Agesilaus II was king of Sparta from c. 400 to c. 360 BC. Generally considered the most important king in the history of Sparta, Agesilaus was the main actor during the period of Spartan hegemony that followed the Peloponnesian War. Although brave in combat, Agesilaus lacked the diplomatic skills to preserve Sparta's position, especially against the rising power of Thebes, which reduced Sparta to a secondary power after its victory at Leuctra in 371 BC.

Xenophon of Athens was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected as one of the leaders of the retreating Greek mercenaries, the Ten Thousand, who had been part of Cyrus's attempt to seize control of the Achaemenid Empire. As the military historian Theodore Ayrault Dodge wrote, "the centuries since have devised nothing to surpass the genius of this warrior". Xenophon established precedents for many logistical operations and was among the first to describe strategic flanking maneuvers and feints in combat.

The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC.
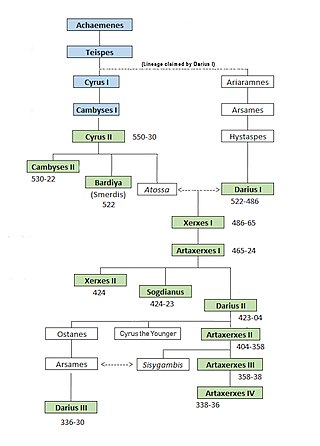
Darius II, also known by his given name Ochus, was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 423 BC to 405 or 404 BC.

This article concerns the period 409 BC – 400 BC.
This decade witnessed the continuing decline of the Achaemenid Empire, fierce warfare amongst the Greek city-states during the Peloponnesian War, the ongoing Warring States period in Zhou dynasty China, and the closing years of the Olmec civilization in modern-day Mexico.
Year 395 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Cossus, Medullinus, Scipio, Fidenas, Ambustus and Lactucinus. The denomination 395 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Ctesias, also known as Ctesias of Cnidus, was a Greek physician and historian from the town of Cnidus in Caria, then part of the Achaemenid Empire.

Cyrus the Younger was an Achaemenid prince and general. He ruled as satrap of Lydia and Ionia from 408 to 401 BC. Son of Darius II and Parysatis, he died in 401 BC in battle during a failed attempt to oust his elder brother, Artaxerxes II, from the Persian throne.

Clearchus or Clearch, also known as Clearchus the Lacedaemonian or Clearchus the son of Rhamphias, was a Spartan general and mercenary, noted for leading the Ten Thousand in battle against the Persian king.

Tissaphernes was a Persian commander and statesman, Satrap of Lydia and Ionia. His life is mostly known from the works of Thucydides and Xenophon. According to Ctesias, he was the son of Hidarnes III and therefore, the great grandson of Hydarnes, one of the six conspirators who had supported the rise of Darius the Great.

Arses, known by his regnal name Artaxerxes II, was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 405/4 BC to 358 BC. He was the son and successor of Darius II and his mother was Parysatis.

The Battle of Cunaxa was fought in the late summer of 401 BC between the Persian king Artaxerxes II and his brother Cyrus the Younger for control of the Achaemenid throne. The great battle of the revolt of Cyrus took place 70 km north of Babylon, at Cunaxa, on the left bank of the Euphrates. The main source is Xenophon, a Greek soldier who participated in the fighting.

Anabasis is the most famous work of the Ancient Greek professional soldier and writer Xenophon. It gives an account of the expedition of the Ten Thousand, an army of Greek mercenaries hired by Cyrus the Younger to help him seize the throne of Persia from his brother, Artaxerxes II, in 401 BC.

The Ten Thousand were a force of mercenary units, mainly Greeks, employed by Cyrus the Younger to attempt to wrest the throne of the Persian Empire from his brother, Artaxerxes II. Their march to the Battle of Cunaxa and back to Greece was recorded by Xenophon, one of their leaders, in his work Anabasis.
Parysatis was a Persian queen, consort of Darius II and had a large influence during the reign of Artaxerxes II.
Meno, son of Alexidemus, was an ancient Thessalian political figure, probably from Pharsalus. He is famous both for the eponymous dialogue written by Plato and his role as one of the generals leading different contingents of Greek mercenaries in Xenophon's Anabasis.
Ariaeus was a Persian general who fought alongside Cyrus the Younger at the Battle of Cunaxa and later was involved in the assassination of Tissaphernes.
Socrates was a Greek mercenary general from Achaea who traveled to Persia to fight at the Battle of Cunaxa. Xenophon describes him as brave in war and a reliable friend. Socrates was summoned by Cyrus, with whom he was already connected, to bring as many troops as he could muster under the pretense that Cyrus intended to attack Tissaphernes. Socrates had previously been besieging Miletus alongside Pasion the Megarian. Socrates brought Cyrus about 500 hoplites. Socrates and the other troops were only later told that Cyrus intended to seize the Persian throne from his brother Artaxerxes. Socrates fought at the Battle of Cunaxa and the Greek forces were able to drive the Persians into retreat, but Cyrus and his force faced heavy casualties and Cyrus himself was killed in battle.

The Falcon of Sparta is an historical fiction novel by British author Conn Iggulden. It is loosely based on the Anabasis written in 370 BC by Xenophon.











