Breeding
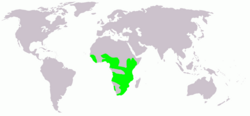
African jacanas breed throughout sub-Saharan Africa. It is sedentary apart from seasonal dispersion. It lays four black-marked brown eggs in a floating nest.
The jacana has evolved a highly unusually polyandrous mating system, meaning that one female mates with multiple males and the male alone cares for the chicks. Such a system has evolved due to a combination of two factors: firstly, the lakes that the jacana lives on are so resource-rich that the relative energy expended by the female in producing each egg is effectively negligible. Secondly the jacana, as a bird, lays eggs, and eggs can be equally well incubated and cared for by a parent bird of either sex. This means that the rate-limiting factor of the jacana's breeding is the rate at which the males can raise and care for the chicks. Such a system of females forming harems of males is in direct contrast to the more usual system of leks seen in animals such as stags and grouse, where the males compete and display in order to gain harems of females.
The parent that forms part of the harem is almost always the one that ends up caring for the offspring; in this case, each male jacana incubates and rears a nest of chicks. The male African jacana has therefore evolved some remarkable adaptations for parental care, such as the ability to pick up and carry chicks underneath its wings. [12] [13]
Actophilornis africanus -
MHNT