
A mammal is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia. Mammals are characterized by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 29 orders.

The meerkat or suricate is a small mongoose found in southern Africa. It is characterised by a broad head, large eyes, a pointed snout, long legs, a thin tapering tail, and a brindled coat pattern. The head-and-body length is around 24–35 cm (9.4–13.8 in), and the weight is typically between 0.62 and 0.97 kg. The coat is light grey to yellowish-brown with alternate, poorly-defined light and dark bands on the back. Meerkats have foreclaws adapted for digging and have the ability to thermoregulate to survive in their harsh, dry habitat. Three subspecies are recognised.

A mongoose is a small terrestrial carnivorous mammal belonging to the family Herpestidae. This family is currently split into two subfamilies, the Herpestinae and the Mungotinae. The Herpestinae comprises 23 living species that are native to southern Europe, Africa and Asia, whereas the Mungotinae comprises 11 species native to Africa. The Herpestidae originated about 21.8 ± 3.6 million years ago in the Early Miocene and genetically diverged into two main genetic lineages between 19.1 and 18.5 ± 3.5 million years ago.

Viverridae is a family of small to medium-sized, feliform mammals. The viverrids comprise 33 species placed in 14 genera. This family was named and first described by John Edward Gray in 1821. Viverrids occur all over Africa, southern Europe, and South and Southeast Asia, across the Wallace Line.

The striped polecat, also called the African polecat, zoril, zorille, zorilla, Cape polecat, and African skunk, is a member of the family Mustelidae that resembles a skunk. The name "zorilla" comes from the Spanish word "zorillo", meaning "skunk", itself a diminutive form of the Spanish "zorro," "fox." It lives predominantly in dry and arid climates, such as the savannahs and open country of Central, Southern, and sub-Saharan Africa, excluding the Congo basin and the more coastal areas of West Africa.

The blesmols, also known as mole-rats, or African mole-rats, are burrowing rodents of the family Bathyergidae. They represent a distinct evolution of a subterranean life among rodents much like the pocket gophers of North America, the tuco-tucos in South America, or the Spalacidae from Eurasia.

Aonyx is a genus of otters, containing three species, the African clawless otter, the Congo clawless otter, and the Asian small-clawed otter. The word aonyx means "clawless", derived from the prefix a- ("without") and onyx ("claw/hoof").

The Abyssinian genet, also known as the Ethiopian genet, is a genet species native to Ethiopia, Eritrea, Somalia, Sudan, and Djibouti. It is listed as Data Deficient on the IUCN Red List. It is one of the least-known genet species.

Taurotragus is a genus of giant antelopes of the African savanna, commonly known as elands. It contains two species: the common eland T. oryx and the giant eland T. derbianus.

Phacochoerus is a genus in the family Suidae, commonly known as warthogs. They are pigs who live in open and semi-open habitats, even in quite arid regions, in sub-Saharan Africa. The two species were formerly considered conspecific under the scientific name Phacochoerus aethiopicus, but today this is limited to the desert warthog, while the best-known and most widespread species, the common warthog, is Phacochoerus africanus.
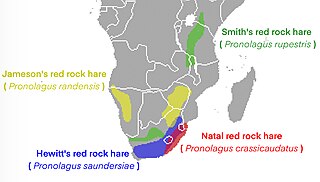
The red rock hares are the four species in the genus Pronolagus. They are African lagomorphs of the family Leporidae.

Smith's red rockhare, Smith's red rock hare or Smith's red rock rabbit is a species of mammal in the family Leporidae, and is the smallest member of the genus Pronolagus. The upperparts and gular collar are reddish brown in colour. It has warm, brown, grizzled, thicker hairs at the back of the body, and white to tawny, thinner underfur. It is native to Africa, found in parts of Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia and Zimbabwe. It is a folivore, and usually forages on grasses, shrubs and herbs. It breeds from September to February, and the female litters one or two offspring. The young leave the nest at three years of age. In 1996, it was rated as a species of least concern on the IUCN Red List of Endangered Species.

Hippotragus is a genus of antelopes which includes two living and one recently extinct species, as well as some fossil relatives. The name comes from Greek ἵππος (híppos), "horse", and τράγος (trágos), "he-goat".

A penis is a male sex organ that is used to inseminate female or hermaphrodite animals during copulation. Such organs occur in both vertebrates and invertebrates, but not in all male animals.

The African linsangs also known as oyans are two species classified in the mammalian subfamily Viverrinae, in the family Viverridae. There is one genus, Poiana.

Hyraxes, also called dassies, are small, stout, herbivorous mammals in the order Hyracoidea. Hyraxes are well-furred, rotund animals with short tails. Modern hyraxes are typically between 30 and 70 cm long and weigh between 2 and 5 kg. They are superficially similar to marmots, or over-large pikas, but are paradoxically much more closely related to elephants and sea cows. Hyraxes have a life span from 9 to 14 years. Both types of 'rock' hyrax live on rock outcrops, including cliffs in Ethiopia and isolated granite outcrops called koppies in southern Africa;

The Hewitt's red rock hare is a species of mammal in the family Leporidae. It had previously been classified as a subspecies of Pronolagus rupestris, but is now regarded as its own species due to differences in morphology and genetic differences in cytochrome b, and 12S rRNA.
Suricata major is an extinct species of meerkat from the Early Pleistocene of Africa.

















