| Urva | |
|---|---|
 | |
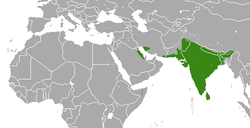
| Indian grey mongoose | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Herpestidae |
| Subfamily: | Herpestinae |
| Genus: | Urva Hodgson, 1837 |
| Type species | |
| Gulo urva Hodgson, 1836 | |
| Species | |
See table and range map | |
 | |
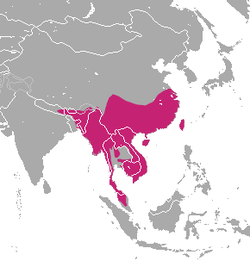
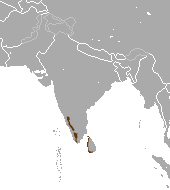
Native distribution of Urva species
| |
Urva is a genus comprising the Asian mongooses within the mongoose family Herpestidae. Species in the genus were formerly classified in the genus Herpestes , which is now thought to comprise exclusively African mongooses; phylogenetic evidence indicates that the Asian mongooses form a monophyletic group and had an Asian common ancestor. Urva forms a clade with Xenogale and Atilax , while Herpestes forms a clade with all other African mongoose species. [1] [2]
Contents
An Urva fossil specimen, an upper molar tooth, was excavated in the Ayeyarwady River valley in central Myanmar and is estimated to date to the late Pliocene. [3]
The scientific name Urva was coined by Brian Houghton Hodgson as the specific name of crab-eating mongoose in 1836, [4] and as the generic name in the following year. [5] Urva species have a wide distribution spanning from the Arabian Peninsula to the Indonesian island of Java. [6] The small Indian mongoose (U. auropunctata) has been introduced to several islands in the late 19th century, where it has become an invasive species. [7] [8]