
Authentication is the act of proving an assertion, such as the identity of a computer system user. In contrast with identification, the act of indicating a person or thing's identity, authentication is the process of verifying that identity. It might involve validating personal identity documents, verifying the authenticity of a website with a digital certificate, determining the age of an artifact by carbon dating, or ensuring that a product or document is not counterfeit.

A smart card (SC), chip card, or integrated circuit card, is a card used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart cards include a pattern of metal contacts to electrically connect to the internal chip. Others are contactless, and some are both. Smart cards can provide personal identification, authentication, data storage, and application processing. Applications include identification, financial, public transit, computer security, schools, and healthcare. Smart cards may provide strong security authentication for single sign-on (SSO) within organizations. Numerous nations have deployed smart cards throughout their populations.
Biometrics are body measurements and calculations related to human characteristics. Biometric authentication is used in computer science as a form of identification and access control. It is also used to identify individuals in groups that are under surveillance.
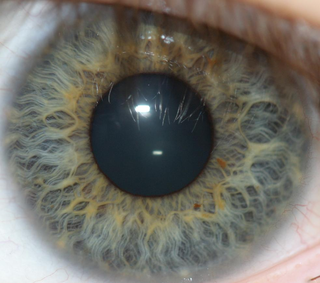
Iris recognition is an automated method of biometric identification that uses mathematical pattern-recognition techniques on video images of one or both of the irises of an individual's eyes, whose complex patterns are unique, stable, and can be seen from some distance. The discriminating powers of all biometric technologies depend on the amount of entropy they are able to encode and use in matching. Iris recognition is exceptional in this regard, enabling the avoidance of "collisions" even in cross-comparisons across massive populations. Its major limitation is that image acquisition from distances greater than a meter or two, or without cooperation, can be very difficult. However, the technology is in development and iris recognition can be accomplished from even up to 10 meters away or in a live camera feed.
Living in the intersection of cryptography and psychology, password psychology is the study of what makes passwords or cryptographic keys easy to remember or guess.
Electronic authentication is the process of establishing confidence in user identities electronically presented to an information system. Digital authentication, or e-authentication, may be used synonymously when referring to the authentication process that confirms or certifies a person's identity and works. When used in conjunction with an electronic signature, it can provide evidence of whether data received has been tampered with after being signed by its original sender. Electronic authentication can reduce the risk of fraud and identity theft by verifying that a person is who they say they are when performing transactions online.
The South African Social Security Agency (SASSA) is a national agency of the South African government created in April 2005 to administer South Africa's social security system, including by distributing social grants, on behalf of the Department of Social Development (DSD). It is under the oversight, but not the operational control, of DSD and the Ministry of Social Development. Established in terms of the Social Assistance Act of 2004 and South African Social Security Agency Act of 2004, SASSA is a public entity in terms of Schedule 3A of the Public Finance Management Act. As of 2022 its chief executive officer was Busisiwe Memela-Khambula.
Password fatigue is the feeling experienced by many people who are required to remember an excessive number of passwords as part of their daily routine, such as to log in to a computer at work, undo a bicycle lock or conduct banking from an automated teller machine. The concept is also known as password chaos, or more broadly as identity chaos.
A government database collects information for various reasons, including climate monitoring, securities law compliance, geological surveys, patent applications and grants, surveillance, national security, border control, law enforcement, public health, voter registration, vehicle registration, social security, and statistics.

Multi-factor authentication is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more pieces of evidence to an authentication mechanism. MFA protects personal data—which may include personal identification or financial assets—from being accessed by an unauthorized third party that may have been able to discover, for example, a single password.

Aadhaar is a 12-digit unique identity number that can be obtained voluntarily by all residents of India, based on their biometrics and demographic data. The data is collected by the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI), a statutory authority established in January 2009 by the Government of India, under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, following the provisions of the Aadhaar Act, 2016.
Cyber crime, or computer crime, refers to any crime that involves a computer and a network. The computer may have been used in the commission of a crime, or it may be the target. Netcrime refers, more precisely, to criminal exploitation of the Internet. Issues surrounding this type of crime have become high-profile, particularly those surrounding hacking, copyright infringement, identity theft, child pornography, and child grooming. There are also problems of privacy when confidential information is lost or intercepted, lawfully or otherwise.
The National Missing and Unidentified Persons System (NamUs) is a national clearinghouse and resource center for missing, unidentified, and unclaimed person cases throughout the United States.

The Ghana Card is the national Identity card that is issued by the Ghanaian authorities to Ghanaian citizens – both resident and non-resident, legal and permanent residents of foreign nationals. It is proof of identity, citizenship and residence of the holder. The current version is in ID1 format and biometric. It is issued by the National Identification Authority of Ghana and Regarded as a property of the country as such. In July 2023, through the initiative of the Vice President, Dr. Mahamudu Bawumia, new card numbers were issued to newborn babies as part of pilot program to incorporate newborn babies unto the database.
Biometrics refers to the automated recognition of individuals based on their biological and behavioral characteristics, not to be confused with statistical biometrics; which is used to analyse data in the biological sciences. Biometrics for the purposes of identification may involve DNA matching, facial recognition, fingerprints, retina and iris scanning, voice analysis, handwriting, gait, and even body odor.
IDEMIA is a multinational technology company headquartered in Courbevoie, France. It provides identity-related security services, and sells facial recognition and other biometric identification products and software to private companies and governments.
Identity-based security is a type of security that focuses on access to digital information or services based on the authenticated identity of an entity. It ensures that the users and services of these digital resources are entitled to what they receive. The most common form of identity-based security involves the login of an account with a username and password. However, recent technology has evolved into fingerprinting or facial recognition.

A biometric device is a security identification and authentication device. Such devices use automated methods of verifying or recognising the identity of a living person based on a physiological or behavioral characteristic. These characteristics include fingerprints, facial images, iris and voice recognition.
Visa requirements for crew members are administrative entry restrictions imposed by countries on members of the crew during transit or turnaround.
Many countries have entry restrictions on foreigners that go beyond the common requirement of having either a valid visa or a visa exemption. Such restrictions may be health related or impose additional documentation requirements on certain classes of people for diplomatic or political purposes.







