Publius Licinius Egnatius Gallienus was Roman emperor with his father Valerian from 253 to 260 and alone from 260 to 268. He ruled during the Crisis of the Third Century that nearly caused the collapse of the empire. He won numerous military victories against usurpers and Germanic tribes, but was unable to prevent the secession of important provinces. His 15-year reign was the longest in half a century.

The 3rd century was the period from AD 201 to AD 300 (CCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar.
The 270s decade ran from January 1, 270, to December 31, 279.
The 360s decade ran from January 1, 360, to December 31, 369.
The 240s decade ran from January 1, 240, to December 31, 249.
The 250s was a decade that ran from January 1, 250, to December 31, 259.
The 260s decade ran from January 1, 260, to December 31, 269.

Aurelian was a Roman emperor who reigned from 270 to 275 during the Crisis of the Third Century. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited the Roman Empire after it had nearly disintegrated under the pressure of barbarian invasions and internal revolts. Born in modest circumstances, most likely in Moesia Superior, he entered the Roman army in 235 and climbed up the ranks. He went on to lead the cavalry of the emperor Gallienus, until Gallienus' assassination in 268. Following that, Claudius Gothicus became emperor until his own death in 270. Claudius' brother Quintillus then ruled for three months, before Aurelian took the empire for himself.

Year 274 (CCLXXIV) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelianus and Capitolinus. The denomination 274 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 272 (CCLXXII) was a leap year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Postumius and Veldumnianus. The denomination 272 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 270 (CCLXX) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Antiochianus and Orfitus. The denomination 270 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 260 (CCLX) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Saecularis and Donatus. The denomination 260 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 268 (CCLXVIII) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known in Rome as the Year of the Consulship of Paternus and Egnatius. The denomination 268 for this year has been used since the early medieval period when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Marcus Aurelius Claudius "Gothicus", also known as Claudius II, was Roman emperor from 268 to 270. During his reign he fought successfully against the Alemanni and decisively defeated the Goths at the Battle of Naissus. He died after succumbing to a "pestilence", possibly the Plague of Cyprian that had ravaged the provinces of the Empire.

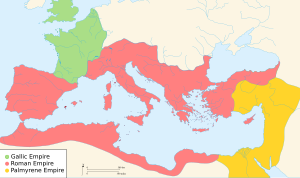
The Gallic Empire or the Gallic Roman Empire are names used in modern historiography for a breakaway part of the Roman Empire that functioned de facto as a separate state from 260 to 274. It originated during the Crisis of the Third Century, when a series of Roman military leaders and aristocrats declared themselves emperors and took control of Gaul and adjacent provinces without attempting to conquer Italy or otherwise seize the central Roman administrative apparatus.

Domitian II was a Roman soldier of the mid 3rd century who was acclaimed emperor, probably in northern Gaul in late 270 or early 271, and struck coins to advertise his elevation. It is now generally assumed that this man is to be equated with the Domitianus who is twice mentioned in the literary sources as a significant figure in the politics of the age, but on neither occasion as an outright contender for the Imperial throne.

Gaius Pius Esuvius Tetricus was a Gallo-Roman nobleman who ruled as emperor of the Gallic Empire from 271 to 274 AD. He was originally the praeses of Gallia Aquitania and became emperor after the murder of Emperor Victorinus in 271, with the support of Victorinus's mother, Victoria. During his reign, he faced external pressure from Germanic raiders, who pillaged the eastern and northern parts of his empire, and the Roman Empire, from which the Gallic Empire had seceded. He also faced increasing internal pressure, which led him to declare his son, Tetricus II, caesar in 273 and possibly co-emperor in 274, although this is debated. The Roman emperor Aurelian invaded in 273 or 274, leading to the Battle of Châlons, at which Tetricus surrendered. Whether this capitulation was the result of a secret agreement between Tetricus and Aurelian or that surrender was necessary after his defeat is debated. Aurelian spared Tetricus, and made him a senator and the corrector (governor) of Lucania et Bruttium. Tetricus died of natural causes a few years after 274.

The Juthungi were a Germanic tribe in the region north of the rivers Danube and Altmühl in what is now the modern German state of Bavaria.

The Palmyrene Empire was a short-lived breakaway state from the Roman Empire resulting from the Crisis of the Third Century. Named after its capital city, Palmyra, it encompassed the Roman provinces of Syria Palaestina, Arabia Petraea, and Egypt, as well as large parts of Asia Minor.