The Boii were a Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul, Pannonia, present-day Bavaria, in and around present-day Bohemia, parts of present-day Slovakia and Poland, and Gallia Narbonensis.

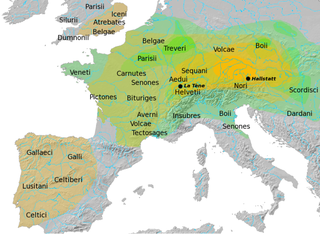
The Celts or Celtic peoples were a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic languages and other cultural similarities. Major Celtic groups included the Gauls; the Celtiberians and Gallaeci of Iberia; the Britons, Picts, and Gaels of Britain and Ireland; the Boii; and the Galatians. The interrelationships of ethnicity, language and culture in the Celtic world are unclear and debated; for example over the ways in which the Iron Age people of Britain and Ireland should be called Celts. In current scholarship, 'Celt' primarily refers to 'speakers of Celtic languages' rather than to a single ethnic group.

The La Tène culture was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age, succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any definite cultural break, under considerable Mediterranean influence from the Greeks in pre-Roman Gaul, the Etruscans, and the Golasecca culture, but whose artistic style nevertheless did not depend on those Mediterranean influences.

S or s, is the nineteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and other latin alphabets worldwide. Its name in English is ess, plural esses.

The Etruscan civilization was an ancient civilization created by the Etruscans, a people who inhabited Etruria in ancient Italy, with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria, and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto, and western Campania.

The Samnites were an ancient Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy.

Bell-bottoms are a style of trousers that become wider from the knees downward, forming a bell-like shape of the trouser leg.

A tunic is a garment for the torso, usually simple in style, reaching from the shoulders to a length somewhere between the hips and the ankles. It might have arm-sleeves, either short or full-length. Most forms have no fastenings. The name derives from the Latin tunica, the basic garment worn by both men and women in Ancient Rome, which in turn was based on earlier Greek garments that covered wearers' waists.

The Etruscan alphabet was used by the Etruscans, an ancient civilization of central and northern Italy, to write their language, from about 700 BC to sometime around 100 AD.

Breeches are an article of clothing covering the body from the waist down, with separate coverings for each leg, usually stopping just below the knee, though in some cases reaching to the ankles. Formerly a standard item of Western men's clothing, they had fallen out of use by the mid-19th century in favour of trousers.
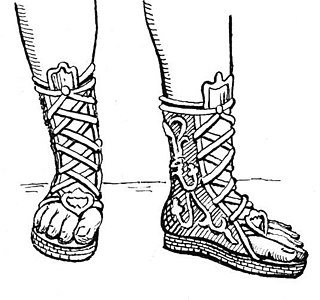
A buskin is a knee- or calf-length boot made of leather or cloth, enclosed by material, and laced, from above the toes to the top of the boot, and open across the toes.

Hose are any of various styles of men's clothing for the legs and lower body, worn from the Middle Ages through the 17th century, when the style fell out of use in favour of breeches and stockings. The old plural form of "hose" was "hosen". In German these terms remained in use and are the generic terms for trousers today. The French equivalent was chausses.

C or c is the third letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is cee, plural cees.

Trousers, slacks, or pants are an item of clothing worn from the waist to anywhere between the knees and the ankles, covering both legs separately. In some parts of the United Kingdom, the word pants is ambiguous: it can mean trousers rather than underpants. Shorts are similar to trousers, but with legs that come down only to around the area of the knee, higher or lower depending on the style of the garment. To distinguish them from shorts, trousers may be called "long trousers" in certain contexts such as school uniform, where tailored shorts may be called "short trousers" in the UK.

The Gauls were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period. Their homeland was known as Gaul (Gallia). They spoke Gaulish, a continental Celtic language.

Thracian clothing refers to types of clothing worn mainly by Thracians, Dacians but also by some Greeks. Its best literal descriptions are given by Herodotus and Xenophon in his Anabasis. Depictions are found in a great number of Greek vases and there are a few Persian representations as well. In contrast to shapes and patterns we have very little evidence on the colours used.
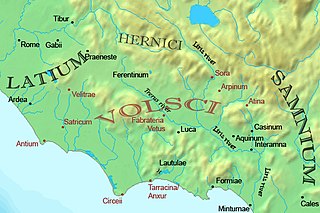
The Latins, sometimes known as the Latials or Latians, were an Italic tribe that included the early inhabitants of the city of Rome. From about 1000 BC, the Latins inhabited the small region known to the Romans as Old Latium, the area in the Italian Peninsula between the river Tiber and the promontory of Mount Circeo 100 km (62 mi) southeast of Rome. Following the Roman expansion, the Latins spread into the Latium adiectum, inhabited by Osco-Umbrian peoples.

Braies are a type of trouser worn by Celtic and Germanic tribes in antiquity and by Europeans subsequently into the Middle Ages. In the later Middle Ages they were used exclusively as undergarments. Braies generally hung to the knees or mid-calf, resembling what are today called shorts. They were made of leather, wool, or, in later years, cotton or linen. They were adopted by the Romans as braccae. By the 11th century, Braies were ankle-length pants held in place by a cord fitted through the top. People from upper classes wore more fitting braies while people of the lower classes typically wore loose braies.

Shalwar kameez is a traditional combination dress worn by men and women in South Asia, and Central Asia.




















