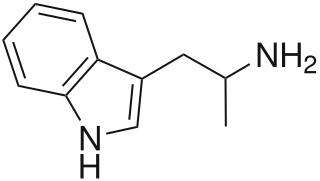
α-Methyltryptamine is a psychedelic, stimulant, and entactogen drug of the tryptamine class. It was originally developed as an antidepressant by chemists at Upjohn in the 1960s, and was used briefly as an antidepressant in Russia under the trade name Indopan before being discontinued.
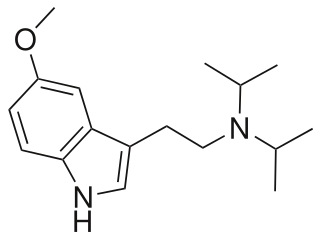
5-Methoxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamine is a psychedelic tryptamine and the methoxy derivative of diisopropyltryptamine (DiPT).
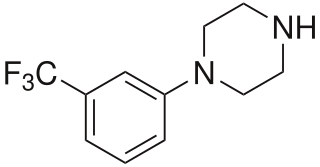
3-Trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine (TFMPP) is a recreational drug of the phenylpiperazine chemical class and is a substituted piperazine. Usually in combination with benzylpiperazine (BZP) and other analogues, it is sold as an alternative to the illicit drug MDMA ("Ecstasy").

5-MeO-MiPT is a psychedelic and hallucinogenic drug, used by some as an entheogen. It has structural and pharmacodynamic properties similar to the drugs 5-MeO-DiPT, DiPT, and MiPT. It is commonly used as a "substitute" for 5-MeO-DiPT because of the very similar structure and effects.

5-MeO-DALT or N,N-di allyl-5-methoxy tryptamine is a psychedelic tryptamine first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin.
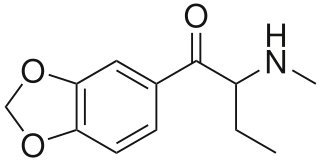
Butylone, also known as β-keto-N-methylbenzodioxolylbutanamine (βk-MBDB), is an entactogen, psychedelic, and stimulant psychoactive drug of the phenethylamine chemical class. It is the β-keto analogue of MBDB and the substituted methylenedioxyphenethylamine analogue of buphedrone.

Desoxypipradrol, also known as 2-diphenylmethylpiperidine (2-DPMP), is a drug developed by Ciba in the 1950s which acts as a norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI).

2-Aminoindane (2-AI) is a research chemical with applications in neurologic disorders and psychotherapy that has also been sold as a designer drug. It acts as a selective substrate for NET and DAT.
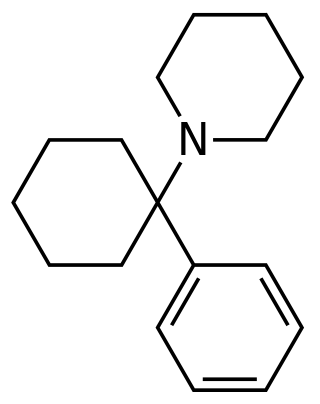
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs.

Dimemebfe (5-MeO-BFE) is a recreational drug and research chemical. It acts as an agonist for the 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 family of serotonin receptors. It is related in structure to the psychedelic tryptamine derivative 5-MeO-DMT, but with the indole nitrogen replaced by oxygen, making dimemebfe a benzofuran derivative. It is several times less potent as a serotonin agonist than 5-MeO-DMT and with relatively more activity at 5-HT1A, but still shows strongest effects at the 5-HT2 family of receptors.
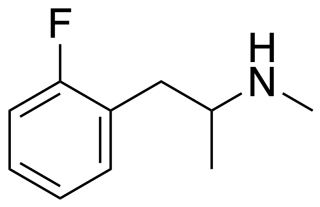
2-Fluoromethamphetamine (2-FMA) is a stimulant drug of the amphetamine family which has been used as a designer drug. 2-FMA is commonly compared to lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), and dextroamphetamine due to its efficacy as a study or productivity aid. 2-FMA is purported to produce somewhat less euphoria than comparable amphetamines, likely due to its main mechanism of action consisting of norepinephrine reuptake inhibition.

JWH-122 is a synthetic cannabimimetic that was discovered by John W. Huffman. It is a methylated analogue of JWH-018. It has a Ki of 0.69 nM at CB1 and 1.2 nM at CB2.

3-Methoxyphencyclidine (3-MeO-PCP) is a dissociative hallucinogen of the arylcyclohexylamine class related to phencyclidine (PCP) which has been sold online as a designer drug. It acts mainly as an NMDA receptor antagonist, though it has also been found to interact with the sigma σ1 receptor and the serotonin transporter. The drug does not possess any opioid activity nor does it act as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor.

4-Methoxyphencyclidine is a dissociative anesthetic drug that has been sold online as a research chemical. The synthesis of 4-MeO-PCP was first reported in 1965 by the Parke-Davis medicinal chemist Victor Maddox. A 1999 review published by a chemist using the pseudonym John Q. Beagle suggested the potency of 4-MeO-PCP in man was reduced relative to PCP, two years later Beagle published a detailed description of the synthesis and qualitative effects of 4-MeO-PCP, which he said possessed 70% the potency of PCP. 4-MeO-PCP was the first arylcyclohexylamine research chemical to be sold online, it was introduced in late 2008 by a company trading under the name CBAY and was followed by several related compounds such as 3-MeO-PCP and methoxetamine. 4-MeO-PCP has lower affinity for the NMDA receptor than PCP, but higher affinity than ketamine, it is orally active in a dosage range similar to ketamine, with some users requiring doses in excess of 100 mg for desired effects. Users have reported substantial differences in active dose, these discrepancies can be partially explained by the presence of unreacted PCC and other impurities in samples sold on the grey market. 4-MeO-PCP has Ki values of 404 nM for the NMDA receptor, 713 nM for the norepinephrine transporter, 844 nM for the serotonin transporter, 296 nM for the σ1 receptor and 143 nM for the σ2 receptor.

Methoxetamine, abbreviated as MXE, is a dissociative hallucinogen that has been sold as a designer drug. It differs from many dissociatives such as ketamine and phencyclidine (PCP) that were developed as pharmaceutical drugs for use as general anesthetics in that it was designed specifically to increase the antidepressant effects of ketamine.

UR-144 (TMCP-018, KM-X1, MN-001, YX-17) is a drug invented by Abbott Laboratories, that acts as a selective full agonist of the peripheral cannabinoid receptor CB2, but with much lower affinity for the psychoactive CB1 receptor.

STS-135 (N-(adamantan-1-yl)-1-(5-fluoropentyl)-1H-indole-3-carboxamide, also called 5F-APICA) is a designer drug offered by online vendors as a cannabimimetic agent. The structure of STS-135 appears to use an understanding of structure-activity relationships within the indole class of cannabimimetics, although its design origins are unclear. STS-135 is the terminally-fluorinated analogue of SDB-001, just as AM-2201 is the terminally-fluorinated analogue of JWH-018, and XLR-11 is the terminally-fluorinated analogue of UR-144. STS-135 acts a potent cannabinoid receptor agonist in vitro, with an EC50 of 51 nM for human CB2 receptors, and 13 nM for human CB1 receptors. STS-135 produces bradycardia and hypothermia in rats at doses of 1–10 mg/kg, suggesting cannabinoid-like activity.

Butyrfentanyl or butyrylfentanyl is a potent short-acting synthetic opioid analgesic drug. It is an analog of fentanyl with around one quarter of its potency. One of the first mentions of this drug can be found in document written by The College on Problem of Drug Dependence, where it is mentioned as N-butyramide fentanyl analog. This document also states that the article describing its clinical effects was published in 1987. It is an agonist for the μ-opioid receptors.
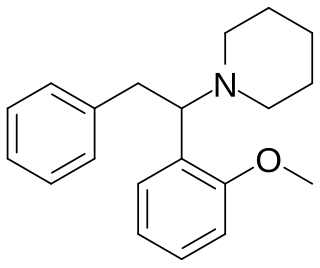
Methoxphenidine is a dissociative of the diarylethylamine class that has been sold online as a designer drug. Methoxphenidine was first reported in a 1989 patent where it was tested as a treatment for neurotoxic injury. Shortly after the 2013 UK ban on arylcyclohexylamines methoxphenidine and the related compound diphenidine became available on the gray market, where it has been encountered as a powder and in tablet form. Though diphenidine possesses higher affinity for the NMDA receptor, anecdotal reports suggest methoxphenidine has greater oral potency. Of the three isomeric anisyl-substituents methoxphenidine has affinity for the NMDA receptor that is higher than 4-MeO-Diphenidine but lower than 3-MeO-Diphenidine, a structure–activity relationship shared by the arylcyclohexylamines.

4-Fluorobutyrylfentanyl (also known as 4-FBF and p-FBF or para-fluorobutyrylfentanyl) is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of butyrfentanyl and has been sold online as a designer drug. It is closely related to 4-fluorofentanyl, which has an EC50 value of 4.2 nM for the human μ-opioid receptor.




















