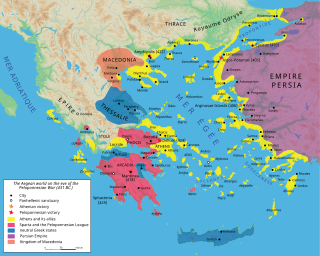
The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Second Persian invasion of Greece. The League functioned as a dual –offensive and defensive– alliance (symmachia) of autonomous states, similar to its rival association, the Peloponnesian League. The League's modern name derives from its official meeting place, the island of Delos, where congresses were held within the sanctuary of the Temple of Apollo; contemporary authors referred to the organization simply as "the Athenians and their Allies".

The Second Peloponnesian War, often called simply the Peloponnesian War, was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided until the later intervention of the Persian Empire in support of Sparta. Led by Lysander, the Spartan fleet finally defeated Athens which began a period of Spartan hegemony over Greece.

The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC.
This article concerns the period 469 BC – 460 BC.
Year 461 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Gallus and Cornutus. The denomination 461 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 369 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Fidenas, Cicurinus, Cossus, Cornelius, Cincinnatus and Ambustus. The denomination 369 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Spartan hegemony refers to the period of dominance by Sparta in Greek affairs from 404 to 371 BC. Even before this period the polis of Sparta was the greatest military land power of classical Greek antiquity and governed, dominated or influenced the entire Peloponnese. The defeat of the Athenians and the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War in 431–404 BC resulted in a short-lived Spartan dominance of the southern Greek world from 404 to 371 BC. Due to their mistrust of others, Spartans discouraged the creation of records about their internal affairs. The only histories of Sparta are from the writings of Xenophon, Thucydides, Herodotus and Plutarch, none of whom were Spartans. Plutarch was writing several centuries after the period of Spartan hegemony had ceased. This creates difficulties in understanding the Spartan political system, which was distinctly different from any other Greek polis.

The Areopagus is a prominent rock outcropping located northwest of the Acropolis in Athens, Greece. Its English name is the Late Latin composite form of the Greek name Areios Pagos, translated "Hill of Ares". The name Areopagus also referred, in classical times, to the Athenian governing council, later restricted to the Athenian judicial council or court that tried cases of deliberate homicide, wounding, and religious matters, as well as cases involving arson of olive trees, because they convened in this location. The war god Ares was supposed to have been tried by the other gods on the Areopagus for the murder of Poseidon's son Halirrhothius.
The helots were a subjugated population that constituted a majority of the population of Laconia and Messenia – the territories ruled by Sparta. There has been controversy since antiquity as to their exact characteristics, such as whether they constituted an Ancient Greek tribe, a social class, or both. For example, Critias described helots as "slaves to the utmost", whereas according to Pollux, they occupied a status "between free men and slaves". Tied to the land, they primarily worked in agriculture as a majority and economically supported the Spartan citizens.
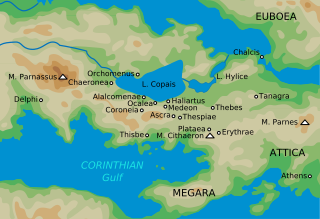
The Battle of Tanagra was a land battle that took place in Boeotia in 457 BC between Athens and Sparta during the First Peloponnesian War. Tension between Athens and Sparta had built up due the rebuilding of Athens' walls and Spartan rejection of Athenian military assistance. The Athenians were led by Myronides and held a strength of 14,000. The Spartans were led by Nicomedes and had a total of 11,500 soldiers. While both the Athenians and Spartans suffered great losses, Sparta ultimately claimed victory in this battle.

Cimon or Kimon was an Athenian strategos and politician.

Pentecontaetia is the term used to refer to the period in Ancient Greek history between the defeat of the second Persian invasion of Greece at Plataea in 479 BC and the beginning of the Peloponnesian War in 431 BC. The term originated with a scholiast commenting on Thucydides, who used it in their description of the period. The Pentecontaetia was marked by the rise of Athens as the dominant state in the Greek world and by the rise of Athenian democracy, a period also known as Golden Age of Athens. Since Thucydides focused his account on these developments, the term is generally used when discussing developments in and involving Athens.
Ephialtes was an ancient Athenian politician and an early leader of the democratic movement there. In the late 460s BC, he oversaw reforms that diminished the power of the Areopagus, a traditional bastion of conservatism, and which are considered by many modern historians to mark the beginning of the radical democracy for which Athens would become famous. These powers included the scrutiny and control of office holders, and the judicial functions in state trials. He reduced the property qualifications for holding a public office, and created a new definition of citizenship. Ephialtes, however, would not live to participate in this new form of government for long. In 461 BC, he was assassinated, probably at the instigation of resentful oligarchs, and the political leadership of Athens passed to his deputy, Pericles.
The First Peloponnesian War was fought between Sparta as the leaders of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, and the Delian League led by Athens with support from Argos. This war consisted of a series of conflicts and minor wars, such as the Second Sacred War. There were several causes for the war including the building of the Athenian long walls, Megara's defection and the envy and concern felt by Sparta at the growth of the Athenian Empire.
The Areopagite constitution is the modern name for a period in ancient Athens described by Aristotle in his Constitution of the Athenians. According to that work, the Athenian political scene was dominated, between the ostracism of Themistocles in the late 470s BC and the reforms of Ephialtes in 462 BC, by the Areopagus, a traditional court composed of former archons. Modern scholars have debated the existence of this phenomenon, with some concluding that Aristotle and his contemporaries invented it to explain Ephialtes' need to limit the Areopagus' powers, and arguing that the lack of concrete measures establishing the Areopagus' dominance shows that the Areopagite constitution is "palpably unhistorical". Other scholars, such as Donald Kagan, have countered that no concrete measures were necessary, as the Areopagus' dominance was established not through actual changes in the laws but through the prestige of its leading members. Aristotle specifically cites the Areopagites' distribution of money to the public as the citizen body prepared to abandon Athens in the face of the advancing Persian army.

The Thasian rebellion was an incident in 465 BC, in which Thasos rebelled against Athenian control, seeking to renounce its membership in the Delian League. The rebellion was prompted by a conflict between Athens and Thasos over control of silver deposits on the Thracian mainland, which Thasos had traditionally mined.

Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years in Ancient Greece, marked by much of the eastern Aegean and northern regions of Greek culture gaining increased autonomy from the Persian Empire; the peak flourishing of democratic Athens; the First and Second Peloponnesian Wars; the Spartan and then Theban hegemonies; and the expansion of Macedonia under Philip II. Much of the early defining mathematics, science, artistic thought, theatre, literature, philosophy, and politics of Western civilization derives from this period of Greek history, which had a powerful influence on the later Roman Empire. Part of the broader era of classical antiquity, the classical Greek era ended after Philip II's unification of most of the Greek world against the common enemy of the Persian Empire, which was conquered within 13 years during the wars of Alexander the Great, Philip's son.

The history of Sparta describes the history of the ancient Doric Greek city-state known as Sparta from its beginning in the legendary period to its incorporation into the Achaean League under the late Roman Republic, as Allied State, in 146 BC, a period of roughly 1000 years. Since the Dorians were not the first to settle the valley of the Eurotas River in the Peloponnesus of Greece, the preceding Mycenaean and Stone Age periods are described as well. Sparta went on to become a district of modern Greece. Brief mention is made of events in the post-classical periods.

Messenia was an ancient district of the southwestern Peloponnese, more or less overlapping the modern Messenia region of Greece. To the north it had a border with Elis along the Neda river. From there the border with Arcadia ran along the tops of Mount Elaeum and Mount Nomia and then through foothills of Taygetus. The eastern border with Laconia went along the Taygetus ridge up to the Koskaraka river, and then along that river to the sea, near the city of Abia.

The Athenian Revolution was a revolt by the people of Athens that overthrew the ruling aristocratic oligarchy, establishing the almost century-long self-governance of Athens in the form of a participatory democracy – open to all free male citizens. It was a reaction to a broader trend of tyranny that had swept through Athens and the rest of Greece.











