Related Research Articles

Alexander II was King of Scotland from 1214 until his death. He concluded the Treaty of York (1237) which defined the boundary between England and Scotland, virtually unchanged today.

Alexander III was King of Scots from 1249 until his death. He concluded the Treaty of Perth, by which Scotland acquired sovereignty over the Western Isles and the Isle of Man. His heir, Margaret, Maid of Norway, died before she could be crowned.

Year 1263 (MCCLXIII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar.

Earl of Orkney, historically Jarl of Orkney, is a title of nobility encompassing the archipelagoes of Orkney and Shetland, which comprise the Northern Isles of Scotland. Originally founded by Norse invaders, the status of the rulers of the Northern Isles as Norwegian vassals was formalised in 1195. Although the Old Norse term jarl is etymologically related to "earl", and the jarls were succeeded by earls in the late 15th century, a Norwegian jarl is not the same thing. In the Norse context the distinction between jarls and kings did not become significant until the late 11th century and the early jarls would therefore have had considerable independence of action until that time. The position of Jarl of Orkney was eventually the most senior rank in medieval Norway except for the king himself.

The Battle of Largs was a battle between the kingdoms of Norway and Scotland, on the Firth of Clyde near Largs, Scotland. Through it, Scotland achieved the end of 500 years of Norse Viking depredations and invasions despite being tremendously outnumbered, without a one-sided military victory in the ensuing battle. The victory caused the complete retreat of Norwegian forces from western Scotland and the realm entered a period of prosperity for almost 40 years. The tactical decision at Largs thus led to a sweeping strategic victory that ended in Scotland purchasing the Hebrides Islands and the Isle of Man in the Treaty of Perth, 1266. Victory was achieved with a crafty three-tiered strategy on the part of the young Scottish king, Alexander III: plodding diplomacy forced the campaign to bad weather months and a ferocious storm ravaged the Norwegian fleet, stripping it of many vessels and supplies and making the forces on the Scottish coast vulnerable to an attack that forced the Norwegians into a hasty retreat that was to end their 500-year history of invasion and leave Scotland to consolidate its resources into building the nation. The conflict formed part of the Norwegian expedition against Scotland in 1263, in which Haakon Haakonsson, King of Norway attempted to reassert Norwegian sovereignty over the western seaboard of Scotland.
This article presents a timeline of events in British history from 1000 AD until 1499 AD.

John de Balliol was an English nobleman, belonging to the House of Balliol. Balliol College, in Oxford, is named after him.

The Treaty of Perth, signed 2 July 1266, ended military conflict between Magnus VI of Norway and Alexander III of Scotland over possession of the Hebrides and the Isle of Man.
Patrick III, 7th Earl of Dunbar was lord of the feudal barony of Dunbar and its castle, which dominated East Lothian, and the most important military personage in the Scottish Borders.

The Battle of Ronaldsway took place in 1275 at Ronaldsway in the southern part of the Isle of Man between a Scottish army and the Manx. The battle crushed the final attempt by the Manx to re-establish the Norse Sudreyar dynasty. As the battle resulted in the death of the last Norse King of Mann, Guðrøðr Magnússon, and the emigration to Norway of the remaining members of the Manx royal family, it also led to the firm establishment of Scottish rule on the Isle of Man.

Lorne is an ancient province in the west of Scotland, which is now a district in the Argyll and Bute council area. The district gives its name to the Lynn of Lorn National Scenic Area, one of forty such areas in Scotland, which have been defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection from inappropriate development. The national scenic areas cover 15,726 ha, of which 10,088 ha are marine seascape, and includes the whole of the island of Lismore, along with neighbouring areas on the mainland such as Benderloch and Port Appin, and the Shuna Island.

Sir Hugh Crawford (1195–1265) was the Second Sheriff of Ayr, Chief of Clan Crawford, and Lord of Loudoun. He probably lived in Loudon Castle even while he administrated quite some distance away in the town of Ayr. But Norse control over traditional Scots in the Western Isles and the underhanded way in which they gained control had been an aggravation to the Scots for years. Alexander III of Scotland began pressing diplomatically and militarily to regain control beginning in 1260. This prompted Haakon IV of Norway to lead a large fleet in 1263 to the maritime boundary between the jurisdictions located along the northwest shore of Ayrshire.

The Hebrides were settled early on in the settlement of the British Isles, perhaps as early as the Mesolithic era, around 8500–8250 BC, after the climatic conditions improved enough to sustain human settlement. There are examples of structures possibly dating from up to 3000 BC, the finest example being the standing stones at Callanish, but some archaeologists date the site as Bronze Age. Little is known of the people who settled in the Hebrides but they were likely of the same Celtic stock that had settled in the rest of Scotland. Settlements at Northton, Harris, have both Beaker & Neolithic dwelling houses, the oldest in the Western Isles, attesting to the settlement.
Events from the 1260s in England.
The Scottish–Norwegian War lasted from 1262 to 1266. The conflict arose because of disagreement over the ownership of the Hebrides. The war consisted of mainly skirmishes and feuds between the kings, and the only major battle was the indecisive Battle of Largs.
Malise mac Gilleain was the second chief of Clan Maclean. He was loyal to Alexander III of Scotland and assisted in the expulsion of Haakon IV of Norway from Scotland.
The History of Shetland concerns the subarctic archipelago of Shetland in Scotland. The early history of the islands is dominated by the influence of the Vikings. From the 14th century, it was incorporated into the Kingdom of Scotland, and later into the United Kingdom.

The Crovan dynasty, from the late 11th century to the mid 13th century, was the ruling family of an insular kingdom known variously in secondary sources as the Kingdom of Mann, the Kingdom of the Isles, and the Kingdom of Mann and the Isles. The eponymous founder of the dynasty was Godred Crovan, who appeared from obscurity in the late 11th century, before his takeover of the Isle of Man and Dublin. The dynasty was of Gaelic-Scandinavian origin, descending from a branch of the Uí Ímair, a dominant kindred in the Irish Sea region which first appears on record in the late 9th century.
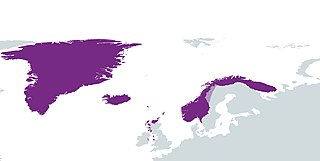
The term Norwegian Realm and Old Kingdom of Norway refer to the Kingdom of Norway's peak of power at the 13th century after a long period of civil war before 1240. The kingdom was a loosely unified nation including the territory of modern-day Norway, modern-day Swedish territory of Jämtland, Herjedalen, Ranrike (Bohuslän) and Idre and Särna, as well as Norway's overseas possessions which had been settled by Norwegian seafarers for centuries before being annexed or incorporated into the kingdom as 'tax territories'. To the North, Norway also bordered extensive tax territories on the mainland. Norway, whose expansionism starts from the very foundation of the Kingdom in 872, reached the peak of its power in the years between 1240 and 1319.
The Manx revolt of 1275 was an uprising on the Isle of Man in 1275, led by Guðrøðr Magnússon. The uprising initially expelled the Scots, who had received the Isle of Man in 1266 by the Treaty of Perth from the Kingdom of Norway. King Alexander III of Scotland responded by sending a large fleet and troops to crush the rebellion.
References
- ↑ "Alexander III: king of Scotland". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2 April 2018.
- 1 2 Sinclair, Robert (2013). The Sinclairs of Scotland. AuthorHouse. p. 36. ISBN 9781481796231.
- ↑ Gilyeat, Dave (27 September 2013). "Woman who founded 'oldest' college". BBC News. Retrieved 2 April 2018.
- ↑ "Treaty of Perth". The Gazetteer for Scotland. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- ↑ "Duns Scotus (c.1266-1308) 1257235". www.nationaltrustcollections.org.uk. Retrieved 14 January 2018.