
Alaric I was the first king of the Visigoths, from 395 to 410. He rose to leadership of the Goths who came to occupy Moesia—territory acquired a couple of decades earlier by a combined force of Goths and Alans after the Battle of Adrianople.

Arcadius was Roman emperor from 383 to his death in 408. He was the eldest son of the Augustus Theodosius I and his first wife Aelia Flaccilla, and the brother of Honorius. Arcadius ruled the eastern half of the empire from 395, when their father died, while Honorius ruled the west. In his time, he was seen as a weak ruler dominated by a series of powerful ministers and by his wife, Aelia Eudoxia.

Honorius was Roman emperor from 393 to 423. He was the younger son of emperor Theodosius I and his first wife Aelia Flaccilla. After the death of Theodosius in 395, Honorius, under the regency of Stilicho, ruled the western half of the empire while his brother Arcadius ruled the eastern half. His reign over the Western Roman Empire was notably precarious and chaotic. In 410, Rome was sacked for the first time since the Battle of the Allia almost 800 years prior.

Year 405 (CDV) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Stilicho and Anthemius. The denomination 405 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 400s decade ran from January 1, 400, to December 31, 409.

Year 410 (CDX) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year after the Consulship of Honorius and Theodosius. The denomination 410 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 380s decade ran from January 1, 380, to December 31, 389.
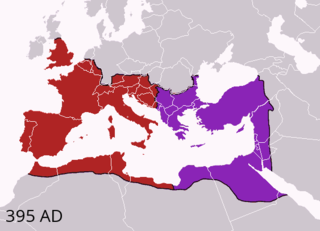
Year 395 (CCCXCV) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Olybrius and Probinus. The denomination 395 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 402 (CDII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Arcadius and Honorius. The denomination 402 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 408 (CDVIII) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Bassus and Philippus. The denomination 408 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 401 (CDI) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vincentius and Fravitus. The denomination 401 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 398 (CCCXCVIII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar, the 395th Year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 398th year of the 1st millennium, the last 3 years of the 4th century, and the 9th and pre-final year of the 390s decade. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Eutychianus. The denomination 398 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 396 (CCCXCVI) was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Augustus. The denomination 396 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 390s decade ran from January 1, 390 to December 31, 399

Year 370 (CCCLXX) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Valens. The denomination 370 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Stilicho was a military commander in the Roman army who, for a time, became the most powerful man in the Western Roman Empire. He was partly of Vandal origins and married to Serena, the niece of emperor Theodosius I. He became guardian for the underage Honorius. After nine years of struggle against barbarian and Roman enemies, political and military disasters finally allowed his enemies in the court of Honorius to remove him from power. His fall culminated in his arrest and execution in 408.
The Battle of Verona was fought in June 402 by Alaric's Visigoths and a Roman force led by Stilicho. Alaric was defeated and forced to withdraw from Italy.
The Battle of Pollentia was fought on 6 April 402 between the Romans under Stilicho and the Visigoths under Alaric I, during the first Gothic invasion of Italy (401–403). The Romans were victorious, and forced Alaric to retreat, though he rallied to fight again in the next year in the Battle of Verona, where he was again defeated. After this, Alaric retreated from Italy, leaving the province in peace until his second invasion in 409, after Stilicho's death.

The sack of Rome on 24 August 410 AD was undertaken by the Visigoths led by their king, Alaric. At that time, Rome was no longer the administrative capital of the Western Roman Empire, having been replaced in that position first by Mediolanum in 286 and then by Ravenna in 402. Nevertheless, the city of Rome retained a paramount position as "the eternal city" and a spiritual center of the Empire. This was the first time in almost 800 years that Rome had fallen to a foreign enemy, and the sack was a major shock to contemporaries, friends and foes of the Empire alike.

The Gothic War of 401–403 fought between the Western Roman Empire and the Visigoths. The commander of the Roman army was Flavius Stilicho, the Visigoths were led by Alaric. The war was fought in the north of Italy and, in addition to a number of small fights, consisted of two major battles, both of which were won by the Romans.














