The 260s decade ran from January 1, 260, to December 31, 269.
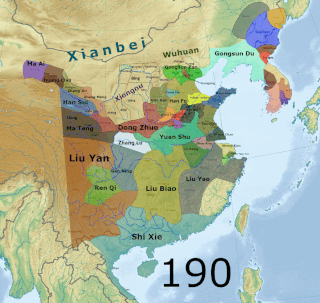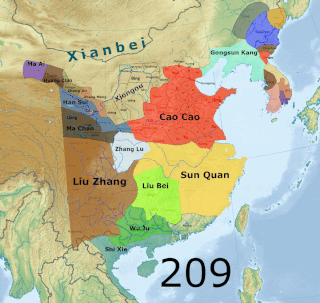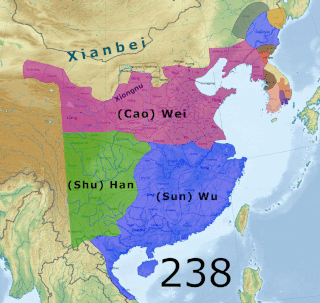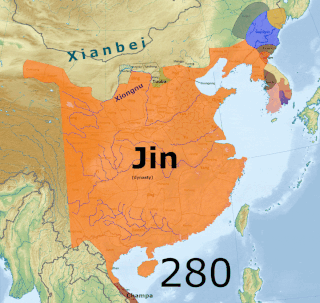
The Three Kingdoms of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu dominated China from 220 to 280 AD following the end of the Han dynasty. This period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and followed by the Western Jin dynasty. Academically, the periodisation begins with the establishment of Cao Wei in 220 and ends with the conquest of Wu by Jin in 280. The period immediately preceding the Three Kingdoms, from 184 to 220, was marked by chaotic infighting among warlords across China as Han authority collapsed. The period from 220 to 263 was marked by a comparatively stable arrangement between Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. This stability broke down with the conquest of Shu by Wei in 263, followed by the usurpation of Cao Wei by Jin in 266 and ultimately the conquest of Wu by Jin in 280.

Year 260 (CCLX) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Saecularis and Donatus. The denomination 260 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Jin dynasty or Jin Empire, sometimes distinguished as the Sima Jin or the Two Jins, was an imperial dynasty in China that existed from 266 to 420. It was founded by Sima Yan, eldest son of Sima Zhao, who had previously been declared the King of Jin. There are two main divisions in the history of the dynasty. The Western Jin (266–316) was established as the successor to Cao Wei after Sima Yan usurped the throne from Cao Huan. The capital of the Western Jin was initially in Luoyang, though it later moved to Chang'an. In 280, after conquering Eastern Wu, the Western Jin ended the Three Kingdoms period and reunited China proper for the first time since the end of the Han dynasty.

Wei was one of the major dynastic states in China during the Three Kingdoms period. The state was established in 220 by Cao Pi based upon the foundations laid by his father Cao Cao during the end of the Han dynasty. Its capital was initially located at Xuchang, and was later moved to Luoyang.
Cao Fang (232–274), courtesy name Lanqing, was the third emperor of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period. He was an adopted son of Cao Rui, the second ruler of Wei. Cao Fang ruled from January 239 to October 254 as a nominal emperor before he was deposed by the regent Sima Shi, after which he became known as the "Prince of Qi". After the fall of Wei in February 266, Cao Fang was conferred the title of "Duke of Shaoling" by Emperor Wu of the Jin dynasty. When he died in 274, he was granted the posthumous name "Li", so his full posthumous title became "Duke Li of Shaoling".
Cao Mao, courtesy name Yanshi, was the fourth emperor of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He was a grandson of Cao Pi, the first emperor of Wei. Described as intelligent and studious, Cao Mao made repeated attempts to seize back state power from the regent Sima Zhao but failed. He was killed in an abortive coup d'état against Sima Zhao.
Cao Huan, courtesy name Jingming, was the fifth and last emperor of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period. On 4 February 266, he abdicated the throne in favour of regent Sima Yan, and brought an end to the Wei regime. After his abdication, Cao Huan was granted the title "Prince of Chenliu" and held it until his death, after which he was posthumously honoured as "Emperor Yuan ".

Emperor Wu of Jin, personal name Sima Yan, courtesy name Anshi (安世), was a grandson of Sima Yi, nephew of Sima Shi and son of Sima Zhao. He became the first emperor of the Jin dynasty after forcing Cao Huan, last emperor of the state of Cao Wei, to abdicate to him. He reigned from 266 to 290, and after conquering the state of Eastern Wu in 280, was the emperor of a reunified China. Emperor Wu was also known for his extravagance and sensuality, especially after the unification of China; legends boasted of his incredible potency among ten thousand concubines.
Sima is a Chinese family name. It is one of the rare two-character Chinese family names; most Chinese family names consist of only a single character. It is an occupational surname, literally meaning "control" (sī) "horses" (mǎ), or "horse officer". The family name originated from one of the offices of the Zhou dynasty.
Wang Yuanji was a Chinese noble lady, aristocrat and later empress dowager of the Jin dynasty, who lived in the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. She was the wife of Sima Zhao, a regent of Cao Wei. She became the empress dowager during the reign of her son Sima Yan, who ended the Wei regime and founded the Jin dynasty. She was posthumously honoured as "Empress Wenming" after her death.
Wei Guan, courtesy name Boyu, was a Chinese military general and politician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He served under the Jin dynasty after the end of the Three Kingdoms period.
Sima Fu, courtesy name Shuda, posthumously known as Prince Xian of Anping, was an imperial prince and statesman of the Jin dynasty of China. He previously served as an official in the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period before his grandnephew, Sima Yan, usurped the Wei throne in February 266 and established the Jin dynasty. Sima Guang, author of Zizhi Tongjian, claimed to be his descendant.
Sima Wang, courtesy name Zichu, posthumously known as Prince Cheng of Yiyang (义阳成王), was an imperial prince and military general of the Jin dynasty of China. He previously served in the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period.
Sima Zhou, courtesy name Zijiang, posthumously known as Prince Wu of Langya (琅琊武王), was an imperial prince and military general of the Jin dynasty of China. He previously served in the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period. His grandson, Sima Rui, was the founding emperor of the Eastern Jin dynasty.
Wang Ye was a Chinese politician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He served under the Jin dynasty (266–420) after the end of the Three Kingdoms period.
Sima Zhao's regicide of Cao Mao, also known as the Ganlu Incident, occurred on 2 June 260 in Luoyang, the capital of the state of Cao Wei, during the Three Kingdoms period. Cao Mao, the nominal emperor of Wei, attempted to oust the regent Sima Zhao, who effectively controlled the Wei government. However, the plot concluded with Cao Mao's death and Sima Zhao retaining his status. Contrary to its intention, the coup actually increased the Sima clan's power and influence in Wei, albeit at the cost of Sima Zhao's personal standing, thus providing a foundation for the eventual usurpation of the Wei throne in February 266 by Sima Zhao's son Sima Yan, who founded the Western Jin dynasty.

Wang Jing, courtesy name Yanwei, was a Chinese politician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China.
Wang Chen, courtesy name Chudao, posthumously known as Duke Yuan of Boling (博陵元公), was a Chinese historian, military general, and politician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. After the Wei regime ended in February 266, he continued serving in the government of the Jin dynasty. He wrote a five-volume text known as the Wang Chudao Collection (王處道集) or Wang Chen Collection (王沈集), which is already lost over the course of history. He also wrote 14 chapters of the Quan Jin Wen (全晉文).

The military history of the Jin dynasty and the Sixteen Kingdoms encompasses the period of Chinese military activities from 266 AD to 420 AD. The Jin dynasty is usually divided into the Western Jin and Eastern Jin in Chinese historiography. Western Jin lasted from its usurpation of Cao Wei in 266 to 316 when the Uprising of the Five Barbarians split the empire and created a number of barbarian states in the north. The Jin court relocated to Jiankang, starting the era of Eastern Jin, which ended in 420 when it was usurped by Liu Yu, who founded the Liu Song dynasty.







