
The Second Peloponnesian War, often called simply the Peloponnesian War, was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided until the later intervention of the Persian Empire in support of Sparta. Led by Lysander, the Spartan fleet finally defeated Athens which began a period of Spartan hegemony over Greece.

The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC.
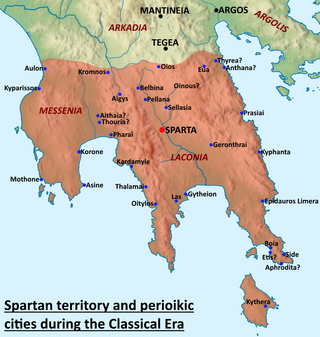
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon, while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in the Eurotas valley of Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece.
This article concerns the period 489 BC – 480 BC.
This article concerns the period 469 BC – 460 BC.
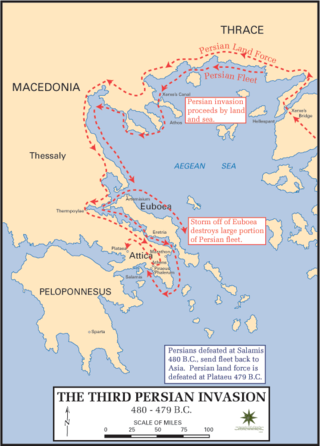
Year 480 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Cincinnatus. The denomination 480 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
This article concerns the period 429 BC – 420 BC.
Year 424 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Crassus, Fidenas, Rutilus and Iullus. The denomination 424 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 425 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Atratinus, Medullinus, Cincinnatus and Barbatus. The denomination 425 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Leonidas I was king of the Ancient Greek city-state of Sparta. He was the son of king Anaxandridas II and the 17th king of the Agiad dynasty, a Spartan royal house which claimed descent from the mythical demigod Heracles. Leonidas I ascended to the throne in c. 489 BC, succeeding his half-brother king Cleomenes I. He ruled jointly along with king Leotychidas until his death in 480 BC, when he was succeeded by his son, Pleistarchus.
The helots were a subjugated population that constituted a majority of the population of Laconia and Messenia – the territories ruled by Sparta. There has been controversy since antiquity as to their exact characteristics, such as whether they constituted an Ancient Greek tribe, a social class, or both. For example, Critias described helots as "slaves to the utmost", whereas according to Pollux, they occupied a status "between free men and slaves". Tied to the land, they primarily worked in agriculture as a majority and economically supported the Spartan citizens.

Pausanias was a Spartan regent and a general. In 479 BC, as a leader of the Hellenic League's combined land forces, he won a pivotal victory against the Achaemenid Empire in the Battle of Plataea. Despite his role in ending the Second Persian invasion of Greece, Pausanias subsequently fell under suspicion of conspiring with the Persian king Xerxes I. After an interval of repeated arrests and debates about his guilt, he was starved to death by his fellow Spartans in 477 BC. What is known of his life is largely according to Thucydides' History of the Peloponnesian War, Diodorus' Bibliotheca historica and a handful of other classical sources.
The First Peloponnesian War was fought between Sparta as the leaders of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, and the Delian League led by Athens with support from Argos. This war consisted of a series of conflicts and minor wars, such as the Second Sacred War. There were several causes for the war including the building of the Athenian long walls, Megara's defection and the envy and concern felt by Sparta at the growth of the Athenian Empire.

The Thasian rebellion was an incident in 465 BC, in which Thasos rebelled against Athenian control, seeking to renounce its membership in the Delian League. The rebellion was prompted by a conflict between Athens and Thasos over control of silver deposits on the Thracian mainland, which Thasos had traditionally mined.

The Spartan army was the principle ground force of Sparta. It stood at the center of the ancient Greek city-state, consisting of citizens trained in the disciplines and honor of a warrior society. Subjected to military drills since early manhood, the Spartans became one of the most feared and formidable military forces in the Greek world, attaining legendary status in their wars against Persia. At the height of Sparta's power—between the 6th and 4th centuries BC—other Greeks commonly accepted that "one Spartan was worth several men of any other state."

The history of Sparta describes the history of the ancient Doric Greek city-state known as Sparta from its beginning in the legendary period to its incorporation into the Achaean League under the late Roman Republic, as Allied State, in 146 BC, a period of roughly 1000 years. Since the Dorians were not the first to settle the valley of the Eurotas River in the Peloponnesus of Greece, the preceding Mycenaean and Stone Age periods are described as well. Sparta went on to become a district of modern Greece. Brief mention is made of events in the post-classical periods.
The Spartan Constitution are the government and laws of the classical Greek city-state of Sparta. All classical Greek city-states had a politeia; the politeia of Sparta however, was noted by many classical authors for its unique features, which supported a rigidly layered social system and a strong hoplite army.

Messenia was an ancient district of the southwestern Peloponnese, more or less overlapping the modern Messenia region of Greece. To the north it had a border with Elis along the Neda river. From there the border with Arcadia ran along the tops of Mount Elaeum and Mount Nomia and then through foothills of Taygetus. The eastern border with Laconia went along the Taygetus ridge up to the Koskaraka river, and then along that river to the sea, near the city of Abia.
The 464 BC Spartan earthquake occurred along the Sparta fault in the year 464 BC destroying much of what was Sparta and many other city-states in ancient Greece. Historical sources suggest that the death toll may have been as high as 20,000, although modern scholars suggest that this figure is likely an exaggeration. The earthquake gave Spartan helots an opportunity to revolt against their aristocratic rulers, and the Spartan Pericleidas was sent to the Athenians to seek their aid. Their immediate dismissal upon arrival is said to have been a key event that led up to the First Peloponnesian War.
Pericleidas was a man of ancient Sparta -- possibly the proxenos of Athens at Sparta -- who played a role during the Peloponnesian War.









