P. j. sumatranus (Horsfield, 1821)
| Sundaland islands of Java, Bali, Borneo, Sumatra and the Philippines
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | |
|---|
| Flat-headed cat  | Prionailurus planiceps [9]
(Vigors & Horsfield, 1827) | Thai-Malay Peninsula, Borneo and Sumatra.
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | EN
|
|---|
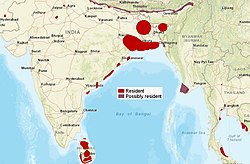
| Fishing cat  | Prionailurus viverrinus [10]
(Bennett, 1833) | South and Southeast Asia
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | VU
|
|---|
| Rusty-spotted cat  | Prionailurus rubiginosus [11]
(Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1834) | Nepal, India and Sri Lanka
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | NT
|
|---|
| Prionailurus kurteni
| Prionailurus kurteni
Jiangzuo et al., 2024 | Anhui, China | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | Fossil species |
|---|
The fossil species Prionailurus kurteni was found in Pleistocene deposits of China. [12]
Molecular analysis of leopard cat populations indicates a clear distinction between northern populations from Tsushima, Korea, Siberia, China and Taiwan and Southeast Asian populations. If these genetic differences indicate a specific distinction, P. b. euptilurus may yet be a valid species. [13] The Iriomote cat (P. bengalensis iriomotensis) has been proposed as a distinct species based on morphology, but is considered a subspecies of P. bengalensis based on genetic analysis. [14]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.











