Washington State's Supreme Court has 9 members elected at large. In 2004, 3 members of the court were up for election. [1]
| Elections in Washington |
|---|
 |
Washington State's Supreme Court has 9 members elected at large. In 2004, 3 members of the court were up for election. [1]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Washington Non Partisan | Jim Johnson | 1,178,194 | 52.0286 | |
| Washington Non Partisan | Mary Kay Becker | 1,086,319 | 47.9714 | |
| Total votes | 2,264,513 | 100.00 | ||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Washington Non Partisan | Barbara Madsen | 1,892,177 | 100.00 | |
| Total votes | 1,892,177 | 100.00 | ||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Washington Non Partisan | Richard B. Sanders | 1,310,998 | 61.0313 | |
| Washington Non Partisan | Terry Sebring | 837,077 | 38.9687 | |
| Total votes | 2,148,075 | 100.00 | ||

The European Convention on Human Rights is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by the then newly formed Council of Europe, the convention entered into force on 3 September 1953. All Council of Europe member states are party to the convention and new members are expected to ratify the convention at the earliest opportunity.
The politics of Hungary takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic. The prime minister is the head of government of a pluriform multi-party system, while the president is the head of state and holds a largely ceremonial position.

The International Court of Justice, or colloquially the World Court, is the only international court that adjudicates general disputes between nations, and gives advisory opinions on international legal issues. It is one of the six organs of the United Nations (UN), and is located in The Hague, Netherlands.
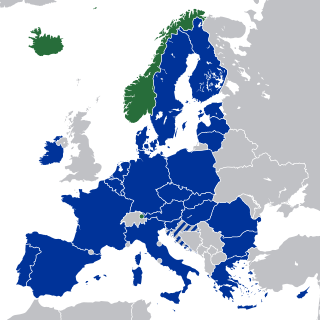
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the Agreement on the European Economic Area, an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade Association. The EEA links the EU member states and three of the four EFTA states into an internal market governed by the same basic rules. These rules aim to enable free movement of persons, goods, services, and capital within the European single market, including the freedom to choose residence in any country within this area. The EEA was established on 1 January 1994 upon entry into force of the EEA Agreement. The contracting parties are the EU, its member states, and Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway. New members of EFTA would not automatically become party to the EEA Agreement, as each EFTA State decides on its own whether it applies to be party to the EEA Agreement or not. According to Article 128 of the EEA Agreement, "any European State becoming a member of the Community shall, and the Swiss Confederation or any European State becoming a member of EFTA may, apply to become a party to this Agreement. It shall address its application to the EEA Council." EFTA does not envisage political integration. It does not issue legislation, nor does it establish a customs union. Schengen is not a part of the EEA Agreement. However, all of the four EFTA States participate in Schengen and Dublin through bilateral agreements. They all apply the provisions of the relevant Acquis.

Roland-Garros, colloquially referred to as the French Open in anglophone countries, is a major tennis tournament held over two weeks at the Stade Roland Garros in Paris, France, beginning in late May each year. The tournament and venue are named after the French aviator Roland Garros. The French Open is the premier clay court championship in the world and the only Grand Slam tournament currently held on this surface. It is chronologically the second of the four annual Grand Slam tournaments, occurring after the Australian Open and before Wimbledon and the US Open. Until 1975, the French Open was the only major tournament not played on grass. Between the seven rounds needed for a championship, the clay surface characteristics, and the best-of-five-set men's singles matches, the French Open is widely regarded as the toughest and most physically demanding tournament in tennis.

Otto Georg Schily is a former Federal Minister of the Interior of Germany, his tenure was from 1998 to 2005, in the cabinet of Chancellor Gerhard Schröder. He is a member of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD).

Rahul Rajiv Gandhi is an Indian politician and a member of the Indian Parliament who represents the constituency of Rae Bareli, Uttar Pradesh and Wayanad, Kerala, in the Lok Sabha. He previously represented the constituency of Amethi, Uttar Pradesh. He is a member of the main opposition party, the Indian National Congress, and was the party president from December 2017 to July 2019. Gandhi is the chairperson of the Indian Youth Congress, the National Students Union of India and a trustee of the Rajiv Gandhi Foundation and Rajiv Gandhi Charitable Trust. He is the son of the former Prime Minister of India, Rajiv Gandhi and Sonia Gandhi.

The 2004 Canadian federal election was held on June 28, 2004, to elect members to the House of Commons of Canada of the 38th Parliament of Canada. The Liberal government of Prime Minister Paul Martin lost its majority but was able to continue in office as a minority government after the election. This was the first election contested by the newly amalgamated Conservative Party of Canada, after it was formed by the two right-of-centre parties, the Progressive Conservative Party and the Canadian Alliance.

The Government of India constitutionally known as the Union Government and also called the Central Government, is the national authority of the Republic of India, a federal republic located in South Asia, consisting of 28 states and eight union territories.

The Supreme Court of the State of Ohio is the highest court in the U.S. state of Ohio, with final authority over interpretations of Ohio law and the Ohio Constitution. The court has seven members, a chief justice and six associate justices, who are elected at large by the voters of Ohio for six-year terms. The court has a total of 1,550 other employees. Since 2004, the court has met in the Thomas J. Moyer Ohio Judicial Center on the east bank of the Scioto River in Downtown Columbus. Prior to 2004, the court met in the James A. Rhodes State Office Tower and earlier in the Judiciary Annex of the Ohio Statehouse.

The government of Maryland is conducted according to the Maryland Constitution. The United States is a federation; consequently, the government of Maryland, like the other 49 state governments, has exclusive authority over matters that lie entirely within the state's borders, except as limited by the Constitution of the United States.

The New York Court of Appeals is the highest court in the Unified Court System of the State of New York. It consists of seven judges: the Chief Judge and six associate judges, who are appointed by the governor and confirmed by the state senate to 14-year terms. The Chief Judge of the Court of Appeals also heads administration of the state's court system, and thus is also known as the Chief Judge of the State of New York. The Court of Appeals was founded in 1847 and is located in the New York Court of Appeals Building in Albany, New York.

The Supreme Court of Chile is the highest court in Chile. It also administers the lower courts in the nation. It is located in the capital Santiago.

The chief justice of New Zealand is the head of the New Zealand judiciary, and presides over the Supreme Court of New Zealand. The chief justice of New Zealand is also the chief justice of Tokelau. Before the establishment of the Supreme Court in 2004, the chief justice was the presiding judge in the High Court of New Zealand, and was also ex officio a member of the Court of Appeal of New Zealand. The office is established by the Senior Courts Act 2016, which describes the chief justice as "senior to all other judges".
The Vermont Supreme Court is the highest judicial authority of the U.S. state of Vermont. Unlike most other states, the Vermont Supreme Court hears appeals directly from the trial courts, as Vermont has no intermediate appeals court.

Clarence Thomas is an American lawyer and jurist who serves as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States. He was nominated by President George H. W. Bush to succeed Thurgood Marshall and has served since 1991. After Marshall, Thomas is the second African American to serve on the Supreme Court and has been its longest-serving member since Anthony Kennedy's retirement in 2018. Since Stephen Breyer's retirement in 2022, he is also the Court's oldest member.

Edna Arbel is an Israeli lawyer who was a justice on the Supreme Court of Israel from May 2004 to June 2014. She is a native of Jerusalem.

The Rajasthan Legislative Assembly or the Rajasthan Vidhan Sabha is the unicameral legislature of the Indian state of Rajasthan.
The Honourable or The Honorable is an honorific style that is used as a prefix before the names or titles of certain people, usually with official governmental or diplomatic positions.

Till Steffen is a German lawyer and politician of Alliance 90/The Greens who has been serving as a member of the German Bundestag since the 2021 elections, representing the Hamburg-Eimsbüttel district.