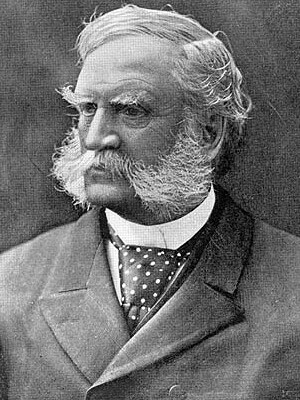Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 2, 1852. Democratic nominee Franklin Pierce defeated Whig nominee General Winfield Scott.
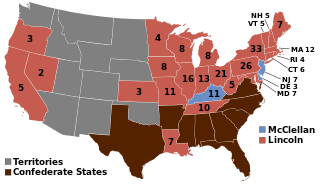
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 8, 1864, near the end of the American Civil War. Incumbent President Abraham Lincoln of the National Union Party easily defeated the Democratic nominee, former General George B. McClellan, by a wide margin of 212–21 in the electoral college, with 55% of the popular vote. For the election, the Republican Party and some Democrats created the National Union Party, especially to attract War Democrats.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 5, 1872. Incumbent President Ulysses S. Grant, the Republican nominee, defeated Democratic-endorsed Liberal Republican nominee Horace Greeley.

Jacob Dolson Cox, Jr., was a statesman, lawyer, Union Army general during the American Civil War, Republican politician from Ohio, Liberal Republican Party founder, educator, author, and recognized microbiologist. He served as president of the University of Cincinnati, the 28th governor of Ohio and as United States Secretary of the Interior. As Governor of Ohio, Cox sided for a time with President Andrew Johnson's Reconstruction plan and was against African American suffrage in the South, though he supported it in Ohio. However, Cox increasingly expressed racist and segregationist viewpoints, advocating a separate colony for blacks to "work out their own salvation." Seeing himself caught between Johnson and the Radical Republicans, Cox decided not to run for reelection. He stayed out of politics for a year, though both Sherman and Grant advocated that Cox replace Stanton as Secretary of War as a means of stemming the demands for Johnson's impeachment. But Johnson declined. When Ulysses S. Grant became president, he nominated Cox Secretary of Interior, and Cox immediately accepted.

The Liberal Republican Party was an American political party that was organized in May 1872 to oppose the reelection of President Ulysses S. Grant and his Radical Republican supporters in the presidential election of 1872. The party emerged in Missouri under the leadership of Senator Carl Schurz and soon attracted other opponents of Grant; Liberal Republicans decried the scandals of the Grant administration and sought civil service reform. The party opposed Grant's Reconstruction policies, particularly the Enforcement Acts. It lost in a landslide, and disappeared from the national stage after the 1872 election.
The Army of the Ohio was the name of two Union armies in the American Civil War. The first army became the Army of the Cumberland and the second army was created in 1863.
The Battle of Princeton Court House was fought May 15–17, 1862 in Mercer County, Virginia in conjunction with Stonewall Jackson's Valley Campaign. It was a minor victory for the Confederate States Army.

Alexander Long was a Democratic United States Congressman who served in Congress from March 4, 1863, to March 3, 1865.
The Massachusetts Republican Party (MassGOP) is the Massachusetts branch of the U.S. Republican Party.
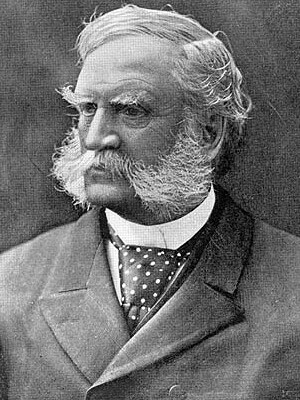
George Washington Morgan was an American soldier, lawyer, politician, and diplomat. He fought in the Texas Revolution and the Mexican–American War, and was a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Morgan later served as a three-term reconstruction era United States Congressman from Ohio. He also served as the United States Ambassador to Portugal from 1858 to 1861, during the term of President James Buchanan.

George Washington Julian was a politician, lawyer, and writer from Indiana who served in the United States House of Representatives during the 19th century. A leading opponent of slavery, Julian was the Free Soil Party's candidate for vice president in the 1852 election and was a prominent Radical Republican during the American Civil War and the Reconstruction era.

Martin Welker was an American politician and judge who was a U.S. Representative from Ohio for three terms from 1865 to 1871 and a district judge of the United States District Court for the Northern District of Ohio from 1873 to 1889.

The 1868–69 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1868 and 1869, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 2000 United States presidential election in Tennessee was held on November 7, 2000, and was part of the 2000 United States presidential election. Voters chose 11 representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1992 United States presidential election in Tennessee took place on November 3, 1992, as part of the 1992 United States presidential election. Voters chose 11 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
Electoral history of John Sherman, Representative, United States Senator, and cabinet member.

The 1920 United States presidential election in Virginia took place on November 2, 1920. Voters chose twelve representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president. This was also the first presidential election after the passage of the Nineteenth Amendment, which granted women the right to vote throughout the United States, including Virginia.

The 1895 New Jersey gubernatorial election was held on November 5, 1895. Republican nominee John W. Griggs defeated Democratic nominee Alexander T. McGill with 52.28% of the vote.
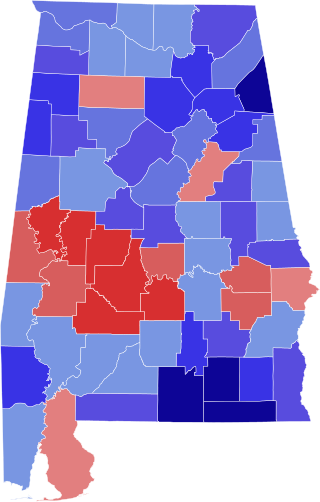
The 1874 Alabama gubernatorial election took place on November 3, 1874, in order to elect the governor of Alabama. Incumbent Republican David P. Lewis unsuccessfully ran for reelection, losing to Democratic former U.S. Representative George S. Houston. This election would end an era of serious competition between the local Democratic and Republican parties, and start a 112-year win streak for Democrats in the gubernatorial level.

The 1865 Connecticut gubernatorial election was held on April 3, 1865, the last such election held during the American Civil War, and the last gubernatorial election in which the Republicans adopted the National Union Party name. It was a rematch of the 1864 Connecticut gubernatorial election. Incumbent governor and National Union nominee William Alfred Buckingham defeated Democratic nominee Origen S. Seymour with 57.48% of the vote. It was the eighth and last of Buckingham's consecutive victories.