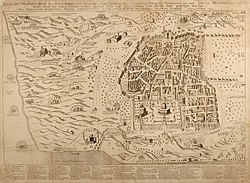
Maps of Jerusalem can be categorised between original factual maps, copied maps and imaginary maps, the latter being based on religious books. [1] The maps were produced in a variety of materials, including parchment, vellum, mosaic, wall paintings and paper. [2] Most extant maps known to scholars from the pre-modern era were prepared by Christian mapmakers for a Christian European audience. [3] [4] All maps marking milestones in the cartography of Jerusalem are listed here following the cartographic histories of the city, from Titus Tobler and Reinhold Röhricht's studies in the 19th century to those of Hebrew University of Jerusalem academics Rehav Rubin and Milka Levy-Rubin in recent decades. The article lists maps that progressed the cartography of Jerusalem before the rise of modern surveying techniques, showing how mapmaking and surveying improved and helped outsiders to better understand the geography of the city. Imaginary maps of the ancient city and copies of existing maps are excluded.
Contents
- Notable maps of Jerusalem
- Early religious (6th–7th centuries)
- Crusader maps (12th–14th centuries)
- Notable 15th–18th century maps
- Notable 19th century maps
- See also
- References
- Bibliography
- Further reading
- External links
The Madaba Map discovered in modern-day Jordan is the oldest known map of Jerusalem, [2] in the form of a mosaic in a Greek Orthodox Church. At least 12 maps survive from the Catholic mapmakers of the Crusades; they were drawn on vellum and mostly show the city as a circle. [2] [5] Approximately 500 maps are known between the late-1400s and the mid-1800s; the significant increase in number is due to the advent of the printing press. The first printed map of the city was drawn by Erhard Reuwich and published in 1486 by Bernhard von Breydenbach in his Peregrinatio in Terram Sanctam, based on his pilgrimage of 1483. [2] Few of the mapmakers had travelled to Jerusalem – most of the maps were either copies of others' maps or were imaginary (i.e. based on reading of religious texts) in nature. [6] The first map based on actual field measurements was published in 1818 by the Czech mapmaker Franz Wilhelm Sieber. [2] [7] The first map based on modern surveying techniques was published by Charles Wilson in 1864–65 for the British Ordnance Survey. [2] [8]