The Trial of Socrates was held to determine the philosopher's guilt of two charges: asebeia (impiety) against the pantheon of Athens, and corruption of the youth of the city-state; the accusers cited two impious acts by Socrates: "failing to acknowledge the gods that the city acknowledges" and "introducing new deities".

The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC.
Year 404 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Volusus, Cossus, Fidenas, Ambustus, Maluginensis and Rutilus. The denomination 404 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
This article concerns the period 469 BC – 460 BC.
This article concerns the period 459 BC – 450 BC.

This article concerns the period 409 BC – 400 BC.
This article concerns the period 389 BC – 380 BC.
This article concerns the period 369 BC – 360 BC

Lysander was a Spartan military and political leader. He destroyed the Athenian fleet at the Battle of Aegospotami in 405 BC, forcing Athens to capitulate and bringing the Peloponnesian War to an end. He then played a key role in Sparta's domination of Greece for the next decade until his death at the Battle of Haliartus.

Thrasybulus was an Athenian general and democratic leader. In 411 BC, in the wake of an oligarchic coup at Athens, the pro-democracy sailors at Samos elected him as a general, making him a primary leader of the ultimately successful democratic resistance to the coup. As general, he was responsible for recalling the controversial nobleman Alcibiades from exile, and the two worked together extensively over the next several years. In 411 and 410, Thrasybulus was in command along with Alcibiades and others at several critical Athenian naval victories.
Year 393 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Potitus and Maluginensis. The denomination 393 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Theramenes was an Athenian military leader and statesman, prominent in the final decade of the Peloponnesian War. He was active during the two periods of oligarchic government at Athens, the 400 and later the Thirty Tyrants, as well as in the trial of the generals who had commanded at Arginusae in 406 BC. A moderate oligarch, he often found himself caught between the democrats on the one hand and the extremist oligarchs on the other. Successful in replacing a narrow oligarchy with a broader one in 411 BC, he failed to achieve the same end in 404 BC, and was executed by the extremists whose policies he had opposed.
Critias was an ancient Athenian poet, philosopher and political leader. He is known today for being a student of Socrates, a writer of some regard, and for becoming the leader of the Thirty Tyrants, who ruled Athens for several months after the conclusion of the Peloponnesian War in 404/403.
The Thirty Tyrants were an oligarchy that briefly ruled Athens from 405 BC to 404 BC. Installed into power by the Spartans after the Athenian surrender in the Peloponnesian War, the Thirty became known for their tyrannical rule, first being called "The Thirty Tyrants" by Polycrates. Although they maintained power for only eight months, their reign resulted in the killing of 5% of the Athenian population, the confiscation of citizens' property, and the exile of other democratic supporters.
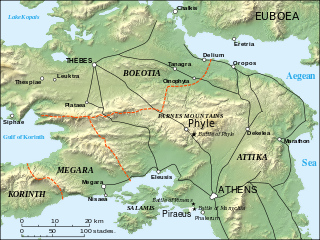
The Battle of Phyle was fought between Athenian exiles who were seeking to restore democracy to Athens and a Spartan garrison trying to protect the oligarchic Thirty Tyrants. In the battle, 700 Athenian exiles under Thrasybulus decisively defeated Spartans and their Athenian cavalry in a dawn ambush.

The Battle of Munychia was fought between Athenians exiled by the oligarchic government of the Thirty Tyrants and the forces of that government, supported by a Spartan garrison. In the battle, a substantially superior force composed of the Spartan garrison of Athens and the army of the oligarchic government attacked a hill in Piraeus which had been seized by 1,000 exiles under Thrasybulus, but was defeated. After this defeat, the Thirty Tyrants were forced to flee to Eleusis.

The Battle of Piraeus was fought in 403 BC between Athenian exiles who had defeated the government of the Thirty Tyrants and occupied Piraeus and a Spartan force sent to combat them. In the battle, the Spartans narrowly defeated the exiles, with both sides suffering appreciable casualties. After the battle, Pausanias arranged a settlement between the two parties which allowed the reestablishment of democratic government in Athens.
The Athenian coup of 411 BC was the result of a revolution that took place during the Peloponnesian War between Athens and Sparta. The coup overthrew the democratic government of ancient Athens and replaced it with a short-lived oligarchy known as the Four Hundred.
The Phyle Campaign was the civil war that resulted from the Spartan imposition of a narrow oligarchy on Athens and resulted in the restoration of Athenian democracy.

Pausanias was the Agiad King of Sparta; the son of Pleistoanax. He ruled Sparta from 445 BC to 427 BC and again from 409 BC to 395 BC. He was the leader of the faction in Sparta that opposed the imperialist policy conducted by Lysander.






