The 6th century BC started on the first day of 600 BC and ended on the last day of 501 BC.
This article concerns the period 489 BC – 480 BC.
This article concerns the period 479 BC – 470 BC.
This article concerns the period 459 BC – 450 BC.
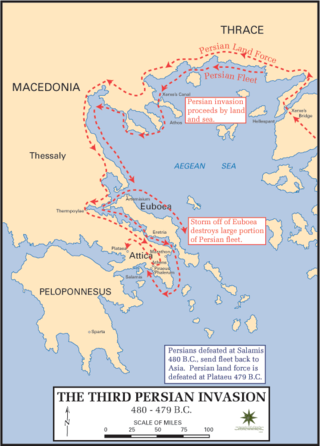
Year 480 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Cincinnatus. The denomination 480 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 85 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Cinna and Carbo. The denomination 85 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 400 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Republic, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Esquilinus, Capitolinus, Vulso, Medullinus, Saccus and Vulscus. The denomination 400 BC for this year has been used in Europe since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became prevalent there.

Year 200 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Maximus and Cotta. The denomination 200 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 450 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Second year of the decemviri. The denomination 450 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 410 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Mamercinus and Volusus. The denomination 410 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 470 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Potitus and Mamercus. The denomination 470 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 425 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Atratinus, Medullinus, Cincinnatus and Barbatus. The denomination 425 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 560 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 194 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 560 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 388 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Capitolinus, Fidenas, Iullus, Corvus, Flavus and Rufus. The denomination 388 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 460 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Poplicola and Sabinus. The denomination 460 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The year 600 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 154 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 600 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 550 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 204 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 550 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 540 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 214 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 540 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 530 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 224 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 530 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The year 570 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 184 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 570 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.





