 |
|---|
| Constitution |
A constitutional referendum was held in Kyrgyzstan on 11 April 2021. The new constitution was approved by 85% of voters.
 |
|---|
| Constitution |
A constitutional referendum was held in Kyrgyzstan on 11 April 2021. The new constitution was approved by 85% of voters.
Following the 2020 parliamentary elections, protests started in October 2020 that led to the resignation of president Sooronbay Jeenbekov. In January 2021 a referendum on the form of government was held alongside presidential elections (won by Sadyr Japarov), with voters asked whether they would prefer a presidential system, a parliamentary system, or opposed both. Just over 84% voted in favour of a presidential system.
Work began on drafting a new constitution, which was debated in the Supreme Council in February 2021. The draft new constitution replaces a parliamentary system with a presidential one, with presidents limited to two five years terms instead of a single six-year term. It also reduces the number of seats in the Supreme Council from 120 to 90 and establishes a constitutional court. [1] The changes were described by Associate Professor William Partlett of Melbourne Law School as moving "toward a form of presidentialism that is close to the authoritarian-style 'crown-presidentialism' in the post-Soviet Eurasian space." [2]
In March 2021 members of the Supreme Council passed a bill, scheduling a referendum on the new constitution for 11 April, the same day as local elections. [1]
| Choice | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| For | 1,048,660 | 85.25 | |
| Against | 181,370 | 14.75 | |
| Total | 1,230,030 | 100.00 | |
| Valid votes | 1,230,030 | 93.08 | |
| Invalid/blank votes | 91,472 | 6.92 | |
| Total votes | 1,321,502 | 100.00 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | 3,606,201 | 36.65 | |
| Source: CEC | |||
The new constitution was adopted on 11 April 2021. President Japarov signed it on 5 May 2021. [3]

The history of the Kyrgyz people and the land now called Kyrgyzstan goes back more than 3,000 years. Although geographically isolated by its mountainous location, it had an important role as part of the historical Silk Road trade route. Turkic nomads, who trace their ancestry to many Turkic states such as the First and Second Turkic Khaganates, have inhabited the country throughout its history. In the 13th century, Kyrgyzstan was conquered by the Mongols; subsequently it regained independence but was invaded by Kalmyks, Manchus, and Uzbeks. In 1876, it became part of the Russian Empire, remaining in the USSR as the Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic after the Russian Revolution. Following Mikhael Gorbachev's democratic reforms in the USSR, in 1990 pro-independence candidate Askar Akayev was elected president of the SSR. On 31 August 1991, Kyrgyzstan declared independence from Moscow, and a democratic government was subsequently established.

The politics of Kyrgyzstan, officially known as the Kyrgyz Republic, takes place in the framework of a presidential system representative democratic republic, whereby the President is head of state and the Chairman of the Cabinet of Ministers is head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament. The Economist Intelligence Unit rated Kyrgyzstan an "authoritarian regime" in 2022.

The Constitution of the Russian Federation was adopted by national referendum on 12 December 1993. The last reform was in 2020, see 2020 amendments to the Constitution of Russia.

Kyrgyzstan elects on the national level a head of state – the president – and a legislature. The president is elected for a tenure of single six-year term by the people. The Supreme Council is composed of 120 members filled by proportional representation.

The president of Kyrgyzstan, officially the president of the Kyrgyz Republic, is the head of state and head of government of the Kyrgyz Republic. The president directs the executive branch of the national government, is the commander-in-chief of the Kyrgyz military and also heads the National Security Council.

The Constitution of the Republic of Belarus is the ultimate law of Belarus. The Constitution is composed of a preamble and nine sections divided into 146 articles.

The Supreme Council of Kyrgyzstan, known as the Jogorku Kengesh, is the unicameral parliament of the Kyrgyz Republic. Before Kyrgyzstan's independence from the Soviet Union in 1991, it was known as the Supreme Soviet of the Kirghiz Soviet Socialist Republic.

A new constitution of Kyrgyzstan was passed by referendum on 21 October 2007. It is based on the first post-Soviet constitution originally adopted on 5 May 1993.

A constitutional referendum was held in Kyrgyzstan on 27 June 2010 to reduce presidential powers and strengthen democracy in the wake of the riots earlier in the year. Parliamentary elections followed on 10 October 2010.

The Constitution of Kyrgyzstan was the supreme law of the Kyrgyz Republic. The constitution in force from 2010 until 2021 was passed by referendum on June 27, 2010, replacing the previous constitution. It introduced a strong parliament to the country, reducing the power of the historically strong president. The constitution is similar in many ways to the previous one.
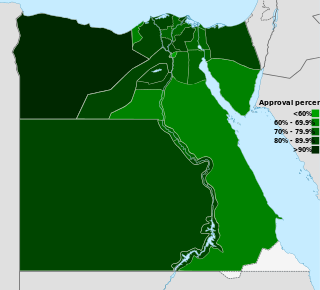
A constitutional referendum was held in Egypt on 19 March 2011, following the 2011 Egyptian revolution. More than 14 million (77%) were in favour, while around 4 million (23%) opposed the changes; 41% of 45 million eligible voters turned out to vote.

The Constitutional Declaration of 2011 was a measure adopted by the Supreme Council of the Armed Forces of Egypt on 30 March 2011. The declaration was intended to serve as the fundamental law of the country pending the enactment of a permanent constitution, following the resignation of President Hosni Mubarak on 11 February.
An Icelandic Constitutional Council (Stjórnlagaráð) for the purpose of reviewing the Constitution of the Republic was appointed by a resolution of Althingi, the Icelandic parliament, on 24 March 2011. Elections were held to create a Constitutional Assembly (Stjórnlagaþing) body, but given some electoral flaws, had been ruled null and void by the Supreme Court of Iceland on 25 January 2011, leading the parliament to place most of the winning candidates into a Constitutional Council with similar mission. The question of whether the text of the proposed constitution should form a base for a future constitution was put to a non-binding referendum, where it won the approval of 67% of voters. However, the government's term finished before the reform bill could be passed, and following governments have not acted upon it.

This national electoral calendar for 2021 lists the national/federal elections held in 2021 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.

Sadyr Nurgojo uulu Japarov is a Kyrgyz politician who has been serving as the president of Kyrgyzstan since 28 January 2021. He previously held the post of acting prime minister of Kyrgyzstan in the 2020 interim government, following the resignation of President Sooronbay Jeenbekov. Japarov also became acting president of Kyrgyzstan after Jeenbekov's resignation, but resigned himself on 14 November 2020 to run for the 2021 presidential election, in which he was elected to succeed the acting president, Talant Mamytov.

Snap parliamentary elections were held in Kyrgyzstan on 28 November 2021. They followed the annulment of the results of the October 2020 elections and the subsequent protests against the election's conduct. Six parties passed the 5% threshold needed to win seats in the parliament. Turnout hit a record low at less than 35%.
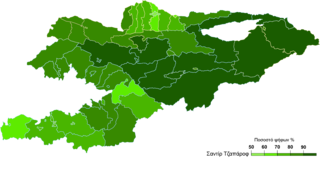
Snap presidential elections were held in Kyrgyzstan on 10 January 2021, alongside a constitutional referendum. The elections were called early following the resignation of President Sooronbay Jeenbekov in the wake of the 2020 Kyrgyzstani protests.
A referendum was held in Kyrgyzstan on 10 January 2021 alongside presidential elections. The referendum asked voters if Kyrgyzstan should adopt a presidential system of government, a parliamentary system, or neither. 84% of voters chose to readopt a presidential system.

A constitutional referendum was planned to be held in Haiti in 2023. It is the first referendum in the country since 1987, and was unilaterally proposed by the administration of Jovenel Moïse. Originally set to be held on 27 June 2021, the referendum was postponed to 26 September 2021, on the same day as the presidential and parliamentary elections. The referendum was again postponed to 7 November. Acting Prime Minister Ariel Henry later postponed it first to February 2022 and then 2023.

The Constitution of Kyrgyzstan is the supreme law of the Kyrgyz Republic. Kyrgyzstan first got a constitution in 1993, a year and a half after the country had gained independence from the Soviet Union in 1991. It has gone through a few constitutions, with the last one being adopted in April 2021.