The 2004 United States presidential election in Utah took place on November 2, 2004. It was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose five representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2008 United States presidential election in Florida took place on November 4, as part of the 2008 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Florida voters chose 27 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1988 United States presidential election in Mississippi took place on November 8, 1988. All fifty states and the District of Columbia, were part of the 1988 United States presidential election. Mississippi voters chose seven electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.

Since Alaska's admission to the Union in January 1959, it has participated in 16 United States presidential elections, always having 3 electoral votes. In the 1960 presidential election, Alaska was narrowly won by the Republican Party's candidate and incumbent vice president Richard Nixon, defeating the Democratic Party's candidate John F. Kennedy by a margin of just 1.88%. In the 1964 presidential election, the Democratic Party's candidate Lyndon B. Johnson won Alaska in a national Democratic landslide victory. Since the 1964 election, Alaska has been won by the Republican Party in every presidential election. However, no Republican candidate has gotten 55% of the statewide vote since 2008. Donald Trump received 54.5% in 2024.

Since Arizona's admission to the Union in February 1912, it has participated in 28 United States presidential elections.

Arkansas is a state in the South Central region of the United States. Since its admission to the Union in June 1836, it has participated in 46 United States presidential elections. In the realigning 1860 election, Arkansas was one of the ten slave states that did not provide ballot access to the Republican nominee, Abraham Lincoln. Subsequently, John C. Breckinridge won the state by a comfortable margin, becoming the first third party candidate to win Arkansas. Soon after this election, Arkansas seceded from the Union and joined the Confederacy. Following the secession, Arkansas did not participate in the 1864 presidential election. After the Civil War, Arkansas was readmitted to the Union in 1868. In the 1872 election, all six of Arkansas's electoral votes were invalidated due to various irregularities including allegations of electoral fraud.

Since being admitted to the Union in 1850, California has participated in 43 presidential elections. A bellwether from 1888 to 1996, voting for the losing candidates only three times in that span, California has become a reliable state for Democratic presidential candidates since 1992.
Connecticut is a state in the New England region of the United States. One of the original Thirteen Colonies, Connecticut has participated in all sixty U.S. presidential elections since the American Revolution. In the early days of the United States, Connecticut was known for supporting the conservative Federalist Party. In the Second Party System, Connecticut leaned towards the anti-Jackson candidates. Following the Civil War, Connecticut was a swing state for a long time until 1896. Thereafter until 1932, Connecticut was a Republican stronghold. During this period, Connecticut Republican Party chairman J. Henry Roraback built up a political machine which was "efficient, conservative, penurious, and in absolute control".

Florida is a state in the South Atlantic region of the United States. Since its admission to the Union in March 1845, it has participated in every United States presidential elections, with the 1848 election being the first. In this election, the Whig Party won Florida's three electoral votes with 57.20% of the vote; this was its only victory in the state.
Hawaii is a state in the Western United States located in the Pacific Ocean about 2,000 miles from the U.S. mainland. Since its admission to the Union in August 1959, it has participated in 16 United States presidential elections. In the 1960 presidential election, Hawaii was narrowly won by the Democratic Party's candidate John F. Kennedy, defeating the Republican Party's candidate and incumbent vice president Richard Nixon by a margin of just 0.06%. In the 1964 presidential election, the Democratic Party's candidate Lyndon B. Johnson won Hawaii by a margin of 57.52%, which remains the largest ever margin of victory in the state's history. Since the 1960 election, Hawaii has been won by the Democratic Party in every presidential election, except in 1972 and 1984, which were both won in a national Republican landslide victory by Nixon and Ronald Reagan respectively.

Since its admission to statehood in 1867, Nebraska has participated in every U.S. presidential election. Since 1992 Nebraska awards two electoral votes based on the statewide vote, and one vote for each of the three congressional districts. The only other state to allow for split electoral college votes is Maine. Republicans in Nebraska have attempted to switch the state back to the Winner-take-all system without success. Proposals to institute winner-take-all passed the Nebraska Legislature in 1995 and 1997 but were vetoed by Democratic governor Ben Nelson. In 2016, an effort to institute winner-take-all failed after two Republicans switched their vote at the last minute. A renewed push for winner-take-all, with support from Republican presidential nominee Donald Trump, was attempted in 2024.
Since New Mexico's admission to the Union in January 1912, it has participated in 29 United States presidential elections. In the 1912 presidential election, Theodore Roosevelt, the Progressive Party's nominee, received the highest vote share (17.1%) ever won by a third-party candidate in New Mexico. In the 1932 presidential election, Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt won New Mexico, defeating Republican Herbert Hoover by 26.96%, which remains the largest ever margin of victory in the state's history. In the 2000 presidential election, Democrat Al Gore won New Mexico, defeating Republican George W. Bush by a margin of just 0.06%.

New York state is one the of initial 13 states of America, but due to a deadlock in the state legislature, it did not join the first presidential election in 1788–89. However, apart from this election, New York State has participated in all 58 other elections in U.S. history.

Oklahoma is a state in the South Central region of the United States. Since it joined the United States in 1907, Oklahoma has participated in 29 presidential elections. It was initially granted seven electoral votes, gaining three following the 1910 census. It was given an additional vote in the 1930 census, which it later lost in the 1940 census. The state's electoral votes were reduced to eight in the 1950 census before returning to its original seven following the 2000 census.
Utah is a state in the Mountain West sub-region of the Western United States. Since its admission to the Union in January 1896, it has participated in 32 United States presidential elections. In the 1896 presidential election, first presidential election in which the state participated, Utah was won in a landslide by Democrat William Jennings Bryan, who received almost 83 percent of the state's vote. 1896 was the only election in which Utah voted for a losing democratic candidate. The state would quickly swing towards the Republican Party in the years that followed, although it would remain a swing state at the presidential level well into the 1940s. In the 1912 election, Utah was one of only two states won by incumbent Republican President William Howard Taft. However, the state would vote for the Democratic nominee by a large margin in 1916, 1932, 1936, 1940, and 1944, and by a narrow margin in 1948. However, since the latter election, the state has become very heavily Republican and has only voted for a Democratic presidential nominee once.

Since becoming a state on July 10, 1890, Wyoming has been involved in 33 presidential elections in the United States, consistently holding 3 electoral votes. Wyoming granted women the right to vote in 1869, prior to joining the Union, and was the first place in America to do so. This was a significant milestone for women's suffrage and paved the way for other states to follow suit. As a state with a strong Republican tradition, Wyoming tends to favor the Republican Party in presidential elections. It has consistently voted for Republican candidates in recent decades and is considered a reliably red state. When Wyoming participated in its first presidential election in 1892, Republican candidate Benjamin Harrison won the state with 50.52% of the vote. Harrison's Democratic opponent, Grover Cleveland, who went on to win the election, did not even appear on the ballot in Wyoming.

Since the enactment of the 23rd amendment to the Constitution in 1961, the District of Columbia has participated in 16 presidential elections. The amendment states that it cannot have any more electoral votes than the state with the smallest number of electors. Since then, it has been allocated three electoral votes in every presidential election. The Democratic Party has immense political strength in the district. In each of the 16 presidential elections, the district has overwhelmingly voted for the Democratic candidate, with no margin less than 56.5 percentage points. It has been won by the losing candidate in 9 of the 16 elections.

The 1864 United States presidential election in Kansas took place on November 8, 1864, as part of the 1864 United States presidential election. Kansas voters chose three representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
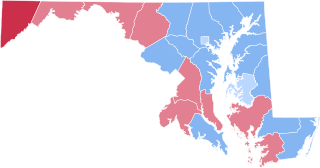
The 1904 United States presidential election in Maryland took place on November 8, 1904. All contemporary 45 states were part of the 1904 United States presidential election. State voters chose eight electors to the Electoral College, which selected the president and vice president.