The 180s decade ran from January 1, 180, to December 31, 189.
The 190s decade ran from January 1, 190, to December 31, 199.
The 210s decade ran from January 1, 210, to December 31, 219.
The 220s decade ran from January 1, 220, to December 31, 229.
The 230s decade ran from January 1, 230, to December 31, 239.
The 240s decade ran from January 1, 240, to December 31, 249.
The 260s decade ran from January 1, 260, to December 31, 269.
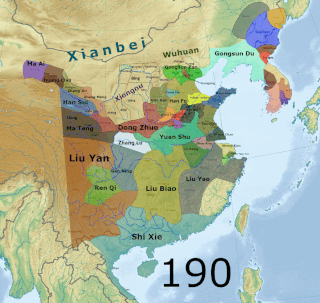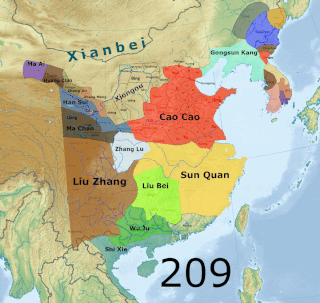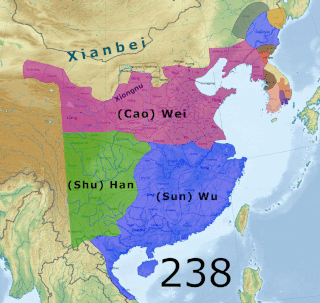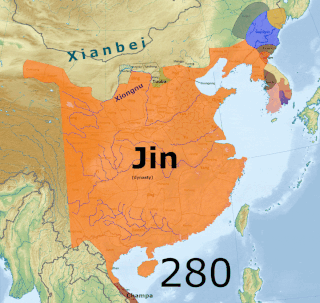
The Three Kingdoms of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu dominated China from 220 to 280 AD following the end of the Han dynasty. This period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and followed by the Western Jin dynasty. Academically, the periodisation begins with the establishment of Cao Wei in 220 and ends with the conquest of Wu by Jin in 280. The period immediately preceding the Three Kingdoms, from 184 to 220, was marked by chaotic infighting among warlords across China as Han authority collapsed. The period from 220 to 263 was marked by a comparatively stable arrangement between Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. This stability broke down with the conquest of Shu by Wei in 263, followed by the usurpation of Cao Wei by Jin in 266 and ultimately the conquest of Wu by Jin in 280.
Year 190 (CXC) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelius and Sura. The denomination 190 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 229 (CCXXIX) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Severus and Cassius. The denomination 229 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Sun Quan, courtesy name Zhongmou (仲謀), posthumously known as Emperor Da of Wu, was the founder of Eastern Wu, one of the Three Kingdoms of China. He inherited control of the warlord regime established by his elder brother, Sun Ce, in 200. He declared formal independence and ruled from November 222 to May 229 as the King of Wu and from May 229 to May 252 as the Emperor of Wu. Unlike his rivals Cao Cao and Liu Bei, Sun Quan was much younger and governed his state mostly separate of politics and ideology. He is sometimes portrayed as neutral considering he adopted a flexible foreign policy between his two rivals with the goal of pursuing the greatest interests for the country.

Wei was one of the major dynastic states in China during the Three Kingdoms period. The state was established in 220 by Cao Pi based upon the foundations laid by his father Cao Cao during the end of the Han dynasty. Its capital was initially located at Xuchang, and was later moved to Luoyang.

Han (漢; 221–263), known in historiography as Shu Han (蜀漢 ) or Ji Han (季漢 "Junior Han"), or often shortened to Shu (Chinese: 蜀; pinyin: Shǔ; Sichuanese Pinyin: Su2 < Middle Chinese: *źjowk < Eastern Han Chinese: *dźok), was a dynastic state of China and one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the Three Kingdoms period. The state was based in the area around present-day Hanzhong, Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, Guizhou, and north Guangxi, an area historically referred to as "Shu" based on the name of the past ancient kingdom of Shu, which also occupied this approximate geographical area. Its core territory also coincided with Liu Bang's Kingdom of Han, the precursor of the Han dynasty.

Wu, known in historiography as Eastern Wu or Sun Wu, was a dynastic state of China and one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the Three Kingdoms period. It previously existed from 220 to 222 as a vassal kingdom nominally under Cao Wei, its rival state, but declared complete independence in November 222. It was elevated to an empire in May 229 after its founding ruler, Sun Quan, declared himself emperor.

Cao Xiu, courtesy name Wenlie, was a Chinese military general of the state of Cao Wei in the Three Kingdoms period of China. A distant younger relative of the warlord Cao Cao, Cao Xiu started his career in the late Eastern Han dynasty as a military officer under Cao Cao. In the early stages of the Hanzhong Campaign of 217–219, he outwitted Zhang Fei and defeated his subordinate officer Wu Lan (吳蘭). Later in his career, he became a provincial-level military commander and fought in various battles against Wei's rival state, Eastern Wu. He died in 228 shortly after the Wei defeat at the Battle of Shiting.
Jia Kui, originally named Jia Qu, courtesy name Liangdao, was a Chinese military general and politician who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He served under the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period.

Year 222 (CCXXII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Antoninus and Severus. The denomination 222 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Wang Chang, courtesy name Wenshu (文舒), was a Chinese military general and politician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China.

The Chu Shi Biao refers to either of two memorials written by Zhuge Liang, the Imperial Chancellor of the state of Shu during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He presented them to Liu Shan, the second emperor of Shu. The first Chu Shi Biao, which is referred to as the "Former Chu Shi Biao", was presented in 227 before Zhuge Liang embarked on the first of a series of military campaigns against Shu's rival state, Wei. The second, known as the "Later Chu Shi Biao", was supposedly submitted in 228 before Zhuge Liang left for the second Northern Expedition.

Wang Shuang, courtesy name Ziquan, was a military officer of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He initially participated in battles against Wei's rival state Eastern Wu but was defeated and captured. Later, he rejoined Wei and was reassigned to the western front to fight against Wei's other rival state, Shu Han. He was killed in battle against Shu forces.







