
Canidae is a biological family of dog-like carnivorans, colloquially referred to as dogs, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid. There are three subfamilies found within the canid family, which are the extinct Borophaginae and Hesperocyoninae, and the extant Caninae. The Caninae are known as canines, and include domestic dogs, wolves, foxes, jackals and other extant and extinct species.

The dhole is a canid native to Central, South, East, and Southeast Asia. Other English names for the species include Asian wild dog, Asiatic wild dog, Indian wild dog, whistling dog, red dog, and mountain wolf. It is genetically close to species within the genus Canis, but distinct in several anatomical aspects: its skull is convex rather than concave in profile, it lacks a third lower molar and the upper molars sport only a single cusp as opposed to between two and four. During the Pleistocene, the dhole ranged throughout Asia, Europe, and North America but became restricted to its historical range 12,000–18,000 years ago.

Jackals are medium-sized canids native to Africa and Eurasia. While the word "jackal" has historically been used for many canines of the subtribe canina, in modern use it most commonly refers to three species: the closely related black-backed jackal and side-striped jackal of sub-Saharan-Africa, and the golden jackal of south-central Europe and Asia.

The dire wolf is an extinct canine. It is one of the most famous prehistoric carnivores in North America, along with its extinct competitor Smilodon. The dire wolf lived in the Americas and eastern Asia during the Late Pleistocene and Early Holocene epochs. The species was named in 1858, four years after the first specimen had been found. Two subspecies are recognized: Aenocyon dirus guildayi and Aenocyon dirus dirus. The largest collection of its fossils has been obtained from the Rancho La Brea Tar Pits in Los Angeles.

The maned wolf is a large canine of South America. The maned wolf, known locally as Lobo Guará, is found in Argentina, Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, Paraguay and is almost extinct in Uruguay. Its markings resemble those of foxes, but it is neither a fox nor a wolf. It is the only species in the genus Chrysocyon.

Canis is a genus of the Caninae which includes multiple extant species, such as wolves, dogs, coyotes, and golden jackals. Species of this genus are distinguished by their moderate to large size, their massive, well-developed skulls and dentition, long legs, and comparatively short ears and tails.

The bush dog is a canine found in Central and South America. In spite of its extensive range, it is very rare in most areas except in Suriname, Guyana and Peru; it was first identified by Peter Wilhelm Lund from fossils in Brazilian caves and was believed to be extinct. The bush dog is the only living species in the genus Speothos, and genetic evidence suggests that its closest living relative is the maned wolf of central South America or the African wild dog. The species is listed as Near Threatened by the IUCN.

The crab-eating fox, also known as the forest fox, wood fox, bushdog or maikong, is an extant species of medium-sized canid endemic to the central part of South America, and which appeared during the Pliocene epoch. Like South American foxes, which are in the genus Lycalopex, it is not closely related to true foxes. Cerdocyon comes from the Greek words kerdo and kyon (dog) referring to the dog- and fox-like characteristics of this animal.

The short-eared dog, also known as the short-eared zorro or small-eared dog, is a unique and elusive canid species endemic to the Amazonian basin. This is the only species assigned to the genus Atelocynus.

Carnassials are paired upper and lower teeth modified in such a way as to allow enlarged and often self-sharpening edges to pass by each other in a shearing manner. This adaptation is found in carnivorans, where the carnassials are the modified fourth upper premolar and the first lower molar, however this may vary in family. These teeth are also referred to as sectorial teeth.
The Pleistocene bush dog is an extinct canid species in the genus Speothos from the Late Pleistocene. It was a relative of the extant bush dog. When compared to the bush dog, S. pacivorus had an overall larger body size, a straighter radial shaft and a double-rooted second lower molar.

Feliformia is a suborder within the order Carnivora consisting of "cat-like" carnivorans, including cats, hyenas, mongooses, viverrids, and related taxa. Feliformia stands in contrast to the other suborder of Carnivora, Caniformia.

The African wild dog, also called the African painted dog and the African hunting dog, is a wild canine which is a native species to sub-Saharan Africa. It is the largest wild canine in Africa, and the only extant member of the genus Lycaon, which is distinguished from Canis by dentition highly specialised for a hypercarnivorous diet, and by a lack of dewclaws. It is estimated that about 6,600 adults live in 39 subpopulations that are all threatened by habitat fragmentation, human persecution, and outbreaks of disease. As the largest subpopulation probably comprises fewer than 250 individuals, the African wild dog has been listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List since 1990.

The European dhole was a paleosubspecies of the dhole, which ranged throughout much of Western and Central Europe during the Middle and Late Pleistocene. Like the modern Asiatic populations, it was a more progressive form than other prehistoric members of the genus Cuon, having transformed its lower molar tooth into a single cusped slicer. It was virtually indistinguishable from its modern counterpart, save for its greater size, which closely approached that of the gray wolf.

The Paleolithic dog was a Late Pleistocene canine. They were directly associated with human hunting camps in Europe over 30,000 years ago and it is proposed that these were domesticated. They are further proposed to be either a proto-dog and the ancestor of the domestic dog or an extinct, morphologically and genetically divergent wolf population.
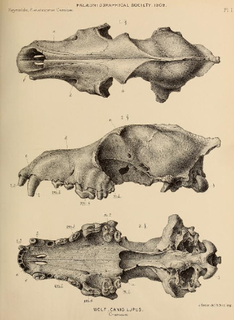
The evolution of the wolf occurred over a geologic time scale of at least 300 thousand years. The grey wolf Canis lupus is a highly adaptable species that is able to exist in a range of environments and which possesses a wide distribution across the Holarctic. Studies of modern grey wolves have identified distinct sub-populations that live in close proximity to each other. This variation in sub-populations is closely linked to differences in habitat – precipitation, temperature, vegetation, and prey specialization – which affect cranio-dental plasticity.

Canis arnensis, the Arno River dog, is an extinct species of canine that was endemic to Mediterranean Europe during the Early Pleistocene. The Arno River dog has been described as a small jackal-like dog. Its anatomy and morphology relate it more to the modern golden jackal than to the larger Etruscan wolf of that time. It is probably the ancestor of modern jackals.

Canis etruscus, the Etruscan wolf, is an extinct species of canine that was endemic to Mediterranean Europe during the Early Pleistocene. The Etruscan wolf has been described as a small wolf-like dog. The Etruscan wolf has been accepted as the ancestor of C. mosbachensis, that is the ancestor of the grey wolf, for a long time. Recent research has suggested that C. borjgali from Dmanisi has to be considered the ancestor of C. mosbachensis.

Canis mosbachensis, sometimes known as the Mosbach wolf, is an extinct small wolf that once inhabited Eurasia from the Middle Pleistocene era to the Late Pleistocene. It is widely accepted as the ancestor of Canis lupus, the grey wolf.



















