| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name (5S,6E,8Z,11Z,14Z)-5-Hydroperoxyicosa-6,8,11,14-tetraenoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Arachidonic+acid+5-hydroperoxide |
PubChem CID | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H32O4 | |
| Molar mass | 336.466 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
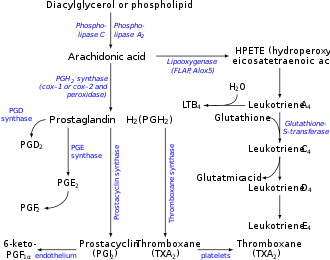
Arachidonic acid 5-hydroperoxide (5-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid, 5-HPETE) is an intermediate in the metabolism of arachidonic acid by the ALOX5 enzyme in humans or Alox5 enzyme in other mammals. The intermediate is then further metabolized to: a) leukotriene A4 which is then metabolized to the chemotactic factor for leukocytes, leukotriene B4, or to contractors of lung airways, leukotriene C4, leukotriene D4, and leukotriene E4; b) the leukocyte chemotactic factors, 5-hydroxyicosatetraenoic acid and 5-oxo-eicosatetraenoic acid; or c) the specialized pro-resolving mediators of inflammation, lipoxin A4 and lipoxin B4. [1] [2]