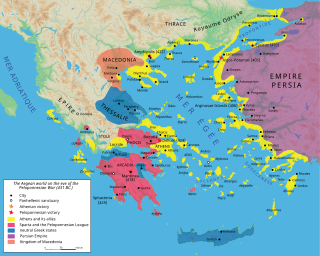
The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Second Persian invasion of Greece. The League functioned as a dual –offensive and defensive– alliance (symmachia) of autonomous states, similar to its rival association, the Peloponnesian League. The League's modern name derives from its official meeting place, the island of Delos, where congresses were held within the sanctuary of the Temple of Apollo; contemporary authors referred to the organization simply as "the Athenians and their Allies".

Ostracism was an Athenian democratic procedure in which any citizen could be expelled from the city-state of Athens for ten years. While some instances clearly expressed popular anger at the citizen, ostracism was often used preemptively. It was used as a way of neutralizing someone thought to be a threat to the state or a potential tyrant, though in many cases popular opinion often informed the expulsion. The word "ostracism" continues to be used for various forms of shunning.

The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC.
Year 404 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Volusus, Cossus, Fidenas, Ambustus, Maluginensis and Rutilus. The denomination 404 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Pericles was a Greek politician and general during the Golden Age of Athens. He was prominent and influential in Ancient Athenian politics, particularly between the Greco-Persian Wars and the Peloponnesian War, and was acclaimed by Thucydides, a contemporary historian, as "the first citizen of Athens". Pericles turned the Delian League into an Athenian empire and led his countrymen during the first two years of the Peloponnesian War. The period during which he led Athens as Archon (ruler), roughly from 461 to 429 BC, is sometimes known as the "Age of Pericles", but the period thus denoted can include times as early as the Persian Wars or as late as the following century.
This article concerns the period 469 BC – 460 BC.
Year 451 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sabinus and Augurinus and the First year of the decemviri. The denomination 451 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe, for naming years.
Year 458 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Rutilus and Carvetus. The denomination 458 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 462 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Tricipitinus and Cicurinus. The denomination 462 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 463 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Priscus and Helva. The denomination 463 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Areopagus is a prominent rock outcropping located northwest of the Acropolis in Athens, Greece. Its English name is the Late Latin composite form of the Greek name Areios Pagos, translated "Hill of Ares". The name Areopagus also referred, in classical times, to the Athenian governing council, later restricted to the Athenian judicial council or court that tried cases of deliberate homicide, wounding, and religious matters, as well as cases involving arson of olive trees, because they convened in this location. The war god Ares was supposed to have been tried by the other gods on the Areopagus for the murder of Poseidon's son Halirrhothius.

Fifth-century Athens was the Greek city-state of Athens in the time from 480 to 404 BC. Formerly known as the Golden Age of Athens, the latter part being the Age of Pericles, it was buoyed by political hegemony, economic growth and cultural flourishing. The period began in 478 BC, after the defeat of the Persian invasion, when an Athenian-led coalition of city-states, known as the Delian League, confronted the Persians to keep the liberated Asian Greek cities free.

The Alcmaeonidae or Alcmaeonids were a wealthy and powerful noble family of ancient Athens, a branch of the Neleides who claimed descent from the mythological Alcmaeon, the great-grandson of Nestor.

Cimon or Kimon was an Athenian strategos and politician.
Ephialtes was an ancient Athenian politician and an early leader of the democratic movement there. In the late 460s BC, he oversaw reforms that diminished the power of the Areopagus, a traditional bastion of conservatism, and which are considered by many modern historians to mark the beginning of the radical democracy for which Athens would become famous. These powers included the scrutiny and control of office holders, and the judicial functions in state trials. He reduced the property qualifications for holding a public office, and created a new definition of citizenship. Ephialtes, however, would not live to participate in this new form of government for long. In 461 BC, he was assassinated, probably at the instigation of resentful oligarchs, and the political leadership of Athens passed to his deputy, Pericles.

The city of Athens during the classical period of ancient Greece was the major urban centre of the notable polis (city-state) of the same name, located in Attica, Greece, leading the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War against Sparta and the Peloponnesian League. Athenian democracy was established in 508 BC under Cleisthenes following the tyranny of Isagoras. This system remained remarkably stable, and with a few brief interruptions, it remained in place for 180 years, until 322 BC. The peak of Athenian hegemony was achieved in the 440s to 430s BC, known as the Age of Pericles.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to ancient Greece:
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to democracy.

Athenian democracy developed around the 6th century BC in the Greek city-state of Athens, comprising the city of Athens and the surrounding territory of Attica. Although Athens is the most famous ancient Greek democratic city-state, it was not the only one, nor was it the first; multiple other city-states adopted similar democratic constitutions before Athens. By the late 4th century BC, as many as half of the over one thousand existing Greek cities might have been democracies. Athens practiced a political system of legislation and executive bills. Participation was open to adult, free male citizens Adult male citizens probably constituted no more than 30 percent of the total adult population.

The Athenian Revolution was a revolt by the people of Athens that overthrew the ruling aristocratic oligarchy, establishing the almost century-long self-governance of Athens in the form of a participatory democracy – open to all free male citizens. It was a reaction to a broader trend of tyranny that had swept through Athens and the rest of Greece.











