
Viverridae is a family of small to medium-sized feliform mammals, comprising 14 genera with 33 species. This family was named and first described by John Edward Gray in 1821. Viverrids occur all over Africa, southern Europe, South and Southeast Asia across the Wallace Line. The word viverridae comes from the Latin word viverra.

The Asian palm civet, also called common palm civet, toddy cat and musang, is a viverrid native to South and Southeast Asia. Since 2008, it is IUCN Red Listed as Least Concern as it accommodates to a broad range of habitats. It is widely distributed with large populations that in 2008 were thought unlikely to be declining. It is threatened by poaching for the illegal wildlife trade.

Sinharaja Forest Reserve is a forest reserve and a biodiversity hotspot in Sri Lanka. It is of international significance and has been designated a Biosphere Reserve and World Heritage Site by UNESCO.

Kopi luwak, also known as civet coffee, is a coffee that consists of partially digested coffee cherries, which have been eaten and defecated by the Asian palm civet. The cherries are fermented as they pass through a civet's intestines, and after being defecated with other fecal matter, they are collected. Asian palm civets are increasingly caught in the wild and traded for this purpose.

Paradoxurus is a genus of three palm civets within the viverrid family that was denominated and first described by Frédéric Cuvier in 1822. The Paradoxurus species have a broad head, a narrow muzzle with a large rhinarium that is deeply sulcate in the middle. Their large ears are rounded at the tip. The tail is nearly as long as the head and body.

The Sulawesi palm civet, also known as Sulawesi civet, musang and brown palm civet is a little-known viverrid endemic to Sulawesi. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List due to population decline estimated to have been more than 30% over the last three generations inferred from habitat destruction and degradation.
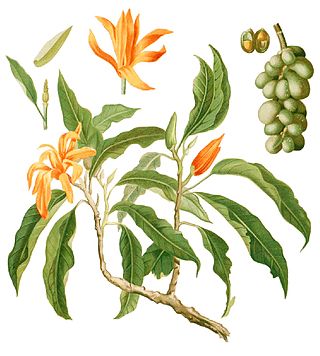
Magnolia champaca, known in English as champak, is a large evergreen tree in the family Magnoliaceae. It was previously classified as Michelia champaca. It is known for its fragrant flowers, and its timber used in woodworking.

The banded palm civet, also called the banded civet, is a viverrid native to Indomalaya. They primarily inhabit lowland conifer habitat, which is under threat from encroaching human activity. It is estimated the population of the banded palm civet has decreased by around 30% in just three generations. Banded palm civets are usually approximately the size of a domestic cat; their fur is pale but with dark bands on the back. They are believed to be closely related to Hose's palm civets, which are similar in appearance and distribution.

The small-toothed palm civet, also known as the three-striped palm civet, is a viverrid native to dense forests of Southeast Asia, from the Assam district of India to Indochina and the Malay Peninsula and on Sumatra, Bangka, Java, Borneo, and numerous small nearby islands of Indonesia.

The golden palm civet is a viverrid endemic to Sri Lanka. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List since 2016.The extent and quality of its habitat in Sri Lanka's hill regions are declining.

The brown palm civet, also called the Jerdon's palm civet, is a viverrid endemic to the Western Ghats of India.
Endangered mammals of India are the mammal species in India that are listed as threatened in the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Animals
Civet cat is an imprecise term that is used for a variety of cat-like creatures including:

A civet is a small, lean, mostly nocturnal mammal native to tropical Asia and Africa, especially the tropical forests. The term civet applies to over a dozen different species, mostly from the family Viverridae. Most of the species's diversity is found in southeast Asia. Civets do not form a monophyletic group, as they consist only of certain members of the Viverridae, Eupleridae, and Nandiniidae.

The Hemigalinae are a subfamily of the viverrids denominated and first described by John Edward Gray in 1864. Hemigalinae species are native to Southeast Asia from southern China through Indochina, Malay Peninsula to Sumatra, Borneo and Sulawesi.

Khao Laem National Park is a park of about 1,500 square kilometers in Western Thailand, located near Myanmar in the northern area of the Tenasserim Hills, Kanchanaburi Province. It is a part of the Western Forest Complex, a system of protected wilderness in the Dawna-Tenasserim Hills area of western Thailand.

Elaeocarpus serratus, the Ceylon olive, is a tropical flowering plant in the family Elaeocarpaceae. It is a medium to large tree, with white flowers. It has a disjunctive distribution, with the species occurring in Sri Lanka and southern India, and in Assam, Bangladesh and other parts in the north of the Indian subcontinent. The fruit is commonly eaten, and people also use the plant for ornamental, religious and folk-medicinal purposes. There are historical records of traditional-medicine use of the plant. Paradoxurus jerdoni consumes parts of the tree.













