The Modified Mercalli intensity scale measures the effects of an earthquake at a given location. This is in contrast with the seismic magnitude usually reported for an earthquake.
The 1857 Fort Tejon earthquake occurred at about 8:20 a.m. on January 9 in central and Southern California. One of the largest recorded earthquakes in the United States, with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.9, it ruptured the southern part of the San Andreas Fault for a length of about 225 miles, between Parkfield and Wrightwood.

The 1987 Whittier Narrows earthquake occurred in the southern San Gabriel Valley and surrounding communities of Southern California, United States, at on October 1. The moderate magnitude 5.9 blind thrust earthquake was centered several miles north of Whittier in the town of Rosemead, had a relatively shallow depth, and was felt throughout southern California and southern Nevada. Many homes and businesses were affected, along with roadway disruptions, mainly in Los Angeles and Orange counties. Damage estimates ranged from $213–358 million, with 200 injuries, three directly related deaths, and five additional fatalities that were associated with the event.
The 1949 Olympia earthquake occurred on April 13 at with a moment magnitude of 6.7 and a maximum Mercalli Intensity of VIII (Severe). The shock was located in the area between Olympia and Tacoma, and was felt throughout the state, as well as parts of Oregon, British Columbia, Idaho, and Montana. It is the largest recorded earthquake to occur in the Puget Sound region of Washington. Eight people were killed, a minimum of 64 people were injured, and the total damage is estimated at $25 million.

The 1983 Borah Peak earthquake occurred on October 28, at in the western United States, in the Lost River Range at Borah Peak in central Idaho.
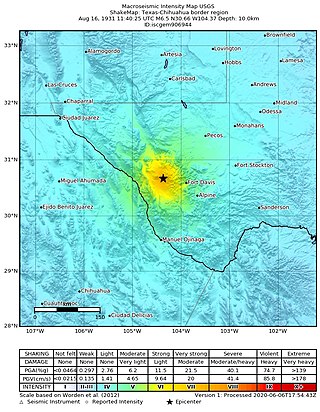
In the early morning hours of August 16, 1931, a powerful earthquake occurred in West Texas with a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). Estimates of its magnitude range between 5.8 and 6.4 mb, making it the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Texas history. Its epicenter was near the town of Valentine, Texas; there, the earthquake caused damage to many homes and buildings. The earthquake may have been caused by movement along oblique-slip faulting in West Texas, the most seismically active region in the state. Shaking from the earthquake was perceptible within a 400 mi (640 km) radius of the epicenter, affecting four U.S. states and northern Mexico. Several foreshocks and aftershocks accompanied the primary temblor, with the aftershocks continuing until at least November 3, 1931. The main earthquake caused no fatalities, though several people sustained minor injuries; the damage in Valentine amounted to $50,000–$75,000.
The 1984 Morgan Hill earthquake occurred on April 24 at in the Santa Clara Valley of Northern California. The shock had a moment magnitude of 6.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The epicenter was located near Mount Hamilton in the Diablo Range of the California Coast Ranges. Nearby communities sustained serious damage with financial losses of at least US$7.5 million.

The 1940 New Hampshire earthquakes struck on December 20 and again on December 24. Both shocks had an estimated magnitude of 5.6, and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. These doublet earthquakes were the largest to hit the state in several hundred years. Damage included minor fractures or knocked over chimneys in a zone extending through New Hampshire and four other states: Maine, New York, Vermont and Massachusetts.
The 1812 San Juan Capistrano earthquake, also known simply as the Capistrano earthquake or the Wrightwood earthquake, occurred on December 8 at in Alta California. At the time, this was a colonial territory of the Spanish Empire. Damage occurred at several of the missions in the region of Pueblo de Los Ángeles, including Mission San Gabriel Arcángel and Mission San Juan Capistrano, where 40 parishioners were killed during the collapse of a church at an early morning service. Tree ring and paleoseismic evidence show that there is a strong likelihood that the earthquake originated along the Mojave segment of the San Andreas Fault near Wrightwood, but other faults have been suggested as the cause.

The 1975 Hawaii earthquake occurred on November 29 with a moment magnitude of 7.7 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The shock affected several of the Hawaiian Islands and resulted in the deaths of two people and up to 28 injured. Significant damage occurred in the southern part of the Big Island totalling $4–4.1 million, and it also triggered a small brief eruption of Kilauea volcano.
The 1991 Sierra Madre earthquake occurred on June 28 at with a moment magnitude of 5.6 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. The thrust earthquake resulted in two deaths, around 100 injuries, and damage estimated at $33.5–40 million. The event occurred beneath the San Gabriel Mountains on the Clamshell–Sawpit Fault, which is a part of the Sierra Madre–Cucamonga Fault System. Instruments captured the event at a number of strong motion stations in Southern California.
The 1979 Coyote Lake earthquake occurred at on August 6 with a moment magnitude of 5.7 and a maximum Mercalli Intensity of VII. The shock occurred on the Calaveras Fault near Coyote Lake in Santa Clara County, California and resulted in a number of injuries, including some that required hospitalization. Most of the $500,000 in damage that was caused was non-structural, but several businesses were closed for repairs. Data from numerous strong motion instruments was used to determine the type, depth, and extent of slip. A non-destructive aftershock sequence that lasted throughout the remainder of the month was of interest to seismologists, especially with regard to fault creep, and following the event local governments evaluated their response to the incident.
The 1957 San Francisco earthquake occurred on March 22 at 11:44:22 local time with a moment magnitude of 5.7 and a maximum Mercalli Intensity of VII. It was located just off the San Francisco Peninsula near the San Andreas Fault and was felt in a limited portion of Northern and Central California. There was a non-destructive foreshock and aftershock sequence that lasted for several months. With financial losses of around US$1 million, damage was considered minimal, with one death and forty injuries.
The 1986 North Palm Springs earthquake occurred on July 8 at with a moment magnitude of 6.0 and a maximum Mercalli Intensity of VII. The shock occurred in a complex setting along the San Andreas Fault Zone where it bisects San Gorgonio Mountain and San Jacinto Peak at the San Gorgonio Pass and was the first in a series of three earthquakes that affected southern California and the northern Owens Valley in July 1986. Numerous strong motion instruments recorded the event, one of which showed relatively high accelerations. Between 29 and 40 people were injured, and financial losses were estimated to be in the range of $4.5–6 million.
The 1980 Eureka earthquake occurred on November 8 at along the northern coastal area of California in the United States. With a moment magnitude of 7.3 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII, this strike-slip earthquake was the largest to occur in California in 28 years. Although damage was considered light, several loss estimates equaled or exceeded $2 million, and six injuries resulted when two vehicles came down with the partial collapse of a highway overpass on US 101 in Fields Landing. The north coast of California experiences frequent plate boundary earthquakes near the Mendocino triple junction and intraplate events also occur within the Gorda plate.
The 1892 Vacaville–Winters earthquakes occurred in northern California as a large doublet on April 19 and April 21. Measured on a seismic scale that is based on an isoseismal map or the event's felt area, the 6.4 and 6.2 Mla events were assigned a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent), and affected the North Bay and Central Valley areas. The total damage was estimated to be between $225,000 and 250,000 and one person was killed. No evidence of fault movement on the surface of the ground was observed as a result of either of the strong shocks. Both occurred in the domain of the San Andreas strike-slip system of faults, but their focal mechanism is uncertain.

The 1918 San Jacinto earthquake occurred in extreme eastern San Diego County in Southern California on April 21 at . The shock had a moment magnitude of 6.7 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). Several injuries and one death occurred with total losses estimated to be $200,000.
The 1932 Eureka earthquake occurred on June 6 at along the northern coastal area of California in the United States. With a moment magnitude of 6.4 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe), this earthquake left one person dead from a falling chimney and several injured. The shock was the largest in the area since 1923 and was felt in southern Oregon and northern California.
The 1981 Westmorland earthquake occurred at 05:09 Pacific Daylight Time on April 26. The moderate strike-slip shock took place in the Imperial Valley of Southern California, just north of the Mexico–United States border. No injuries or deaths occurred, but damage was estimated at $1–3 million. With a Mercalli intensity of VII, this was one of fifteen intensity VII or greater shocks in the Imperial Valley that were observed in the 20th century up until April 1981. The region experiences large stand-alone events and earthquake swarms due to its position in an area of complex conditions where faulting transitions from strike-slip movement to the north and divergence to the south.






