Related Research Articles
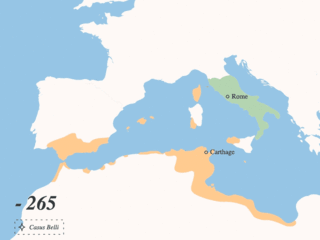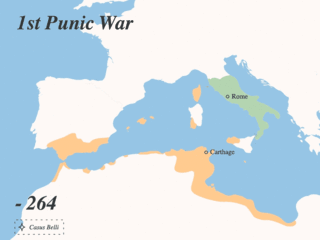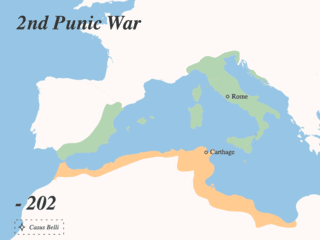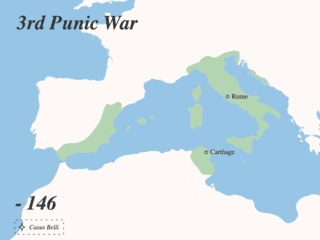
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146 BC fought between the Roman Republic and Ancient Carthage. Three wars took place, on both land and sea, across the western Mediterranean region and involved a total of forty-three years of warfare. The Punic Wars are also considered to include the four-year-long revolt against Carthage which started in 241 BC. Each war involved immense materiel and human losses on both sides.

The 2nd century BC started the first day of 200 BC and ended the last day of 101 BC. It is considered part of the Classical era, although depending on the region being studied, other terms may be more suitable. It is also considered to be the end of the Axial Age. In the context of the Eastern Mediterranean, it is the mid-point of the Hellenistic period.
Year 202 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Geminus and Nero. The denomination 202 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

This article concerns the 200 BC decade, that lasted from 209 BC to 200 BC.
This article concerns the period 159 BC – 150 BC.
This article concerns the period 219 BC – 210 BC.
This article concerns the period 189 BC – 180 BC.
This article concerns the period 199 BC – 190 BC.

The Third Punic War was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between Carthage and Rome. The war was fought entirely within Carthaginian territory, in what is now northern Tunisia. When the Second Punic War ended in 201 BC one of the terms of the peace treaty prohibited Carthage from waging war without Rome's permission. Rome's ally, King Masinissa of Numidia, exploited this to repeatedly raid and seize Carthaginian territory with impunity. In 149 BC Carthage sent an army, under Hasdrubal, against Masinissa, the treaty notwithstanding. The campaign ended in disaster as the Battle of Oroscopa ended with a Carthaginian defeat and the surrender of the Carthaginian army. Anti-Carthaginian factions in Rome used the illicit military action as a pretext to prepare a punitive expedition.

Year 201 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Paetus. The denomination 201 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 203 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caepio and Geminus. The denomination 203 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 206 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Philo and Metellus. The denomination 206 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 185 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Pulcher and Puditanus. The denomination 185 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The Battle of Zama was fought in 202 BC in what is now Tunisia between a Roman army commanded by Scipio Africanus and a Carthaginian army commanded by Hannibal. The battle was part of the Second Punic War and resulted in such a severe defeat for the Carthaginians that they capitulated, while Hannibal was forced into exile. The Roman army of approximately 30,000 men was outnumbered by the Carthaginians who fielded either 40,000 or 50,000; the Romans were stronger in cavalry, but the Carthaginians had 80 war elephants.

The siege of Carthage was the main engagement of the Third Punic War fought between Carthage and Rome. It consisted of the nearly three-year siege of the Carthaginian capital, Carthage. In 149 BC, a large Roman army landed at Utica in North Africa. The Carthaginians hoped to appease the Romans, but despite the Carthaginians surrendering all of their weapons, the Romans pressed on to besiege the city. The Roman campaign suffered repeated setbacks through 149 BC, only alleviated by Scipio Aemilianus, a middle-ranking officer, distinguishing himself several times. A new Roman commander took over in 148 BC, and fared equally badly. At the annual election of Roman magistrates in early 147 BC, the public support for Scipio was so great that the usual age restrictions were lifted to allow him to be appointed commander in Africa.

The battle of the Great Plains was fought in 203 BC in modern Tunisia between a Roman army commanded by Publius Cornelius Scipio, and allied Carthaginian and Numidian armies commanded by Hasdrubal Gisco and Syphax respectively. The battle was part of the Second Punic War and resulted in a heavy defeat for Carthage.

The Battle of Lilybaeum was the first clash between the navies of Carthage and Rome in 218 BC during the Second Punic War. The Carthaginians had sent 35 quinqueremes to raid Sicily, starting with Lilybaeum. The Romans, warned by Hiero of Syracuse of the coming raid, had time to intercept the Carthaginian contingent with a fleet of 20 quinqueremes and managed to capture several Carthaginian ships.

The battle of Utica was fought in 203 BC between a Roman army commanded by Publius Cornelius Scipio and the allied armies of Carthage and Numidia, commanded by Hasdrubal Gisgo and Syphax respectively. The battle was part of the Second Punic War and resulted in a heavy defeat for Carthage.
The Battle of Oroscopa was fought between a Carthaginian army of more than 30,000 men commanded by the general Hasdrubal and a Numidian force of unknown size under its king, Masinissa. It took place in late 151 BC near the ancient town of Oroscopa in what is now north western Tunisia. The battle resulted in a heavy Carthaginian defeat.
References
- ↑ Sinha, Binod (1977). History of the Shunga Dynasty. Bharatiya Publishing House.