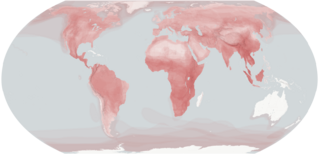
Carnivora is an order of placental mammals that have specialized in primarily eating flesh, whose members are formally referred to as carnivorans. The order Carnivora is the fifth largest order of mammals, comprising at least 279 species.

The Mustelidae are a diverse family of carnivorous mammals, including weasels, badgers, otters, martens, and wolverines. Otherwise known as mustelids, they form the largest family in the suborder Caniformia of the order Carnivora with about 66 to 70 species in nine subfamilies.

Mephitidae is a family of mammals comprising the skunks and stink badgers. They are noted for the great development of their anal scent glands, which they use to deter predators. Skunks were formerly classified as a subfamily of the Mustelidae ; however, in the 1990s, genetic evidence caused skunks to be treated as a separate family. Similarly, the stink badgers had been classified with badgers, but genetic evidence shows they share a more recent common ancestor with skunks, so they are now included in the skunk family. A 2017 study using retroposon markers indicated that they are most closely related to the Ailuridae and Procyonidae.

Badgers are short-legged omnivores in the family Mustelidae. Badgers are a polyphyletic rather than a natural taxonomic grouping, being united by their squat bodies and adaptions for fossorial activity. All belong to the caniform suborder of carnivoran mammals.

The honey badger, also known as the ratel, is a mammal widely distributed in Africa, Southwest Asia, and the Indian subcontinent. Because of its wide range and occurrence in a variety of habitats, it is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.

Caniformia is a suborder within the order Carnivora consisting of "dog-like" carnivorans. They include dogs, bears, raccoons, and mustelids. The Pinnipedia are also assigned to this group. The center of diversification for the Caniformia is North America and northern Eurasia. Caniformia stands in contrast to the other suborder of Carnivora, the Feliformia, the center of diversification of which was in Africa and southern Asia.

Meles is a genus of badgers containing four living species known as Eurasian badgers, the Japanese badger, Asian badger, Caucasian badger and European badger. In an older categorization, they were seen as a single species with three subspecies. There are also several extinct members of the genus. They are members of the subfamily Melinae of the weasel family, Mustelidae.

Polecat is a common name for several mustelid species in the order Carnivora and subfamilies Ictonychinae and Mustelinae. Polecats do not form a single taxonomic rank. The name is applied to several species with broad similarities to European polecats, such as having a dark mask-like marking across the face.

Mustelinae is a subfamily of family Mustelidae, which includes weasels, ferrets, and minks.

The Chinese ferret-badger, also known as the small-toothed ferret-badger is a member of the Mustelidae, and widely distributed in Southeast Asia. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List and considered tolerant of modified habitat.

Guloninae is a subfamily of the mammal family Mustelidae distributed across Eurasia and the Americas. It includes martens and the fisher, tayra and wolverine. These genera were formerly included within a paraphyletic definition of the mustelid subfamily Mustelinae.

Stink badgers or false badgers are the species of the genus Mydaus of the skunk family of carnivorans, the Mephitidae. They resemble the better-known members of the family Mustelidae also termed 'badgers'. There are only two extant species – the Palawan stink badger or pantot, and the Sunda stink badger or teledu. They live west of the Wallace Line; the Sunda species on islands of the Greater Sunda Islands, being Sumatra, Java, and Borneo; in Borneo the badger is found in Indonesia, Malaysia and Brunei. The Palawan species lives in the Philippine island of Palawan as well as the islands surrounding it.

Musteloidea is a superfamily of carnivoran mammals united by shared characteristics of the skull and teeth. Musteloids are the sister group of pinnipeds, the group which includes seals.

The Burmese ferret-badger, also known as the large-toothed ferret-badger, is a mustelid native to Southeast Asia.
The Vietnam ferret-badger is a member of the family Mustelidae native to Vietnam. It was described in 2011 and is known from only two specimens.

Pekania is a genus of mustelid that contains a single living species, the fisher (Pekania pennanti). Formerly placed in the genus Martes, it was determined to be distinct enough to be placed within its own genus. A 2013 study also identified several fossil species formerly in Martes that are more closely related – and probably ancestral – to the fisher, moving them into Pekania as well.

Ictonychinae is a subfamily of the mammal family Mustelidae found mainly in the Neotropics and Africa, with one Eurasian member. It includes the grisons, Patagonian weasel, striped polecats, African striped weasel, and marbled polecat. These genera were formerly included within a paraphyletic definition of the mustelid subfamily Mustelinae.

The Formosan ferret-badger is a mustelid species endemic to Taiwan.

Neogale is a genus of mustelid native to the Americas, ranging from Alaska south to Bolivia. Members of this genus are known as New World weasels.


















