Related Research Articles

Sabratha, in the Zawiya District of Libya, was the westernmost of the ancient "three cities" of Roman Tripolis, alongside Oea and Leptis Magna. From 2001 to 2007 it was the capital of the former Sabratha wa Sorman District. It lies on the Mediterranean coast about 70 km (43 mi) west of modern Tripoli. The extant archaeological site was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1982.

Klina is a town and municipality located in the District of Peja of north-western Kosovo. According to the 2011 census, the town of Klina has 5,542 inhabitants, while the municipality has 38,496 inhabitants. It is located at the confluence of the river Klina into the White Drin. A symbol of Klina are the Mirusha Waterfalls.

Ulpiana was an ancient Roman city located in what is today Kosovo. It was also named Justiniana Secunda. Ulpiana is situated in the municipality of Gračanica, 12km to the southeast of Pristina. The Minicipium Ulpiana - Iustiniana Secunda was proclaimed archaeological park under permanent protection of Kosovo by the Kosova Council for Cultural Heritage in 2016. The Archaeological Park has a surface of 161.10 hectares and a surrounding protection zone of 96.23 hectares. Ulpiana was among the largest settlements in the Balkans of the late antiquity.

Prizren Fortress is a hilltop fortification in Prizren in Kosovo. It overlooks the Prizren River which flows through Prizren, which developed around the fortress. The site of the fortress of Prizren has seen habitation and use since the Bronze Age. In late antiquity it was part of the defensive fortification system in western Dardania and was reconstructed in the era of eastern Roman Emperor Justinian. Byzantine rule in the region ended definitively in 1219–20 as the Serbian Nemanjić dynasty controlled the fort until 1371.
Dresnik is a settlement in the Klina municipality of Kosovo.

Megiddo church, near Tel Megiddo, Israel, is an archaeological site which preserves the foundations of one of the oldest church buildings ever discovered by archaeologists, dating to the 3rd century AD. The ‘Megiddo Church’, as the room became known, was dated to circa 230 AD on the basis of pottery, coins, and the inscriptional style. The site’s abandonment, circa 305 AD, is evident in the purposeful covering of the mosaic, and relates well to the crisis of 303 AD, when the Christian communities of Judea experienced the Diocletianic Persecution.
Part of a series of articles upon Archaeology of Kosovo

A Roman mosaic is a mosaic made during the Roman period, throughout the Roman Republic and later Empire. Mosaics were used in a variety of private and public buildings, on both floors and walls, though they competed with cheaper frescos for the latter. They were highly influenced by earlier and contemporary Hellenistic Greek mosaics, and often included famous figures from history and mythology, such as Alexander the Great in the Alexander Mosaic.

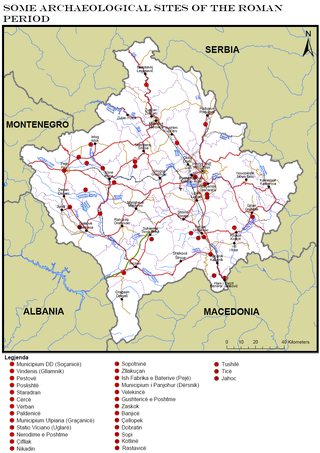
The Roman heritage sites in Kosovo represent a multitude of monuments of material and spiritual culture, which reflect the Roman period in this region. Among them, a special place is occupied by those that represent the development of art, such as the plastic monuments that are more frequent, and at the same time occupy an important place, because with the presentation of figures in relief and with numerous inscriptions they speak to us enough for this period.

Part of a series of articles upon Archaeology of Kosovo

Part of a series of articles upon Archaeology of Kosovo


Part of a series of articles on Archaeology of Kosovo

Part of a series of articles upon Archaeology of Kosovo

Part of a series of articles upon Archaeology of Kosovo
Nerodimë e Poshtme or Donje Nerodimlje is an archaeological site and village situated west of the city of Ferizaj, Kosovo. Several archaeological trenches were investigated at this location in 1988.
The strategic position of the region of Mitrovica in the middle of two great rivers Ibar and Sitnica and its mineral wealth in Albanik, made this location populated since prehistoric period. This region was populated by Illyrians, respectively members of the Dardan tribe. The first data for the archaeological sites in the region of Mitrovica, begin with the researches of Sir Artur John Evans, who was the first to pinpoint the Roman town of the Municipium Dardanourm. In the archaeological sites of the region of Mitrovica were found traces and objects from different periods such as; Neolithic, Roman, late antiquity and medieval period. Objects and figurines include: fortress vestiges, necropolis, Terpsichore figure, statues, sarcophagus, altar, jewelry, etc.
Kosovo has a rich heritage in archaeology, however the field suffers from a lack of substantial institutional research. Since prehistory, the advantageous geostrategic position and abundant natural resources of the area have been suitable for the emergence of life. This is shown by the by traces of hundreds of archaeological sites discovered throughout the country, displaying the abundant archaeological legacy.
The Rutland Roman villa is a Romano-British villa site in Rutland, England. The site was listed as a scheduled monument by Historic England on 23 November 2021. The villa includes the first example of a mosaic in Britain which depicts scenes from Homer's Iliad.
This page lists significant events of 2022 in archaeology.
References
- ↑ "The government paves the way for the expropriation of the archaeological site of Dresnik". koha.net.
- ↑ "Tour the Dresnik Archaeological Park in 360". Prishtina Insight. 2017-11-22. Retrieved 2023-11-18.
- ↑ "Kosovo Hails Discovery of Ancient Roman Site". balkaninsight.com.