Related Research Articles

Alexander III of Macedon, most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20 and spent most of his ruling years conducting a lengthy military campaign throughout Western Asia, Central Asia, parts of South Asia, and Egypt. By the age of 30, he had created one of the largest empires in history, stretching from Greece to northwestern India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders.
The 4th century BCE started the first day of 400 BCE and ended the last day of 301 BCE. It is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period.

Year 334 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caudinus and Calvinus. The denomination 334 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 323 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Longus and Cerretanus. The denomination 323 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 48 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Vatia. The denomination 48 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
This article concerns the period 489 BC – 480 BC.
This article concerns the period 369 BC – 360 BC
This article concerns the period 339 BC – 330 BC.

This article concerns the period 329 BC – 320 BC.
Year 336 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Crassus and Duillius. The denomination 336 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
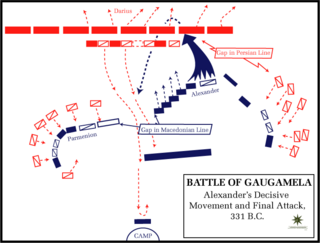
Year 331 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Potitus and Marcellus. The denomination 331 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Antipater was a Macedonian general and statesman under the successive kingships of Philip II of Macedon and his son, Alexander the Great. In the wake of the collapse of the Argead house, his son Cassander would eventually come to rule Macedonia as a king in his own right.
A calendar era is the period of time elapsed since one epoch of a calendar and, if it exists, before the next one. For example, it is the year 2024 as per the Gregorian calendar, which numbers its years in the Western Christian era.

The ancient history of Cyprus shows a precocious sophistication in the Neolithic era visible in settlements such as at Choirokoitia dating from the 9th millennium BC, and at Kalavassos from about 7500 BC.

The Late Period of ancient Egypt refers to the last flowering of native Egyptian rulers after the Third Intermediate Period in the 26th Saite Dynasty founded by Psamtik I, but includes the time of Achaemenid Persian rule over Egypt after the conquest by Cambyses II in 525 BC as well. The Late Period existed from 664 BC until 332 BC, following a period of foreign rule by the Nubian 25th Dynasty and beginning with a short period of Neo-Assyrian suzerainty, with Psamtik I initially ruling as their vassal. The period ended with the conquests of the Persian Empire by Alexander the Great and establishment of the Ptolemaic dynasty by his general Ptolemy I Soter, one of the Hellenistic diadochi from Macedon in northern Greece. With the Macedonian Greek conquest in the latter half of the 4th century BC, the age of Hellenistic Egypt began.

The Ptolemaic Kingdom or Ptolemaic Empire was an Ancient Greek state based in Egypt during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 305 BC by the Macedonian general Ptolemy I Soter, a companion of Alexander the Great, and ruled by the Ptolemaic dynasty until the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC. Reigning for nearly three centuries, the Ptolemies were the longest and final dynasty of ancient Egypt heralding a distinctly new era for religious syncretism and the blending of a new Greco-Egyptian culture.

The siege of Gaza, as part of the Wars of Alexander the Great, took place in October of 332 BCE. Resulting in a victory for Macedon, it ended the 31st Dynasty of Egypt, which functioned as a satrapy under the Achaemenid Persian Empire.
Pharnabazus III was a Persian satrap who fought against Alexander the Great. His father was Artabazos II, and his mother a Greek from Rhodes.

Sabaces was an Achaemenid Persian satrap of the Achaemenid Thirty-first Dynasty of Egypt during the reign of king Darius III of Persia.

The Thirty-first Dynasty of Egypt, also known as the Second Egyptian Satrapy, was effectively a satrapy of the Achaemenid Persian Empire between 343 BC to 332 BC. It was founded by Artaxerxes III, the King of Persia, after his reconquest of Egypt and subsequent crowning as Pharaoh of Egypt, and was disestablished upon the conquest of Egypt by Alexander the Great.
References
- ↑ George Frederick Kunz, The Magic of Jewels and Charms (Courier Corporation, 1915) p323
- ↑ Walkbank, Frank W. (February 21, 2024). "Alexander the Great". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved February 25, 2024.