
The State Emergency Service (SES) is the name used by a number of organisations in Australia that provide assistance during and after major incidents. Specifically, the service deals with floods, storms and tsunamis, but can also assist in other emergencies, such as vertical rescue and road crash rescues, missing persons searches, and medical evacuations. In other scenarios the SES may provide a support role to other agencies, particularly police and fire. The SES is operational 24 hours a day. The SES is constituted as separate organisations operating in the various Australian states and territories. Eight of the SES organisations co-ordinate through the Australian Council of State and Territory Emergency Services (ACSES).

Cooperative Research Centres (CRCs) are an Australian Federal Government program and are key bodies for Australian scientific research. The Cooperative Research Centres Programme was established in 1990 to enhance Australia's industrial, commercial and economic growth through the development of sustained, user-driven, cooperative public-private research centres that achieve high levels of outcomes in adoption and commercialisation. The program emphasises the importance of collaborative arrangements to maximise the benefits of research through an enhanced process of utilisation, commercialisation, and technology transfer. It also has a strong education component with a focus on producing graduates with skills relevant to industry needs. Most CRCs offer scholarships for postgraduate students.

The Country Fire Authority (CFA) is a volunteer fire service responsible for fire suppression, rescues, and response to other accidents and hazards across most of the state Victoria, Australia. CFA comprises over 1,200 brigades organised in 21 districts, and shares responsibility for fire services with Fire Rescue Victoria, which employs full-time paid firefighters in major urban areas; and Forest Fire Management Victoria (FFMV), which manages fire prevention and suppression on Victoria's public lands. CFA operations and equipment are partly funded by the Victorian Government through its Fire Services Levy, and supplemented by individual brigades' fundraising for vehicles and equipment.

The New South Wales Rural Fire Service is a volunteer-based firefighting agency and statutory body of the Government of New South Wales.

The New South Wales Office of Environment and Heritage (OEH), a former division of the Government of New South Wales between April 2011 and July 2019, was responsible for the care and protection of the environment and heritage, which includes the natural environment, Aboriginal country, culture and heritage, and built heritage in New South Wales, Australia. The OEH supported the community, business and government in protecting, strengthening and making the most of a healthy environment and economy within the state. The OEH was part of the Department of Planning and Environment cluster and managed national parks and reserves.

Fire and Rescue New South Wales, an agency of the Government of New South Wales, Australia, is responsible for firefighting, rescue and HazMat services in the major cities, metropolitan areas and towns across New South Wales. Fire and Rescue NSW is the fourth largest urban fire service in the world, with over 6,800 firefighters serving at 335 fire stations throughout the state, supported by 465 administrative and trades staff and 5,700 community fire unit volunteers. FRNSW are also the busiest fire service in Australia, attending over 124,000 incidents a year.
In Australia, the Australasian Inter-Service Incident Management System (AIIMS) is the nationally recognised system of incident management for the nation's fire and emergency service agencies. Organisational principles and structure are used to manage bushfires and other large emergencies utilising the all agencies approach. AIIMS was first developed in the 1980s as a derivative of the United States’ NIIMS, and is based on the principles of management by objectives, functional management and span of control. AIIMS is a trademark of AFAC and the material in the AIIMS manual and training materials is copyright of AFAC.

The state of Victoria in Australia has had a long history of catastrophic bushfires, the most deadly of these, the Black Saturday bushfires of 2009 claiming 173 lives. Legislation, planning, management and suppression are the responsibilities of the Victorian State Government through its departments and agencies including the Country Fire Authority (CFA) and the Department of Environment, Land, Water and Planning (DELWP).

Bushfires in Australia are a widespread and regular occurrence that have contributed significantly to shaping the nature of the continent over millions of years. Eastern Australia is one of the most fire-prone regions of the world, and its predominant eucalyptus forests have evolved to thrive on the phenomenon of bushfire. However, the fires can cause significant property damage and loss of both human and animal life. Bushfires have killed approximately 800 people in Australia since 1851, and billions of animals.

The Black Saturday bushfires were a series of fires that ignited across the Australian state of Victoria during extreme weather conditions on 7 February 2009. Burning around 450,000 ha for over a month, the fires destroyed over 2,100 homes, destroyed several regional towns and were fought by over 5,000 firefighting personnel. The Fires devastated many.
National biosecurity in Australia is governed and administered by two federal government departments, the Department of Health and the Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment. The Biosecurity Act 2015 and related legislation is administered by the two departments and manages biosecurity risks at the national border. The Act aims to manage biosecurity risks to human health, agriculture, native flora and fauna and the environment. It also covers Australia's international rights and obligations, and lists specific diseases which are contagious and capable of causing severe harm to human health. Each state and territory has additional legislation and protocols to cover biosecurity in their jurisdiction (post-border).

Victoria State Emergency Service (VICSES) is a volunteer-based organisation responding to natural disasters and working to ensure the safety of communities around Victoria, Australia. Each State and territory of Australia has its own independent State Emergency Service (SES), and VICSES is only one of these services spread across Australia. At times of great need or catastrophic disaster, it is common that assistance be sought from other states.
Emergency Management in Australia is a shared responsibility between the Government appointed body Emergency Management Australia and local councils.

The 2010–2011 Queensland Flood and Cyclone Citation is a Queensland honour established by the Governor-of-Queensland-in-Council in 2011.
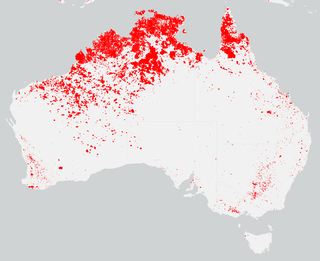
The bushfire season in the summer of 2014–15, was expected to have the potential for many fires in eastern Australia after lower than expected rainfall was received in many areas. Authorities released warnings in the early spring that the season could be particularly bad.
The Bushfire and Natural Hazards Cooperative Research Centre, commonly abbreviated to Bushfire and Natural Hazards CRC, from 2013 to 2021 drew together all of Australia and New Zealand's fire and emergency service authorities, land management agencies, as well as non-government organisations and leading experts across a range of scientific fields to explore the causes, consequences and mitigation of natural disasters.

The development of aerial firefighting and forestry in southern Australia ran in parallel with the rapid improvements in aircraft technology over the last century. As more advanced and capable aircraft became available firefighters and foresters quickly sought opportunities to utilise and adapt them.
Anne Leadbeater was awarded an Order of Australia OAM for services to the community following the 2019 bushfires, and is a fellow of the EMPA.

The 2019–20 Australian bushfire season, was a period of bushfires in many parts of Australia, which, due to its unusual intensity, size, duration, and uncontrollable dimension, is considered a megafire.













