
The papaya, papaw, or pawpaw is the plant species Carica papaya, one of the 21 accepted species in the genus Carica of the family Caricaceae. It was first domesticated in Mesoamerica, within modern-day southern Mexico and Central America. It is grown in several countries in regions with a tropical climate. In 2020, India produced 42% of the world's supply of papayas.

Mealybugs are insects in the family Pseudococcidae, unarmored scale insects found in moist, warm habitats. Of the more than 2000 described species, many are considered pests as they feed on plant juices of greenhouse plants, house plants and subtropical trees and also act as a vector for several plant diseases. Some ants live in symbiotic relationships with them, protecting them from predators and feeding off the honeydew which they excrete.

The glassy-winged sharpshooter is a large leafhopper, similar to other species of sharpshooter.
Citrus tristeza virus (CTV) is a viral species of the genus Closterovirus that causes the most economically damaging disease to its namesake plant genus, Citrus. The disease has led to the death of millions of Citrus trees all over the world and has rendered millions of others useless for production. Farmers in Brazil and other South American countries gave it the name "tristeza", meaning sadness in Portuguese and Spanish, referring to the devastation produced by the disease in the 1930s. The virus is transmitted most efficiently by the brown citrus aphid.

Cecidophyopsis ribis is an eriophyid mite which is best known for being a plant parasite, a pest of Ribes species, the genus that includes gooseberries and blackcurrants. It is commonly known as the blackcurrant gall mite or big bud mite. It feeds on the plants' buds, forming galls, and transmits a virus which causes blackcurrant reversion disease. The mite is a serious pest of blackcurrant crops in Europe, but rarely on other continents.
Paratrichodorus minor is a species of nematode in the family Trichodoridae, the stubby-root nematodes. It occurs in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. It damages plants by feeding on the roots and it is a vector of plant viruses. It is a pest of some agricultural crops.
Xiphinema americanum, the American dagger nematode, is a species of plant pathogenic nematodes. It is one of many species that belongs to the genus Xiphinema. It was first described by N. A. Cobb in 1913, who found it on both sides of the United States on the roots of grass, corn, and citrus trees. Not only is Xiphinema americanum known to vector plant viruses, but also X. americanum has been referred to as "the most destructive plant parasitic nematode in America", and one of the four major nematode pests in the Southeastern United States.
Xiphinema index, the California dagger nematode, is a species of plant-parasitic nematodes.

Cymbidium mosaic virus (CymMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Alphaflexiviridae.

Impatiens necrotic spot orthotospovirus(INSV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the order Bunyavirales. It was originally believed to be another strain of Tomato spotted wilt virus, but genetic investigations revealed them to be separate viruses. It is a negative-strand RNA virus which has a tripartite genome. It is largely spread by the insect vector of the western flower thrips. The virus infects more than 648 species of plants including important horticultural and agricultural species such as fuchsia, tomato, orchids, and lettuce (especially romaine). As the name implies, the main symptom on plants is necrotic spots that appear on the leaves. The INSV virus infects by injecting the RNA the virus contains into the cell which then starts using the cell resources to transcribe what the virus RNA states. Viral infection can often result in the death of the plant. The disease is mainly controlled by the elimination of the western flower thrip vector and by destroying any infected plant material.

Tobacco rattle virus (TRV) is a pathogenic plant virus. Over 400 species of plants from 50 families are susceptible to infection.

The western flower thrips [Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande)] is an invasive pest insect in agriculture. This species of thrips is native to the Southwestern United States but has spread to other continents, including Europe, Australia, and South America via transport of infested plant material.

Orthotospovirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses, in the family Tospoviridae of the order Bunyavirales, which infects plants. Tospoviruses take their name from the species Tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus (TSWV) which was discovered in Australia in 1919. TSWV remained the only known member of the family until the early 1990s when genetic characterisation of plant viruses became more common. There are now at least twenty species in the genus with more being discovered on a regular basis. Member viruses infect over eight hundred plant species from 82 different families.
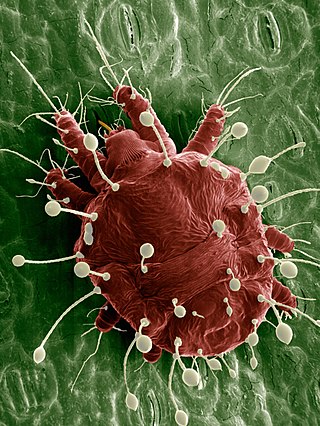
Tenuipalpidae, also called flat mites or false spider mites, are a family of mites, closely related to the Tetranychidae. They are reddish and slow-moving and normally feed near the midrib or veins on the underside of leaves. Several species, among them Raoiella indica, are important crop pests. Other common species include Acaricis urigersoni and the Brevipalpus species B. phoenicis, B. californicus, B. obovatus, and B. lewisi.

Brevipalpus phoenicis, also known as the false spider mite, red and black flat mite, and in Australia as the passionvine mite, is a species of mite in the family Tenuipalpidae. This species occurs globally, and is a serious pest to such crops as citrus, tea, papaya, guava and coffee, and can heavily damage numerous other crops. They are unique in having haploid females, a condition caused by a bacterium that change haploid males into females.
Cilevirus is a genus of viruses in the family Kitaviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are two species: Citrus leprosis virus C and Citrus leprosis virus C2.
Orchid fleck dichorhavirus, commonly called Orchid fleck virus (OFV), is a non-enveloped, segmented, single-stranded (ss) RNA negative-strand virus, transmitted by the false spider mite, Brevipalpus californicus. OFV causes necrotic and chlorotic lesions on the leaves of many genera in the family Orchidaceae.
Citrus leprosis(CL) is an economically important viral disease affecting citrus crops. This emerging disease is widely distributed in South and Central America, from Argentina to Mexico. The disease is associated with up to three different non-systemic viruses, which cause similar symptoms in the citrus hosts and are transmitted by the same vector, mites of the genus Brevipalpus; although they have vastly different genomes. Citrus leprosis virus nuclear type (CiLV-N) is found in the nuclei and cytoplasm of infected cells, while Citrus leprosis virus cytoplasmic type (CiLV-C) is found in the endoplasmic reticulum. In 2012, a new virus causing similar symptoms was found in Colombia and it was named Citrus leprosis virus cytoplasmic type 2 (CiLV-C2) due to its close similarity to CiLV-C. The cytoplasmic type viruses are the most prevalent and widely distributed of the three species.

Carnation Italian Ringspot Virus (CIRV) is a plant virus that impacts carnation plants. These flowers are a popular choice in ornamental flower arrangements. This article will provide an overview of CIRV. This will include the history of the virus, information on transmission, symptoms, and characteristics, and research about how it relates to plant physiology.












