In logic and related fields such as mathematics and philosophy, "if and only if" is a biconditional logical connective between statements, where either both statements are true or both are false.
Propositional calculus is a branch of logic. It is also called propositional logic, statement logic, sentential calculus, sentential logic, or sometimes zeroth-order logic. It deals with propositions and relations between propositions, including the construction of arguments based on them. Compound propositions are formed by connecting propositions by logical connectives. Propositions that contain no logical connectives are called atomic propositions.

Q, or q, is the seventeenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is pronounced, most commonly spelled cue, but also kew, kue and que.
RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman) is a public-key cryptosystem, one of the oldest, that is widely used for secure data transmission. The acronym "RSA" comes from the surnames of Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman, who publicly described the algorithm in 1977. An equivalent system was developed secretly in 1973 at Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ) by the English mathematician Clifford Cocks. That system was declassified in 1997.

Q is a fictional character, as well as the name of a race, in Star Trek appearing in the Next Generation, Deep Space Nine, Voyager, Lower Decks, and Picard series and in related media. The most familiar Q is portrayed by John de Lancie. He is an extra-dimensional being of unknown origin who possesses immeasurable power over time, space, the laws of physics, and reality itself, being capable of altering it to his whim. Despite his vast knowledge and experience spanning untold eons, and he is not above practical jokes for his own personal amusement, for a Machiavellian or manipulative purpose, or to prove a point. He is said to be almost completely omnipotent and he is continually evasive regarding his true motivations.
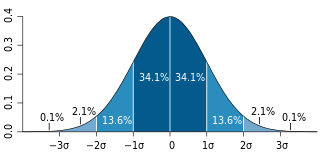
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range.

An electric field is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles and exerts force on all other charged particles in the field, either attracting or repelling them. It also refers to the physical field for a system of charged particles. Electric fields originate from electric charges and time-varying electric currents. Electric fields and magnetic fields are both manifestations of the electromagnetic field, one of the four fundamental interactions of nature.
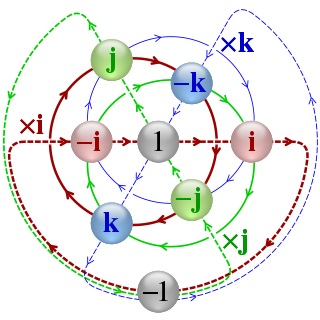
In mathematics, the quaternion number system extends the complex numbers. Quaternions were first described by the Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton in 1843 and applied to mechanics in three-dimensional space. Hamilton defined a quaternion as the quotient of two directed lines in a three-dimensional space, or, equivalently, as the quotient of two vectors. Multiplication of quaternions is noncommutative.

The Dead Sea Scrolls are ancient Jewish religious manuscripts discovered between 1946 and 1956 at the Qumran Caves in what was then Mandatory Palestine, near Ein Feshkha in the West Bank, on the northern shore of the Dead Sea. Dating from the 3rd century BCE to the 1st century CE, the Dead Sea Scrolls are considered to be a keystone in the history of archaeology with great historical, religious, and linguistic significance because they include the oldest surviving manuscripts of entire books later included in the biblical canons, along with deuterocanonical and extra-biblical manuscripts which preserve evidence of the diversity of religious thought in late Second Temple Judaism. At the same time they cast new light on the emergence of Christianity and of Rabbinic Judaism. Almost all of the 15,000 scrolls and scroll fragments are held by Israel in the Shrine of the Book at the Israel Museum. Israel's custody of the scrolls is disputed by Jordan and the State of Palestine on territorial, legal and humanitarian grounds – they were mostly discovered during the period of Jordanian control of the West Bank and captured by Israel in the 1967 Six Day War – whilst Israel's claims are primarily based on religious grounds given their significance in the heritage of Judaism.

Exclusive or or exclusive disjunction is a logical operation that is true if and only if its arguments differ.

In Islam, Jesus is believed to be the penultimate prophet and messenger of God and the Messiah sent to guide the Children of Israel with a book called the Injīl.

Hamiltonian mechanics emerged in 1833 as a reformulation of Lagrangian mechanics. Introduced by Sir William Rowan Hamilton, Hamiltonian mechanics replaces (generalized) velocities used in Lagrangian mechanics with (generalized) momenta. Both theories provide interpretations of classical mechanics and describe the same physical phenomena.

Q was a popular music magazine published monthly in the United Kingdom. It was founded in 1986 by broadcast journalists Mark Ellen and David Hepworth, who were presenters of the BBC television music series The Old Grey Whistle Test. Q's final issue was published in July 2020.

Kamaal Ibn John Fareed, better known by his stage name Q-Tip, is an American rapper, record producer, singer, and DJ. Nicknamed The Abstract, he is noted for his innovative jazz-influenced style of hip hop production and his philosophical, esoteric and introspective lyrical themes. He embarked on his music career in the late 1980s, as an MC and main producer of the influential alternative hip hop group A Tribe Called Quest. In the mid-1990s, he co-founded the production team The Ummah, followed by the release of his gold-certified solo debut Amplified in 1999. In the following decade, he released the Grammy Award-nominated album The Renaissance (2008) and the experimental album Kamaal the Abstract (2009).

The De Havilland Canada DHC-8, commonly known as the Dash 8, is a series of turboprop-powered regional airliners, introduced by de Havilland Canada (DHC) in 1984. DHC was later bought by Boeing in 1988, then by Bombardier in 1992; then by Longview Aviation Capital in 2019, reviving the De Havilland Canada brand. Powered by two Pratt & Whitney Canada PW100s, it was developed from the Dash 7 with improved cruise performance and lower operational costs, but without STOL performance. Three sizes were offered: initially the 37–40 seat -100 until 2005 and the more powerful -200 from 1995, the stretched 50–56 seats -300 from 1989, both until 2009, and the 68–90 seats -400 from 1999, still in production. The QSeries are post-1997 variants fitted with active noise control systems.
In linear algebra, a rotation matrix is a transformation matrix that is used to perform a rotation in Euclidean space. For example, using the convention below, the matrix

QAnon is an American political conspiracy theory and political movement. It originated in the American far-right political sphere in 2017. QAnon centers on fabricated claims made by an anonymous individual or individuals known as "Q". Those claims have been relayed, developed and supplemented by numerous communities and influencers associated with the movement.

A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.

In mathematics, a rational number is a number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers, a numerator p and a non-zero denominator q. For example, is a rational number, as is every integer. The set of all rational numbers, also referred to as "the rationals", the field of rationals or the field of rational numbers is usually denoted by boldface Q, or blackboard bold
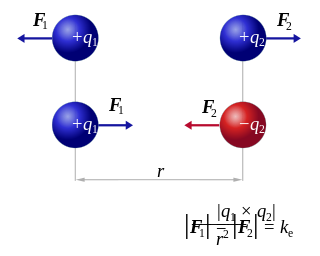
Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law of physics that quantifies the amount of force between two stationary, electrically charged particles. The electric force between charged bodies at rest is conventionally called electrostatic force or Coulomb force. Although the law was known earlier, it was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb, hence the name. Coulomb's law was essential to the development of the theory of electromagnetism, maybe even its starting point, as it made it possible to discuss the quantity of electric charge in a meaningful way.
















