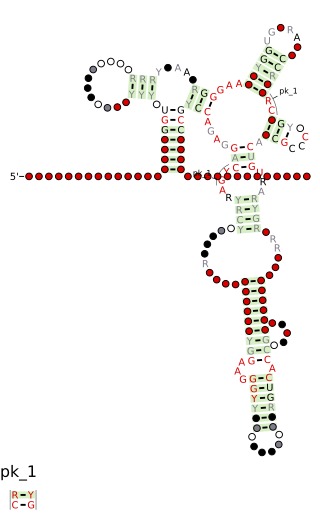
Cobalamin riboswitch is a cis-regulatory element which is widely distributed in 5' untranslated regions of vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) related genes in bacteria.

1-Aminopropan-2-ol is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH(OH)CH2NH2. It is an amino alcohol. The term isopropanolamine may also refer more generally to the additional homologs diisopropanolamine (DIPA) and triisopropanolamine (TIPA).
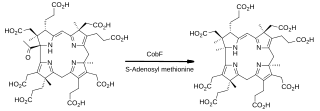
In enzymology, precorrin-6A synthase (deacetylating) (EC 2.1.1.152) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a precorrin-6A reductase (EC 1.3.1.54) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a precorrin-3B synthase (EC 1.14.13.83) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a cob(II)yrinic acid a,c-diamide reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme threonine-phosphate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.81) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an adenosylcobyric acid synthase (glutamine-hydrolysing) (EC 6.3.5.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Cobalt chelatase (EC 6.6.1.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a hydrogenobyrinic acid a,c-diamide synthase (glutamine-hydrolysing) (EC 6.3.5.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The primary biochemical reaction catalyzed by the enzyme adenosylcobalamin/α-ribazole phosphatase (formerly α-ribazole phosphatase) (EC 3.1.3.73) is

In enzymology, a nicotinate-nucleotide-dimethylbenzimidazole phosphoribosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an adenosylcobinamide kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an adenosylcobinamide-phosphate guanylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Cob(I)yrinic acid a,c-diamide adenosyltransferase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MMAB gene.

Bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) are organelle-like structures found in bacteria. They consist of a protein shell that encloses enzymes and other proteins. BMCs are typically about 40–200 nanometers in diameter and are made entirely of proteins. The shell functions like a membrane, as it is selectively permeable. Other protein-based compartments found in bacteria and archaea include encapsulin nanocompartments and gas vesicles.

Cobalamin biosynthesis is the process by which bacteria and archea make cobalamin, vitamin B12. Many steps are involved in converting aminolevulinic acid via uroporphyrinogen III and adenosylcobyric acid to the final forms in which it is used by enzymes in both the producing organisms and other species, including humans who acquire it through their diet.
Propionate kinase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:propanoate phosphotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Adenosylcobinamide-GDP ribazoletransferase is an enzyme with systematic name adenosylcobinamide-GDP:alpha-ribazole ribazoletransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Adenosylcobinamide-phosphate synthase is an enzyme with systematic name adenosylcobyric acid:(R)-1-aminopropan-2-yl phosphate ligase (ADP-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction












