
The Pinkenba railway line is a railway line in the City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. It is the part of the Doomben railway line that still operates a regular passenger service. Doomben, or dumben, is the Indigenous Yuggera name for a tree fern which was prolific in the area. The railway line branches from the North Coast line at Eagle Junction, extending 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) to the industrial suburb of Pinkenba, situated on the northern bank at the mouth of the Brisbane River. It is part of the Queensland Rail Citytrain network.

The Ipswich and Rosewood line refers to the section of the Main Line to Toowoomba that has a regular suburban rail service, extending southwest from the Brisbane central business district. It is part of the Queensland Rail City network.

The Cleveland railway line is a suburban railway line extending 37.3 kilometres (23.2 mi) east-southeast from Brisbane, the state capital of Queensland, Australia. It is part of the Queensland Rail Citytrain network.

South Brisbane railway station is a heritage-listed railway station at 133 Grey Street, South Brisbane, City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. It is one of two stations serving the South Brisbane area, the other being South Bank. It was built from 1891 to 1918, making it the second oldest railway station in central Brisbane. It is also known as Cultural Centre Station, Melbourne Street Station, and South Brisbane (Interstate) Station. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 21 October 1992.

Boggo Road / Park Road railway station, formerly Park Road railway station, is the junction station for the Cleveland and Gold Coast lines in Queensland, Australia. It is located in the Brisbane suburb of Dutton Park.

The Gold Coast railway line is an interurban railway line operated by Queensland Rail in Queensland, Australia, connecting Brisbane with the Gold Coast. The line has 17 stations. In 2021, a journey from Central station to the terminus of this line was scheduled to take 1 hour 23 minutes. There are plans for several new stations along the existing line, as well as an extension south.

Dutton Park railway station is located on the Beenleigh line in Queensland, Australia. It serves the Brisbane suburb of Dutton Park. The station is one of the oldest on the network.

Fairfield railway station is located on the Beenleigh line in Queensland, Australia. It serves the Brisbane suburb of Fairfield.

Yeronga railway station is located on the Beenleigh line in Queensland, Australia. It serves the Brisbane suburb of Yeronga.

Yeerongpilly railway station is located on the Beenleigh line in Queensland, Australia. It serves the Brisbane suburb of Yeerongpilly. Immediately south-west of the station, the Corinda line branches off.

Moorooka railway station is located on the Beenleigh line in Queensland, Australia. It serves the Brisbane suburb of Moorooka. The station opened in 1887.

Rocklea railway station is located on the Beenleigh line in Queensland, Australia. It serves the Brisbane suburb of Rocklea. The station opened in 1885 at the same time as the line.

Salisbury railway station is located on the Beenleigh Line in Queensland, Australia. It serves the Brisbane suburb of Salisbury. The station opened in 1885 at the same time as the line.

Loganlea railway station is located on the Beenleigh line in Queensland, Australia. It serves the suburbs of Loganlea and Meadowbrook in Logan City. It is within a short distance of Logan Hospital, TAFE college, Griffith University, Loganlea State High School and Meadowbrook Shopping Centre.
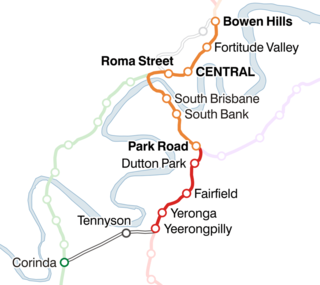
The Corinda–Yeerongpilly line is a railway line in Brisbane, the state capital of Queensland, Australia. It connects the Beenleigh and Ipswich lines for freight trains, but is no longer used for revenue passenger services in normal operation.

Yeerongpilly is a southern suburb in the City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, Yeerongpilly had a population of 2,033 people.

Railways in South East Queensland consist of a large passenger and freight rail network centred on Brisbane, the capital city of the Australian state of Queensland. Suburban and interurban passenger rail services are operated by Queensland Rail, which also operates long-distance services connecting Brisbane to the rest of the state. Aurizon and Pacific National are private companies which operate freight services. The passenger rail network in South East Queensland is known as the Citytrain network.
In the late 1970s and 1980s, a significant rail electrification program was completed in the Australian state of Queensland. The electrified Queensland network is the largest in Australia with over 2,000 kilometres electrified, the next biggest is New South Wales with 640 kilometres, that is served mainly as passenger operations.

Cross River Rail (CRR) is an underground heavy rail project currently under construction in Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. The project will see the development of a new rail line underneath the Brisbane River, together with the redevelopment of a number of stations in the Brisbane central business district as well as the Beenleigh railway line. The business case for the project was released in August 2017, with construction officially beginning in September 2017. The project replaced the planned 2013 BaT Tunnel, which in turn replaced the original 2010 Cross River Rail proposal. It is the largest infrastructure megaproject ever undertaken within Queensland. It has been widely reported that the cost of completion and date of the Cross City Rail Queensland Project was delayed and blown-out to $17 billion and expected to be opened in the year 2029, respectively.
The BaT (Bus and Train) project was a proposed north–south tunnel that would provide bus and rail modes of transportation by combining a new underground rail line and busway in a single, double-decked, 15m-wide tunnel beneath the Brisbane River and Brisbane central business district. The tunnel was to have three underground stations at Woolloongabba, George Street and Roma Street with Dutton Park upgraded.


























