| Chinese pond heron | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Adult in breeding plumage | |
 | |
| Adult in winter plumage | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Pelecaniformes |
| Family: | Ardeidae |
| Genus: | Ardeola |
| Species: | A. bacchus |
| Binomial name | |
| Ardeola bacchus (Bonaparte, 1855) | |
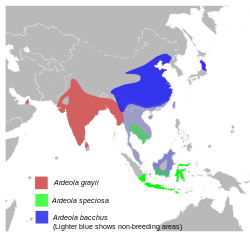 | |
| Global range of A. bacchus, compared to its presumed closest relatives Ardeola bacchus Breeding range Ardeola bacchus Non-breeding range | |
The Chinese pond heron (Ardeola bacchus) is an East Asian freshwater bird of the heron family, (Ardeidae). It is one of six species of birds known as "pond herons" (genus Ardeola ). It is parapatric (or nearly so) with the Indian pond heron (A. grayii) to the west and the Javan pond heron (A. speciosa) to the south, and these three are presumed to form a superspecies.[ citation needed ] As a group they are variously affiliated with the squacco heron (A. ralloides) or the Malagasy pond heron (A. idae). As of mid-2011 there are no published molecular analyses of pond heron interrelationships [2] and osteological data is likewise not analyzed for all relevant comparison taxa. [3]

