
Amyntas III was king of the ancient kingdom of Macedon in 393 BC and again from 392 to 370 BC. He was the son of Arrhidaeus and grandson of Amyntas, one of the sons of Alexander I. His most famous son is Philip II, father of Alexander the Great. He is historically considered the founder of the unified Macedonian kingdom.

Year 323 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Longus and Cerretanus. The denomination 323 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
This article concerns the period 349 BC – 340 BC.
This article concerns the period 379 BC – 370 BC.
This article concerns the period 389 BC – 380 BC.
This article concerns the period 369 BC – 360 BC
This article concerns the period 359 BC – 350 BC.
This article concerns the period 339 BC – 330 BC.

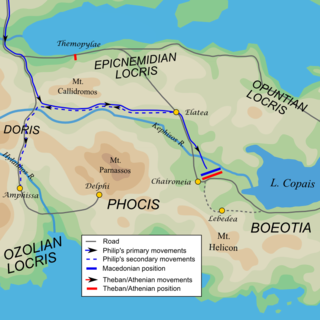
Philip II of Macedon was the king (basileus) of the kingdom of Macedon from 359 BC until his assassination in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty of Macedonian kings, the third son of King Amyntas III of Macedon, and father of Alexander the Great and Philip III. The rise of Macedon, its conquest and political consolidation of most of Classical Greece during the reign of Philip II was achieved in part by his reformation of the Ancient Macedonian army, establishing the Macedonian phalanx that proved critical in securing victories on the battlefield. After defeating the Greek city-states of Athens and Thebes at the Battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC, Philip II led the effort to establish a federation of Greek states known as the League of Corinth, with him as the elected hegemon and commander-in-chief of Greece for a planned invasion of the Achaemenid Empire of Persia. However, his assassination by a royal bodyguard, Pausanias of Orestis, led to the immediate succession of his son Alexander, who would go on to invade the Achaemenid Empire in his father's stead.
Year 338 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Camillus and Maenius. The denomination 338 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 336 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Crassus and Duillius. The denomination 336 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 356 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Ambustus and Laenas. The denomination 356 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 357 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Rutilus and Imperiosus. The denomination 357 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 358 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Ambustus and Proculus. The denomination 358 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 369 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Fidenas, Cicurinus, Cossus, Cornelius, Cincinnatus and Ambustus. The denomination 369 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Chares of Athens was a 4th-century BC Athenian military commander (Strategos), who for a number of years was one of Athens's foremost commanders. He was also a well connected politician enabling him to procure the commands he desired. Commands he primarily used to enrich himself and his adherents.

Under the reign of Philip II, the kingdom of Macedonia, initially at the periphery of classical Greek affairs, came to dominate Ancient Greece in the span of just 25 years, largely thanks to the personality and policies of its king. In addition to utilising effective diplomacy and marriage alliances to achieve his political aims, Philip II was responsible for reforming the ancient Macedonian army into an effective fighting force. The Macedonian phalanx became the hallmark of the Macedonian army during his reign and the subsequent Hellenistic period. His army and engineers also made extensive use of siege engines.

The kingdom of Macedonia was an ancient state in what is now the Macedonian region of northern Greece, founded in the mid-7th century BC during the period of Archaic Greece and lasting until the mid-2nd century BC. Led first by the Argead dynasty of kings, Macedonia became a vassal state of the Achaemenid Empire of ancient Persia during the reigns of Amyntas I of Macedon and his son Alexander I of Macedon. The period of Achaemenid Macedonia came to an end in roughly 479 BC with the ultimate Greek victory against the second Persian invasion of Greece led by Xerxes I and the withdrawal of Persian forces from the European mainland.

The Siege of Perinthus was an unsuccessful attempt by Philip II of Macedon to defeat the Athenian forces at Perinthus, and take the city. The siege was conducted alongside an unsuccessful siege of Byzantium. Both sieges took place in the period just before the Fourth Sacred War.






