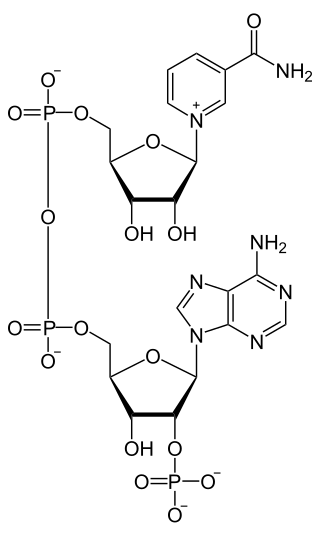
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP+ or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). NADPH is the reduced form of NADP+, the oxidized form. NADP+ is used by all forms of cellular life.
Thioredoxin reductases are enzymes that reduce thioredoxin (Trx). Two classes of thioredoxin reductase have been identified: one class in bacteria and some eukaryotes and one in animals. In bacteria TrxR also catalyzes the reduction of glutaredoxin like proteins known as NrdH. Both classes are flavoproteins which function as homodimers. Each monomer contains a FAD prosthetic group, a NADPH binding domain, and an active site containing a redox-active disulfide bond.
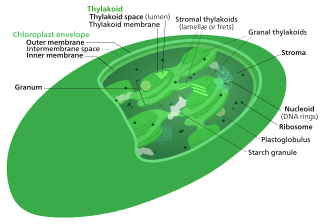
The Calvin cycle,light-independent reactions, bio synthetic phase,dark reactions, or photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR) cycle of photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into glucose. The Calvin cycle is present in all photosynthetic eukaryotes and also many photosynthetic bacteria. In plants, these reactions occur in the stroma, the fluid-filled region of a chloroplast outside the thylakoid membranes. These reactions take the products of light-dependent reactions and perform further chemical processes on them. The Calvin cycle uses the chemical energy of ATP and reducing power of NADPH from the light dependent reactions to produce sugars for the plant to use. These substrates are used in a series of reduction-oxidation reactions to produce sugars in a step-wise process; there is no direct reaction that converts several molecules of CO2 to a sugar. There are three phases to the light-independent reactions, collectively called the Calvin cycle: carboxylation, reduction reactions, and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) regeneration.

Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is the inability to properly digest food due to a lack or reduction of digestive enzymes made by the pancreas. EPI can occur in humans and is prevalent in many conditions such as cystic fibrosis, Shwachman–Diamond syndrome, different types of pancreatitis, multiple types of diabetes mellitus, advanced renal disease, older adults, celiac disease, IBS-D, IBD, HIV, alcohol-related liver disease, Sjogren syndrome, tobacco use, and use of somatostatin analogues.

Dicarbonyl/L-xylulose reductase, also known as carbonyl reductase II, is an enzyme that in human is encoded by the DCXR gene located on chromosome 17.
In enzymology, a 3-methyleneoxindole reductase (EC 1.3.1.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a taxane 10beta-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.76) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a taxane 13alpha-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.77) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a D-nopaline dehydrogenase (EC 1.5.1.19) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NADPH—hemoprotein reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a saccharopine dehydrogenase (NADP+, L-lysine-forming) (EC 1.5.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a copalyl diphosphate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme aristolochene synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction

In molecular biology, this protein domain belongs to the terpene synthase family (TPS). Its role is to synthesize terpenes, which are part of primary metabolism, such as sterols and carotene, and also part of the secondary metabolism. This entry will focus on the N terminal domain of the TPS protein.
In molecular biology, this protein domain belongs to the terpene synthase family (TPS). Its role is to synthesize terpenes, which are part of primary metabolism, such as sterols and carotene, and also part of the secondary metabolism. This entry will focus on the C terminal domain of the TPS protein.
Carboxynorspermidine synthase (EC 1.5.1.43, carboxynorspermidine dehydrogenase, carboxyspermidine dehydrogenase, CASDH, CANSDH) is an enzyme with systematic name carboxynorspermidine:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reactions
Epi-isozizaene 5-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.106, CYP170A1) is an enzyme with systematic name (+)-epi-isozizaene,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (5-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
3-Epi-6-deoxocathasterone 23-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.112, cytochrome P450 90C1, CYP90D1, CYP90C1) is an enzyme with systematic name 3-epi-6-deoxocathasterone,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (C-23-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Premnaspirodiene oxygenase (EC 1.14.13.121, HPO, Hyoscymus muticus premnaspirodiene oxygenase) is an enzyme with systematic name (-)-vetispiradiene,NADPH:oxygen 2alpha-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
5-Epiaristolochene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name (2E,6E)-farnesyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase ( -5-epiaristolochene-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction







