
Ancient art refers to the many types of art produced by the advanced cultures of ancient societies with different forms of writing, such as those of ancient China, India, Mesopotamia, Persia, Palestine, Egypt, Greece, and Rome. The art of pre-literate societies is normally referred to as prehistoric art and is not covered here. Although some pre-Columbian cultures developed writing during the centuries before the arrival of Europeans, on grounds of dating these are covered at pre-Columbian art and articles such as Maya art, Aztec art, and Olmec art.

A stele, or occasionally stela, when derived from Latin, is a stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected in the ancient world as a monument. The surface of the stele often has text, ornamentation, or both. These may be inscribed, carved in relief, or painted.

North Picene, also known as North Picenian or Northern Picene, is a supposed ancient language, which may have been spoken in part of central-eastern Italy. The evidence for the language consists of four inscriptions dating from the 1st millennium BC, three of them no more than small broken fragments. It is written in a form of the Old Italic alphabet. While its texts are easily transliterated, none of them have been translated so far. It is not possible to determine whether it is related to any other known language. Despite the use by modern scholars of a similar name, it does not appear that North Picene is closely related to South Picene, and they may not be related at all. The total number of words in the inscriptions is about 60. It is not even certain that the inscriptions are all in one language. A recent study of the techniques used on the stone and other considerations have led to the conclusion that all supposed North Picene inscriptions are in fact forgeries created in the 1800s.

The François Vase is a large Attic volute krater decorated in the black-figure style. It stands at 66 cm in height and was inspired by earlier bronze vases. It was used for wine. A milestone in the development of ancient Greek pottery due to the drawing style used as well as the combination of related stories depicted in the numerous friezes, it is dated to circa 570/560 BCE. The François Vase was discovered in 1844 in Chiusi where an Etruscan tomb in the necropolis of Fonte Rotella was found located in central Italy. It was named after its discoverer Alessandro François, and is now in the Museo Archeologico in Florence. It remains uncertain whether the krater was used in Greece or in Etruria, and whether the handles were broken and repaired in Greece or in Etruria. The François Vase may have been made for a symposium given by a member of an aristocratic family in Solonian Athens, then broken and, after being carefully repaired, sent to Etruria, perhaps as an instance of elite-gift exchange. It bears the inscriptions Ergotimos mepoiesen and Kleitias megraphsen, meaning 'Ergotimos made me' and 'Kleitias painted me'. It depicts 270 figures, 121 of which have accompanying inscriptions. It is highly unusual for so many to be identifiable: the scenes depicted represent a number of mythological themes. In 1900 the vase was smashed into 638 pieces by a museum guard by hurling a wooden stool against the protective glass. It was later restored by Pietro Zei in 1902, followed by a second reconstruction in 1973 incorporating previously missing pieces.

Kurgan stelae or Balbals are anthropomorphic stone stelae, images cut from stone, installed atop, within or around kurgans, in kurgan cemeteries, or in a double line extending from a kurgan. The stelae are also described as "obelisks" or "statue menhirs".
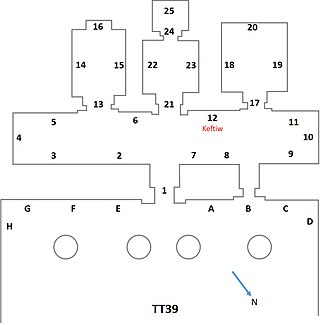
The Theban Tomb TT39 is located in El-Khokha, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official, Puimre.

Apulian vase painting was a regional style of South Italian vase painting from ancient Apulia in Magna Graecia. It comprises geometric pottery and red-figure pottery.

The Daunians were an Iapygian tribe that inhabited northern Apulia in classical antiquity. Two other Iapygian tribes, the Peucetians and the Messapians, inhabited central and southern Apulia respectively. All three tribes spoke the Messapic language, but had developed separate archaeological cultures by the seventh century BC.

Minoan art is the art produced by the Bronze Age Aegean Minoan civilization from about 3000 to 1100 BC, though the most extensive and finest survivals come from approximately 2300 to 1400 BC. It forms part of the wider grouping of Aegean art, and in later periods came for a time to have a dominant influence over Cycladic art. Since wood and textiles have decomposed, the best-preserved surviving examples of Minoan art are its pottery, palace architecture, small sculptures in various materials, jewellery, metal vessels, and intricately-carved seals.

Illyrian weaponry played an important role in the makeup of Illyrian armies and in conflicts involving the Illyrians. Of all the ancients sources the most important and abundant writings are those of Ennius, a Roman poet of Messapian origin. Weapons of all sorts were also placed intact in the graves of Illyrian warriors and provide a detailed picture for archaeologists on the distribution and development of Illyrian weaponry.

The Cantabrian stelae are monolithic stone disks of different sizes, whose early precedents were carved in the last centuries before the romanization of Cantabria in northern Iberian Peninsula. Cantabrian stelae include swastikas, triskeles, crosses, spirals, helixes, warriors or pre-Roman funerary representations among their usual ornamentation. The most famous is called Estela de Barros which can be visited in the Parque de las Estelas in the town of Barros, in Los Corrales de Buelna. This stele is part of the current coat of arms of Cantabria and the meaning of tetraskelion would be related to solar worship. The Barros stele giant size represents the main difference to the smaller stelae found in other parts of northern Spain. In addition to the Estela de Barros, we can see another larger, fragmented stele in the Parque de las Estelas.

Ancient Greek funerary practices are attested widely in literature, the archaeological record, and in ancient Greek art. Finds associated with burials are an important source for ancient Greek culture, though Greek funerals are not as well documented as those of the ancient Romans.

The Monterozzi necropolis is an Etruscan necropolis on a hill east of Tarquinia in Lazio, Italy. The necropolis has about 6,000 graves, the oldest of which dates to the 7th century BC. About 200 of the tomb chambers are decorated with frescos.

Baal with Thunderbolt or the Baal stele is a white limestone bas-relief stele from the ancient kingdom of Ugarit in northwestern Syria. The stele was discovered in 1932, about 20 metres (66 ft) from the Temple of Baal in the acropolis of Ugarit, during excavations directed by French archaeologist Claude F. A. Schaeffer. The stele depicts Baal, the Aramean god of storm and rain, and is considered the most important of the Ugaritic stelae. The stele is on display at the Musée du Louvre in Paris.

The theme of death within ancient Greek art has continued from the Early Bronze Age all the way through to the Hellenistic period. The Greeks used architecture, pottery, and funerary objects as different mediums through which to portray death. These depictions include mythical deaths, deaths of historical figures, and commemorations of those who died in war. This page includes various examples of the different types of mediums in which death is presented in Greek art.

There were a number of grave stelai or stelae found among the six shaft graves at Grave Circle A in the site of Mycenae. These stelai mark the burial sites of the Mycenaean dead, much like modern headstones. At least 21 stelai have been discovered from Grave Circle A, with 12 having identifiable relief sculpture. Most were upright, rectangular slabs of oolithic limestone, ranging in date from 1600 to 1500 BCE. The iconography depicted on these stelai include chariot scenes, hunting scenes, and circular and spiral designs characteristic of the Greek Mycenaean Period. Scholars argue that these scenes demonstrate the prevalence of warfare in Mycenaean culture, in addition to signifying a socially stratified society.

The Thanatos Painter was an Athenian Ancient Greek vase painter who painted scenes of death on white-ground cylindrical lekythoi. All of the Thanatos Painter's found lekythoi have scenes of or related to death on them, including the eponymous god of death Thanatos carrying away dead bodies.

Armor in the Indian subcontinent was used since antiquity. Its earlier reference is found in the vedic period. Armor has been described in religious texts; including the Itihasa epics Ramayana and Mahabharat, as well as in the Puranas.

The art of Kazakhstan covers all forms of art created throughout history by the peoples living on the territory of modern-day Kazakhstan. Throughout most periods, much of the population of Kazakhstan was nomadic, or at least moved regularly across the vast country. The great majority of the art of Kazakhstan is applied art: the decoration of practical objects, including household utensils and patterned harnesses, through art forms such as carpet-weaving, pottery, and leatherwork. The art of Kazakhstan also includes architecture, fine arts, and sculpture.

The Macmillan aryballos is a Protocorinthian pottery aryballos in the collection of the British Museum. Dating to about 640 BC, it is 6.9 cm high and 3.9 cm in diameter, and weighs 65 grams.




















