Analysis
The amendment is deeply intertwined with the 2004 presidential election, in which Republican George W. Bush ran against Democrat John Kerry.
As Colorado was expected to lean towards Bush, the passage of this amendment (generally favored by Democrats and opposed by Republicans), could have taken some electoral votes from Bush and assigned them to Kerry. Had such an apportionment been in place in 2000, Al Gore would have won the electoral college vote and become president.
However, as November 2004 neared, Colorado began to look increasingly like a swing state in which it was possible that Kerry would win. Many Democrats who had pushed for Amendment 36 therefore began to have second thoughts and withdrew their advocacy for and support of the amendment. This withdrawal of Democratic support has been blamed for the defeat of the ballot initiative on Election Day. In the end, Bush won the state, but this amendment would not have been sufficient for Kerry to win the election.
The applicability of this amendment to a presidential vote being conducted simultaneously was questioned and might have been the subject of a legal dispute had the amendment passed.
Despite being favored by the Republicans, Amendment 36 didn't seem to benefit them in the next three elections, as a Democrat would win all 9 of Colorado's electoral votes. (Barack Obama in 2008 and 2012 and Hillary Clinton in 2016, the worst performing Democrat in the general election in more than 30 years as of 2019.)
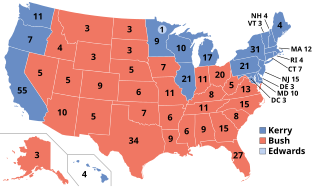
The 2004 United States presidential election was the 55th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 2, 2004. Incumbent Republican President George W. Bush defeated Democratic nominee John Kerry, a United States Senator from Massachusetts.

The 2004 United States presidential election in California took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose 55 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2004 United States presidential election in Illinois took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose 21 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2004 United States presidential election in Iowa took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose seven representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2004 United States presidential election in New Jersey took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose 15 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

In United States presidential elections, a faithless elector is a member of the United States Electoral College who does not vote for the presidential or vice presidential candidate for whom they had pledged to vote. That is, they break faith with the candidate they were pledged to and vote for another candidate, or fail to vote. A pledged elector is only considered a faithless elector by breaking their pledge; unpledged electors have no pledge to break.

The 2004 United States presidential election in Colorado took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose nine representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2004 United States presidential election in Connecticut took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose 7 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2004 United States presidential election in New York took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose 31 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2004 United States presidential election in Idaho took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 presidential election. Voters chose four representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The National Popular Vote Interstate Compact (NPVIC) is an agreement among a group of U.S. states and the District of Columbia to award all their electoral votes to whichever presidential candidate wins the overall popular vote in the 50 states and the District of Columbia. The compact is designed to ensure that the candidate who receives the most votes nationwide is elected president, and it would come into effect only when it would guarantee that outcome. As of July 2020, it has been adopted by fifteen states and the District of Columbia, although it is suspended in Colorado. Together, they have 196 electoral votes counting Colorado, which is 36% of the Electoral College and 73% of the 270 votes needed to give the compact legal force. Certain legal questions, however, may affect implementation of the compact.

The 2004 United States presidential election in Indiana took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose 11 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2004 United States presidential election in Massachusetts took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose 12 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2004 United States presidential election in Oregon took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose seven representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2004 United States presidential election in North Carolina took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose 15 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2004 United States presidential election in Michigan took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose 17 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2004 United States presidential election in Mississippi took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose 6 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president. It was the first presidential election since the 2000 United States census led to Mississippi losing an electoral vote, bringing its number of electoral votes from seven to six. This was the fewest electoral votes Mississippi had had in a presidential election since 1848.

The 2004 United States presidential election in West Virginia took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose 5 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2004 United States presidential election in Wyoming took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Voters chose three representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2008 United States presidential election in Colorado took place on November 4, 2008, as a part of the 2008 United States presidential election throughout all 50 states and the District of Columbia. Voters chose nine representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.






