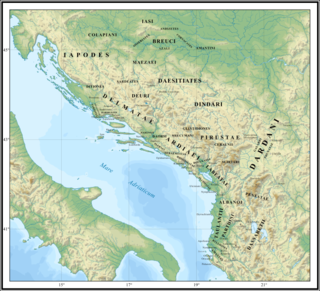
In classical antiquity, Illyria was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyrians.

The Iapydes were an ancient people who dwelt north of and inland from the Liburnians, off the Adriatic coast and eastwards of the Istrian peninsula. They occupied the interior of the country between the Colapis (Kupa) and Oeneus (Una) rivers, and the Velebit mountain range which separated them from the coastal Liburnians. Their territory covered the central inlands of modern Croatia and Una River Valley in today's Bosnia and Herzegovina. Archaeological documentation confirms their presence in these countries at least from 9th century BC, and they persisted in their area longer than a millennium. The ancient written documentation on inland Iapydes is scarcer than on the adjacent coastal peoples that had more frequent maritime contacts with ancient Greeks and Romans.
The Scordisci were a Celtic Iron Age cultural group centered in the territory of present-day Serbia, at the confluence of the Savus (Sava), Dravus (Drava), Margus (Morava) and Danube rivers. They were historically notable from the beginning of the third century BC until the turn of the common era, and consolidated into a tribal state. At their zenith, their core territory stretched over regions comprising parts of present-day Serbia, Croatia, Bulgaria and Romania, while their influence spread even further. After the Roman conquest in the 1st century AD, their territories were included into the Roman provinces of Pannonia, Moesia and Dacia.

The Illyrians were a group of Indo-European-speaking people who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan populations, along with the Thracians and Greeks.
The Delmatae, alternatively Dalmatae, during the Roman period, were a group of Illyrian tribes in Dalmatia, contemporary southern Croatia and western Bosnia and Herzegovina. The region of Dalmatia takes its name from the tribe.

The Liburnians or Liburni were an ancient tribe inhabiting the district called Liburnia, a coastal region of the northeastern Adriatic between the rivers Arsia (Raša) and Titius (Krka) in what is now Croatia. According to Strabo's Geographica, they populated Kerkyra until shortly after the Corinthians settled the island, c. 730 BC.

Bato the Daesitiate was a chieftain of the Daesitiates, an Illyrian tribe which fought against the Roman Empire between 6 and 9 AD in a conflict known as Bellum Batonianum.
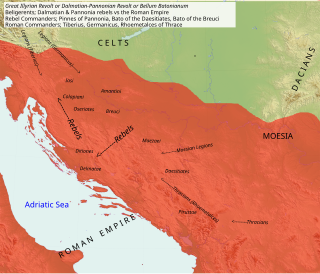
The Bellum Batonianum was a military conflict fought in the Roman province of Illyricum in the 1st century AD, in which an alliance of native peoples of the two regions of Illyricum, Dalmatia and Pannonia, revolted against the Romans. The rebellion began among native peoples who had been recruited as auxiliary troops for the Roman army. They were led by Bato the Daesitiate, a chieftain of the Daesitiatae in the central part of present-day Bosnia and Herzegovina, and were later joined by the Breuci, a tribe in Pannonia led by Bato the Breucian. Many other tribes in Illyria also joined the revolt.
The Amantini was the name of a Pannonian Illyrian tribe.

Daesitiates were an Illyrian tribe that lived on the territory of today's central Bosnia, during the time of the Roman Republic. Along with the Maezaei, the Daesitiates were part of the western group of Pannonians in Roman Dalmatia. They were prominent from the end of the 4th century BC up until the beginning of the 3rd century CE. Evidence of their daily activities can be found in literary sources, as well as in the rich material finds from Central Bosnian cultural group that is commonly associated with tribe of Daesitiates.

The pileus was a brimless felt cap worn in Ancient Greece, Etruria, Illyria, later also introduced in Ancient Rome. The pileus also appears on Apulian red-figure pottery.
Celticisation, or Celticization, was historically the process of conquering and assimilating by the ancient Celts, or via cultural exchange driven by proximity and trade. Today, as the Celtic inhabited-areas significantly differ, the term still refers to making something Celtic, usually focusing around the Celtic nations and their languages.
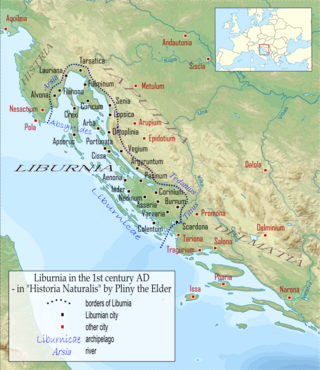
Delminium was an Illyrian city and the capital of Dalmatia which was located somewhere near today's Tomislavgrad, Bosnia and Herzegovina, under which name it also was the seat of a Latin bishopric.
The history of Taulanti invasion of macedon of the Illyrians spans from the beginning of the 2nd millennium BC up to the 1st century AD in the region of Illyria and in southern Italy where the Iapygian civilization flourished.
The Siculotae were an Illyrian people in antiquity.
The Illyrians were a group of Indo-European speaking peoples, who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan populations, along with the Thracians and Greeks.
The Roman–Dalmatian wars were a series of conflicts between the Dalmatae (Delmatae) and the Romans. After the fall of the Ardiaei in southern Illyria, the Dalmatae were to pose the greatest force against the Romans in their conquest of Illyria.
Enkyklon was a kind of himation. Enkyklon was most likely used as a wraparound outer garment, a mantle or 'encircling'. It was worn by ancient Greek women from the archaic through the Hellenistic periods. The garment has been recorded at the ancient Greek sanctuary of Artemis, Brauron. Contemporary wraps such as Ampechonon, Epiblēma are also included in the inventories at Delos, Brauron, Tanagra and Samos (Hera).







