
Schisandra, the magnolia vines, is a genus of twining shrubs that generally climb on other vegetation. Various authors have included the plants in the Illiciaceae

Vallaris is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1768. It is native to China, the Indian Subcontinent, and Southeast Asia.
- Vallaris anceps = Kibatalia macrophylla
- Vallaris angustifolia = Kibatalia gitingensis
- Vallaris arborea = Kibatalia macrophylla
- Vallaris clavata = Echites clavatus
- Vallaris daronensis = Kibatalia maingayi
- Vallaris divaricata = Strophanthus divaricatus
- Vallaris fimbriata = Euphorbia mammillaris
- Vallaris gitingensis = Kibatalia gitingensis
- Vallaris ipecacuanhae = Euphorbia ipecacuanhae
- Vallaris lancifolia = Micrechites lancifolius
- Vallaris laxiflora = Pottsia laxiflora
- Vallaris macrantha = Beaumontia macrantha
- Vallaris maingayi = Kibatalia maingayi
- Vallaris missurica = Euphorbia missurica
- Vallaris portulacoides = Euphorbia portulacoides
- Vallaris × uniflora = Euphorbia × uniflora
Pseudostachyum polymorphum is a monotypic Asian species of bamboo in the grass family.

Trachelospermumstar jasmine, Confederate jasmine, is a genus of evergreen woody vines in the dogbane family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1851. All species are native to southern and eastern Asia.

Rohdea is a genus of plants native to eastern Asia. It was long thought to contain only a single species, R. japonica, but recent studies have resulted in several other taxa being transferred into the genus.
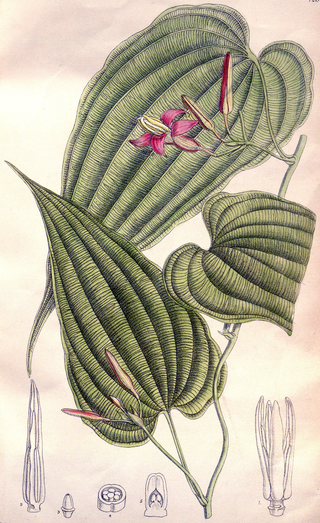
Stemona is a genus of vines and subshrubs in the family Stemonaceae, described as a genus in 1790.

Anodendron is a genus of plant in the family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1844. It is native to most of tropical Asia: China, the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, New Guinea, and some islands of the western Pacific.

Amydrium is a genus of primarily epiphytic, vining flowering plants in the arum and aroid family, Araceae, that is native to Southeast Asia, South China and New Guinea.

Dendrobium aduncum is a species of orchid. It is native to southern China, the eastern Himalayas, and northern Indochina. It is an epiphyte and grows on the tree trunks of mountain forests.

Dendrobium chrysanthum is a species of orchid. It is native to China, Indochina and the Himalayas.

Dendrobium devonianum is a species of orchid. It is native to southern China, the eastern Himalayas, and northern Indochina. It is an epiphyte that grows on tree trunks in mountain forests.

Dendrobium williamsonii is a species of orchid, commonly known as Williamson's dendrobium. It is native to southern China, Assam, and Indochina. It is an epiphyte and grows on tree trunks in forests.

Chonemorpha is a genus that consists of large evergreen vigorous woody vines with milky sap from India, Sri Lanka, to Southeast Asia, the Philippines and South China. Growing dormant in sub-tropical and tropical climates and usually losing leaves if temperature gets below 60F. The plants have pubescent to almost tomentose branches, leaves and inflorescences. Large, corrugated, ovate leaves to 40 cm long, deep glossy green, opposite, pale and hairy beneath. Very fragrant, funnel-shaped, showy flowers to 8 cm across with long-peduncled and terminal cymes. Corolla cream with yellow center. Disk cupular with many seeds, ovate-shaped, compressed, with scanty endosperm, with a tuft of hairs at one end, dark brown. The plant is widely grown as a fence cover.
- Chonemorpha assamensisFurtado - Assam, Bangladesh
- Chonemorpha eriostylisPit. in H.Lecomte - Yunnan, Guangdong, Vietnam
- Chonemorpha floccosaTsiang & P.T.Li - Guangxi
- Chonemorpha fragrans(Moon) Alston - China, Indian Subcontinent, Indochina, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines
- Chonemorpha megacalyxPierre ex Spire - Yunnan, Laos, Thailand
- Chonemorpha mollisMiq. - Java
- Chonemorpha parvifloraTsiang & P.T.Li - Yunnan, Guangxi
- Chonemorpha pedicellataRao - W Himalayas
- Chonemorpha splendensChun & Tsiang - Yunnan, Hainan
- Chonemorpha verrucosa(Blume) D.J.Middleton - Guangdong, Hainan, Yunnan, Bhutan, Assam, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Malaysia, Indochina

Peliosanthes is a genus of flowering plants found in eastern Asia. In the APG III classification system, it is placed in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Nolinoideae.

Disporopsis is a genus of plants in the Asparagaceae. It is native to China, Indochina and the Philippines.
Hymenopyramis is a genus of plants in the family Lamiaceae, first described in 1843. It is native to Indochina and to the Hainan Province of southern China.
- Hymenopyramis acuminataH.R.Fletcher - Thailand, Vietnam
- Hymenopyramis brachiataWall. ex Griff. - Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar; naturalized in India
- Hymenopyramis canaCraib - Hainan, Laos, Cambodia, Thailand
- Hymenopyramis parvifoliaMoldenke - Thailand
- Hymenopyramis pubescensMoldenke - Thailand
- Hymenopyramis siamensisCraib - Laos, Cambodia, Thailand
- Hymenopyramis vesiculosaH.R.Fletcher - Thailand

Aganosma is a genus of plants in family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1837. It is native to China, the Indian Subcontinent, and Southeast Asia.
- Aganosma brevilobaKerr - Guizhou, Myanmar, Thailand
- Aganosma cymosa(Roxb.) G.Don - Guangxi, Yunnan, Bangladesh, Assam, Sri Lanka, Indochina
- Aganosma gracilisHook.f. - Assam, Bhutan, Arunachal Pradesh
- Aganosma heynei(Spreng.) ined. - India
- Aganosma laceiRaizada - Myanmar
- Aganosma petelotiiLý - N Vietnam
- Aganosma schlechterianaH.Lév. - S China, Assam, N Indochina
- Aganosma siamensisCraib - Thailand, Vietnam, Guangxi, Guizhou, Yunnan
- Aganosma wallichiiG.Don - Myanmar, Thailand, W Malaysia, Java, Sumatra

Heterostemma is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described in 1834. It is native to India, China, Taiwan, Southeast Asia, Australia, and certain islands in the Pacific.

Ilex umbellulata is an evergreen tree species related to holly, generally four to fifteen metres in height. It is found in Southeast Asia. This tree is most often found growing in forests.
Zanthoxylum laetum is a species of woody plant from the Rutaceae family.





















