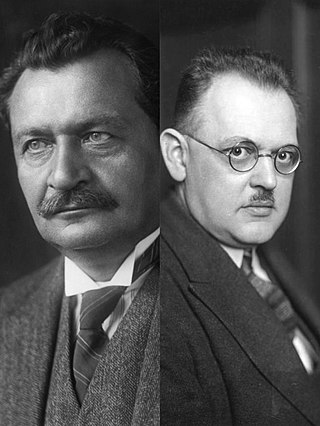General elections were held in Denmark on 11 March 1998. Although the centre-right parties led by Venstre had been expected to win, the Social Democratic Party-led government of Poul Nyrup Rasmussen remained in power in a very close vote that required several recounts.
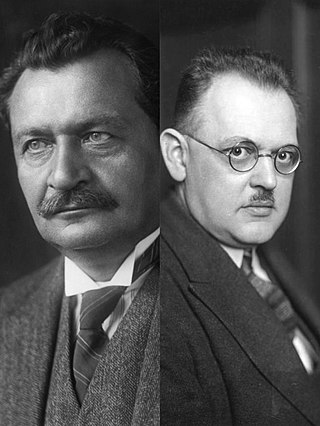
Federal elections were held in Germany on 6 June 1920. Territorial disputes meant that voting was delayed in East Prussia and Schleswig-Holstein until 20 February 1921, and until 19 November 1922 in Oppeln. The Social Democratic Party remained the largest party in the Reichstag although it lost over a third of its seats. Voter turnout was about 79.2%.
Federal elections were held in Germany on 4 May 1924, after the Reichstag had been dissolved on 13 March. The Social Democratic Party remained the largest party, winning 100 of the 472 seats. Voter turnout was 77.4%.

Parliamentary elections were held in Russia on 12 December 1993. They were the first parliamentary elections in post-Soviet Russia and the only time to the Federation Council, with future members appointed by provincial legislatures and governors.

General elections were held in Liechtenstein on 1 February 1970. The Patriotic Union won 8 of the 15 seats in the Landtag, the first time it had held a majority since its formation in 1936. However, it continued the coalition government with the Progressive Citizens' Party, which had been in power since 1938. Voter turnout was 94.8%, although only male citizens were allowed to vote.

A non-binding referendum on nuclear power was held in Sweden on 23 March 1980. Three proposals were put to voters. The second option, the gradual phasing out of nuclear power, won a narrow plurality of the vote, receiving 39.1% of the ballots cast to 38.7% for option 3. Option 1 was the least popular, receiving only 18.9% of the votes.
A constitutional referendum was held in Albania on 7 November 1994. Voters were asked whether they approved of the new constitution published on 6 October, which would have given more power to the country's president. However, it was rejected by voters, with just 43.6% in favour. Voter turnout was 84.4%.

A referendum on the use of nuclear power was held in Austria on 5 November 1978. Voters were asked whether they approved a law allowing the peaceful use of nuclear power, particularly relating to the start-up of the Zwentendorf Nuclear Power Plant. Voters narrowly rejected it, with 50.5% voting against. As a result, although the Power Plant was finished, it never operated and has been repurposed for various projects over the years.

Full general elections were held in Belgium on 14 October 1894, with run-off elections held on 21 October 1894.

Parliamentary elections were held in Bulgaria on 24 December 1939, although voting continued in some areas into January 1940. The elections were officially held on a non-partisan basis with the Bulgarian Agrarian National Union and Bulgarian Communist Party banned, and in a process tightly controlled by Tsar Boris III, by then the real power in the country. However, candidates representing parties did contest the elections. Pro-government candidates won a majority of seats. Voter turnout was 67.2%.
General elections were held in Italy on 7 March 1909, with a second round of voting on 14 March. The "ministerial" left-wing bloc remained the largest in Parliament, winning 329 of the 508 seats.

Three referendums were held in Liechtenstein during 1925. The first on 13 September was on the subject of the Lawena power plant and was approved by 56.1% of voters. The second and third were held on 13 December and concerned two proposals on civil order, the Gassner Initiative and a counterproposal from the Landtag. The Landtag's proposal was approved by 81.7% of voters, whilst the Gassner Initiative was rejected by 89.1%.

A referendum on fire insurance was held in Liechtenstein on 7 February 1926. Voters were asked whether a state insurance scheme for fire damage should be established. The proposal was rejected by 65.8% of voters.

Two referendums were held in Liechtenstein during 1947. The first was held on 10 January, on an initiative to reduce the rate of taxation, backdated to 1946, and was approved by 58.7% of voters. The second was held on 15 June concerning the law on power plants, and was approved by 91% of voters.

General elections were held in Liechtenstein on 29 April 1945. Following the "silent elections" of 1939, they were the first to use the new proportional representation system. The Progressive Citizens' Party won eight of the 15 seats in the Landtag, but remained in coalition with the Patriotic Union.
General elections were held in Romania in June 1939. The Chamber of Deputies was elected on 1 June, whilst the Senate was elected a day later. They were the first since the introduction of the royal dictatorship of King Carol II under the 1938 constitution. Voters were presented with a single list from the National Renaissance Front, which had been the only legally permitted party in Romania since December.
Parliamentary elections were held in Romania on 30 November 1952. They were the second held under communist rule, and the first under a constitution adopted that September. They were also the first held after longtime Prime Minister Petru Groza handed the post to Gheorghe Gheorghiu-Dej, who as leader of the communist Romanian Workers' Party (PMR) had been the country's de facto leader since the communists seized full power in 1947.

General elections were held in San Marino on 28 August 1932. After it had risen to power over the country in April 1923, the Sammarinese Fascist Party was the only party to contest the elections, winning all 60 seats.
Ten referendums were held in Switzerland in 1990. The first six were held on 1 April on four popular initiatives, a federal resolution on viticulture and an amendment to the federal law on the organisation of the federal judiciary. The four popular initiatives were all related to roadbuilding; "Stop the concrete – for a limitation on road making," "for an autobahn-free countryside between Murten and Yverdon," "for an autobahn-free Knonauer Amt," and "for a free Aarelandschaft between Biel and Solothurn/Zuchwil." All six were rejected by voters.
Thirteen referendums were held in Switzerland during 1994. The first five were held on 20 February on federal resolutions on roadbuilding, continuing existing truck tolls and varying tolls based on engine power or mileage, as well as a popular initiative "for the protection of the alpine region from through traffic" and an amendment to the aeronautical law. All five were approved by voters. The second set of referendums was held on 12 June on federal resolutions on an article on the Swiss Federal Constitution on the promotion of culture and a review of the procedure for naturalising young immigrants, as well as a federal law on Swiss troops in peacekeeping operations. Whilst the resolutions were both approved by a majority of voters, they did not receive the approval from the majority of cantons, so were rejected, as was the law on troops.