
Andrew Johnson was the 17th president of the United States, serving from 1865 to 1869. He assumed the presidency following the assassination of Abraham Lincoln, as he was vice president at that time. Johnson was a Southern Democrat who ran with Abraham Lincoln on the National Union Party ticket, coming to office as the Civil War concluded. He favored quick restoration of the seceded states to the Union without protection for the newly freed people who were formerly enslaved as well as pardoning ex-Confederates. This led to conflict with the Republican-dominated Congress, culminating in his impeachment by the House of Representatives in 1868. He was acquitted in the Senate by one vote.
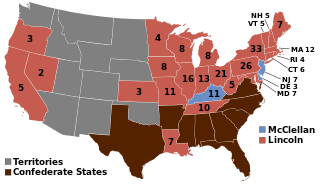
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 8, 1864, near the end of the American Civil War. Incumbent President Abraham Lincoln of the National Union Party easily defeated the Democratic nominee, former General George B. McClellan, by a wide margin of 212–21 in the electoral college, with 55% of the popular vote. For the election, the Republican Party and some Democrats created the National Union Party, especially to attract War Democrats.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 3, 1868. In the first election of the Reconstruction Era, Republican nominee Ulysses S. Grant defeated Horatio Seymour of the Democratic Party. It was the first presidential election to take place after the conclusion of the American Civil War and the abolition of slavery. It was the first election in which African Americans could vote in the reconstructed Southern states, in accordance with the First Reconstruction Act.

The Reconstruction era was a period in United States history and Southern United States history that followed the American Civil War and was dominated by the legal, social, and political challenges of the abolition of slavery and the reintegration of the eleven former Confederate States of America into the United States. During this period, three amendments were added to the United States Constitution to grant citizenship and equal civil rights to the newly freed slaves. To circumvent these legal achievements, the former Confederate states imposed poll taxes and literacy tests and engaged in terrorism to intimidate and control black people and to discourage or prevent them from voting.

James Lusk Alcorn was a governor, and U.S. senator during the Reconstruction era in Mississippi. A Moderate Republican and Whiggish "scalawag", he engaged in a bitter rivalry with Radical Republican Adelbert Ames, who defeated him in the 1873 gubernatorial race. Alcorn was the first elected Republican governor of Mississippi.
The Radical Republicans were a political faction within the Republican Party originating from the party's founding in 1854—some six years before the Civil War—until the Compromise of 1877, which effectively ended Reconstruction. They called themselves "Radicals" because of their goal of immediate, complete, and permanent eradication of slavery in the United States. The Radical faction also included, though, very strong currents of Nativism, anti-Catholicism, and in favor of the Prohibition of alcoholic beverages. These policy goals and the rhetoric in their favor often made it extremely difficult for the Republican Party as a whole to avoid alienating large numbers of American voters of Irish Catholic, German, and other White ethnic backgrounds. In fact, even German-American Freethinkers and Forty-Eighters who, like Hermann Raster, otherwise sympathized with the Radical Republicans' aims, fought them tooth and nail over prohibition. They later became known as "Stalwarts".
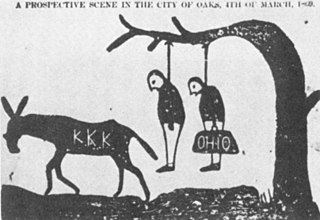
In United States history, scalawag was a pejorative slur referred to white Southerners who supported Reconstruction policies and efforts after the conclusion of the American Civil War.

Hiram Rhodes Revels was an American Republican politician, minister in the African Methodist Episcopal Church, and college administrator. Born free in North Carolina, he later lived and worked in Ohio, where he voted before the Civil War. Elected by the Mississippi legislature to the United States Senate as a Republican to represent Mississippi in 1870 and 1871 during the Reconstruction era, he was the first African American to serve in either house of the U.S. Congress.

The Liberal Republican Party was an American political party that was organized in May 1872 to oppose the reelection of President Ulysses S. Grant and his Radical Republican supporters in the presidential election of 1872. The party emerged in Missouri under the leadership of Senator Carl Schurz and soon attracted other opponents of Grant; Liberal Republicans decried the scandals of the Grant administration and sought civil service reform. The party opposed Grant's Reconstruction policies, particularly the Enforcement Acts. It lost in a landslide, and disappeared from the national stage after the 1872 election.
The Committee of Nine was a group of conservative political leaders in Virginia, led by Alexander H. H. Stuart, following the American Civil War, when Virginia was required to adopt a new Constitution acknowledging the abolition of slavery before its readmission into the Union. They engineered the federal and state political machinery so that separate votes would be taken on the constitution and provisions restricting voting and office-holding rights of former Confederates.

The Constitution of Mississippi is the primary organizing law for the U.S. state of Mississippi delineating the duties, powers, structures, and functions of the state government. Mississippi's original constitution was adopted at a constitutional convention held at Washington, Mississippi in advance of the western portion of the territory's admission to the Union in 1817. The current state constitution was adopted in 1890 following the reconstruction period. It has been amended and updated 100 times in since its adoption in 1890, with some sections being changed or repealed altogether. The most recent modification to the constitution occurred in November 2020, when Section 140 was amended, and Sections 141-143 were repealed.

The history of the state of Mississippi extends back to thousands of years of indigenous peoples. Evidence of their cultures has been found largely through archeological excavations, as well as existing remains of earthwork mounds built thousands of years ago. Native American traditions were kept through oral histories; with Europeans recording the accounts of historic peoples they encountered. Since the late 20th century, there have been increased studies of the Native American tribes and reliance on their oral histories to document their cultures. Their accounts have been correlated with evidence of natural events.

Henry Horatio Wells, a Michigan lawyer and Union Army officer in the American Civil War, succeeded Francis Harrison Pierpont as the appointed provisional governor of Virginia from 1868 to 1869 during Reconstruction. A Radical Republican labeled a carpetbagger, Wells was defeated for election in 1869 by Gilbert C. Walker, who also became his appointed successor. Wells then served as U.S. Attorney for Virginia and later for the District of Columbia.

The First Military District of the U.S. Army was one of five temporary administrative units of the U.S. War Department that existed in the American South. The district was stipulated by the Reconstruction Acts during the Reconstruction period following the American Civil War. It only included Virginia, and was the smallest of the five military districts in terms of size. The district was successively commanded by Brigadier General John Schofield (1867–1868), Colonel George Stoneman (1868–1869) and Brigadier General Edward Canby (1869–1870).

The American Civil War significantly affected Tennessee, with every county witnessing combat. During the War, Tennessee was a Confederate state, and the last state to officially secede from the Union to join the Confederacy. Tennessee had been threatening to secede since before the Confederacy was even formed, but didn’t officially do so until after the fall of Fort Sumter when public opinion throughout the state drastically shifted. Tennessee seceded in protest to President Lincoln's April 15 Proclamation calling forth 75,000 members of state militias to suppress the rebellion. Tennessee provided the second largest number of troops for the Confederacy, and would also provide more southern unionist soldiers for the Union Army than any other state within the Confederacy.

John Curtiss Underwood was an attorney, abolitionist politician and a United States district judge of the United States District Court for the District of Virginia and the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Virginia.

The presidency of Andrew Johnson began on April 15, 1865, when Andrew Johnson became President of the United States upon the assassination of President Abraham Lincoln, and ended on March 4, 1869. He had been Vice President of the United States for only six weeks when he succeeded to the presidency. The 17th president, Johnson was a member of the Democratic Party before the Civil War and had been Lincoln's 1864 running mate on the National Union ticket, which was supported by Republicans and War Democrats. Johnson took office as the Civil War came to a close, and his presidency was dominated by the aftermath of the war. As president, Johnson attempted to build his own party of Southerners and conservative Northerners, but he was unable to unite his supporters into a new party. Republican Ulysses S. Grant succeeded Johnson as president.

After the Civil War, Ulysses S. Grant spent four years as head of the United States Army in peacetime. With his defeat of Robert E. Lee and the Confederacy, Grant was the most popular man in the country. As the Civil War ended Grant turned his attention to the Plains in the American West where there were numerous conflicts between white settlers, railroads, and Native Americans that resulted in wars between the Natives and the U.S. military. While the attempted Fenian invasion of Canada and French intervention in Mexico took some of his time, Grant's biggest focus was on Reconstruction of the defeated Southern states. Grant found himself caught between President Andrew Johnson, who wanted leniency to the South and a continuation of the social structure there, and the Radical Republicans in Congress, who wanted harsher punishment to rebel leaders and more government assistance to the freed slaves. Grant preserved his popularity and authority throughout the crisis that culminated in Johnson's impeachment. In 1868, the Republicans nominated Grant for president, and he won easily over his Democratic challenger.

In 1868, the Democrats nominated former New York Governor Horatio Seymour for President and Francis Preston Blair Jr. for Vice President. The Seymour-Blair ticket ran on a platform which supported national reconciliation and states' rights, opposed Reconstruction, and opposed both Black equality and Black suffrage. Meanwhile, the Republican presidential ticket led by General Ulysses S. Grant benefited from Grant's status as a war hero and ran on a pro-Reconstruction platform. Ultimately, the Seymour-Blair ticket ended up losing to the Republican ticket of General Ulysses S. Grant and House Speaker Schuyler Colfax in the 1868 U.S. presidential election.
Lewis T. Dent was an American explorer, judge, and politician. He was the brother-in-law of Ulysses S. Grant.


















