Viverridae is a family of small to medium-sized, feliform mammals. The viverrids comprise 33 species placed in 14 genera. This family was named and first described by John Edward Gray in 1821. Viverrids occur all over Africa, southern Europe, and South and Southeast Asia, across the Wallace Line.

The Asian palm civet, also called common palm civet, toddy cat and musang, is a viverrid native to South and Southeast Asia. Since 2008, it is IUCN Red Listed as Least Concern as it accommodates to a broad range of habitats. It is widely distributed with large populations that in 2008 were thought unlikely to be declining. It is threatened by poaching for the illegal wildlife trade.

The African palm civet, also known as the two-spotted palm civet, is a small feliform mammal widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa. It is listed as least concern on the IUCN Red List.

The African civet is a large viverrid native to sub-Saharan Africa, where it is considered common and widely distributed in woodlands and secondary forests. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List since 2008. In some countries, it is threatened by hunting, and wild-caught individuals are kept for producing civetone for the perfume industry.

The otter civet is a semiaquatic viverrid native to Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia and Brunei. It is believed to be undergoing severe population decline due to habitat destruction and is classified as an endangered species by the IUCN Red List.

The Malabar large-spotted civet, also known as the Malabar civet, is a viverrid endemic to the Western Ghats of India. It is listed as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List as the population is estimated to number fewer than 250 mature individuals. It has not been recorded during surveys carried out between 1990 and 2014. In the early 1990s, isolated populations still survived in less disturbed areas of South Malabar but were seriously threatened by habitat destruction and hunting outside protected areas.

Paradoxurus is a genus of three palm civets within the viverrid family that was denominated and first described by Frédéric Cuvier in 1822. The Paradoxurus species have a broad head, a narrow muzzle with a large rhinarium that is deeply sulcate in the middle. Their large ears are rounded at the tip. The tail is nearly as long as the head and body.

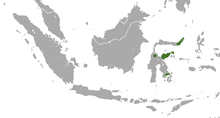
Hose's palm civet, also known as Hose's civet, is a viverrid species endemic to the island of Borneo. It is listed on the IUCN Red List as Vulnerable because of an ongoing population decline, estimated to be more than 30% over the last three generations and suspected to be more than 30% in the next three generations due to declines in population inferred from habitat destruction and degradation.

The small Indian civet is a civet native to South and Southeast Asia. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List because of its widespread distribution, widespread habitat use and healthy populations living in agricultural and secondary landscapes of many range states.

Owston's palm civet is a viverrid native to Vietnam, Laos and a very small portion of southern China, in three counties located in the Yunnan province: Hekou, Luchun, and Jinping, and has never been found west of the Mekong River. It is listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List because of an ongoing population decline, estimated to be more than 50% over the last three generations, inferred from over-exploitation, habitat destruction and degradation.

The banded palm civet, also called the banded civet, is a viverrid native to Indomalaya. They primarily inhabit lowland conifer habitat, which is under threat from encroaching human activity. It is estimated the population of the banded palm civet has decreased by around 30% in just three generations. Banded palm civets are usually approximately the size of a domestic cat; their fur is pale but with dark bands on the back. They are believed to be closely related to Hose's palm civets, which are similar in appearance and distribution.

The small-toothed palm civet, also known as the three-striped palm civet, is a viverrid native to dense forests of Southeast Asia, from the Assam district of India to Indochina and the Malay Peninsula and on Sumatra, Bangka, Java, Borneo, and numerous small nearby islands of Indonesia.

The masked palm civet, also called the gem-faced civet or Himalayan palm civet, is a viverrid species native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. It has been listed as least concern on the IUCN Red List since 2008 as it occurs in many protected areas, is tolerant to some degree of habitat modification, and widely distributed with presumed large populations that are unlikely to be declining.

The golden palm civet is a viverrid endemic to Sri Lanka. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List since 2016.The extent and quality of its habitat in Sri Lanka's hill regions are declining.

The brown palm civet, also called the Jerdon's palm civet, is a viverrid endemic to the Western Ghats of India.

The Malayan civet, also known as the Malay civet and Oriental civet, is a viverrid native to the Malay Peninsula and the islands of Sumatra, Bangka, Borneo, the Riau Archipelago, and the Philippines. It is listed as "Least Concern" by IUCN as it is a relatively widely distributed, appears to be tolerant of degraded habitats, and occurs in a number of protected areas.

A civet is a small, lean, mostly nocturnal mammal native to tropical Asia and Africa, especially the tropical forests. The term civet applies to over a dozen different species, mostly from the family Viverridae. Most of the species's diversity is found in southeast Asia. Civets do not form a monophyletic group, as they consist only of certain members of the Viverridae, Eupleridae, and Nandiniidae.

Alaungdaw Kathapa National Park is a national park in Myanmar covering 541.6 sq mi (1,403 km2). It was established in 1989 and is listed as one of the ASEAN Heritage Parks. It spans an elevation of 443–4,380 ft (135–1,335 m) in the Kani and Mingin Townships in Sagaing Region.

The Hemigalinae are a subfamily of the viverrids denominated and first described by John Edward Gray in 1864. Hemigalinae species are native to Southeast Asia from southern China through Indochina, Malay Peninsula to Sumatra, Borneo and Sulawesi.