Liver tumors are abnormal growth of liver cells on or in the liver. Several distinct types of tumors can develop in the liver because the liver is made up of various cell types. Liver tumors can be classified as benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) growths. They may be discovered on medical imaging, and the diagnosis is often confirmed with liver biopsy. Signs and symptoms of liver masses vary from being asymptomatic to patients presenting with an abdominal mass, hepatomegaly, abdominal pain, jaundice, or some other liver dysfunction. Treatment varies and is highly specific to the type of liver tumor.

Caroli disease is a rare inherited disorder characterized by cystic dilatation of the bile ducts within the liver. There are two patterns of Caroli disease: focal or simple Caroli disease consists of abnormally widened bile ducts affecting an isolated portion of liver. The second form is more diffuse, and when associated with portal hypertension and congenital hepatic fibrosis, is often referred to as "Caroli syndrome". The underlying differences between the two types are not well understood. Caroli disease is also associated with liver failure and polycystic kidney disease. The disease affects about one in 1,000,000 people, with more reported cases of Caroli syndrome than of Caroli disease.

Steatosis, also called fatty change, is abnormal retention of fat (lipids) within a cell or organ. Steatosis most often affects the liver – the primary organ of lipid metabolism – where the condition is commonly referred to as fatty liver disease. Steatosis can also occur in other organs, including the kidneys, heart, and muscle. When the term is not further specified, it is assumed to refer to the liver.

Alcoholic hepatitis is hepatitis due to excessive intake of alcohol. Patients typically have a history of at least 10 years of heavy alcohol intake, typically 8–10 drinks per day. It is usually found in association with fatty liver, an early stage of alcoholic liver disease, and may contribute to the progression of fibrosis, leading to cirrhosis. Symptoms may present acutely after a large amount of alcoholic intake in a short time period, or after years of excess alcohol intake. Signs and symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis include jaundice, ascites, fatigue and hepatic encephalopathy. Mild cases are self-limiting, but severe cases have a high risk of death. Severity in alcoholic hepatitis is determined several clinical prediction models such as the Maddrey's Discriminant Function and the MELD score.

Biliary atresia, also known as extrahepatic ductopenia and progressive obliterative cholangiopathy, is a childhood disease of the liver in which one or more bile ducts are abnormally narrow, blocked, or absent. It can be congenital or acquired. It has an incidence of one in 10,000–15,000 live births in the United States, and a prevalence of one in 16,700 in the British Isles. Biliary atresia is most common in East Asia, with a frequency of one in 5,000.

Portal hypertension is defined as increased portal venous pressure, with a hepatic venous pressure gradient greater than 5 mmHg. Normal portal pressure is 1–4 mmHg; clinically insignificant portal hypertension is present at portal pressures 5–9 mmHg; clinically significant portal hypertension is present at portal pressures greater than 10 mmHg. The portal vein and its branches supply most of the blood and nutrients from the intestine to the liver.
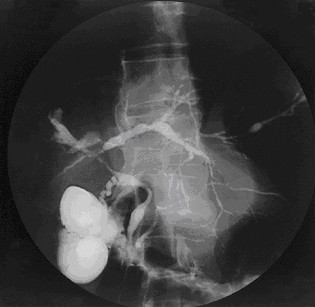
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a long-term progressive disease of the liver and gallbladder characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, which normally allow bile to drain from the gallbladder. Affected individuals may have no symptoms or may experience signs and symptoms of liver disease, such as yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes, itching, and abdominal pain.
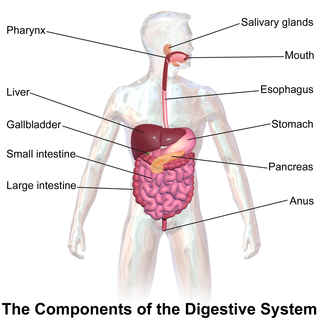
Gastrointestinal diseases refer to diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract, namely the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum; and the accessory organs of digestion, the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
A portosystemic shunt or portasystemic shunt, also known as a liver shunt, is a bypass of the liver by the body's circulatory system. It can be either a congenital or acquired condition and occurs in humans as well as in other species of animals. Congenital PSS are extremely rare in humans but are relatively common in dogs. Improvements in imaging and awareness have contributed to an increase in cases.Thus a large part of medical and scientific literature on the subject is grounded in veterinary medicine.

Peliosis hepatis is an uncommon vascular condition characterised by multiple, randomly distributed, blood-filled cavities throughout the liver. The size of the cavities usually ranges between a few millimetres and 3 cm in diameter. In the past, it was a mere histological curiosity occasionally found at autopsies, but has been increasingly recognised with wide-ranging conditions from AIDS to the use of anabolic steroids. It also occasionally affects spleen, lymph nodes, lungs, kidneys, adrenal glands, bone marrow, and other parts of gastrointestinal tract.

The liver is a major metabolic organ exclusively found in vertebrate animals, which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and various other biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm and mostly shielded by the lower right rib cage. Its other metabolic roles include carbohydrate metabolism, the production of hormones, conversion and storage of nutrients such as glucose and glycogen, and the decomposition of red blood cells.
Diffuse infiltrative lymphocytosis syndrome (DILS) is a rare multi-system complication of HIV believed to occur secondary to an abnormal persistence of the initial CD8+ T cell expansion that regularly occurs in an HIV infection. This persistent CD8+ T cell expansion occurs in the setting of a low CD4+/CD8+ T cell ratio and ultimately invades and destroys tissues and organs resulting in the various complications of DILS. DILS classically presents with bilateral salivary gland enlargement (parotitis), cervical lymphadenopathy, and sicca symptoms such as xerophthalmia and xerostomia, but it may also involve the lungs, nervous system, kidneys, liver, digestive tract, and muscles. Once suspected, current diagnostic workups include (1) confirming HIV infection, (2) confirming six or greater months of characteristic signs and symptoms, (3) confirming organ infiltration by CD8+ T cells, and (4) exclusion of other autoimmune conditions. Once the diagnosis of DILS is confirmed, management includes highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) and as-needed steroids. With proper treatment, the overall prognosis of DILS is favorable.

Bile duct hamartoma or biliary hamartoma, are benign lesions of the intrahepatic bile duct. They are classically associated with polycystic liver disease, as may be seen in the context of polycystic kidney disease, and represent a malformation of the liver plate.

Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) is the recessive form of polycystic kidney disease. It is associated with a group of congenital fibrocystic syndromes. Mutations in the PKHD1 cause ARPKD.

Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is a condition of the liver in which the normal functioning tissue, or parenchyma, is replaced with scar tissue (fibrosis) and regenerative nodules as a result of chronic liver disease. Damage to the liver leads to repair of liver tissue and subsequent formation of scar tissue. Over time, scar tissue and nodules of regenerating hepatocytes can replace the parenchyma, causing increased resistance to blood flow in the liver's capillaries—the hepatic sinusoids—and consequently portal hypertension, as well as impairment in other aspects of liver function. The disease typically develops slowly over months or years.
Vanishing bile duct syndrome is a loose collection of diseases which leads to the injury to hepatic bile ducts and eventual ductopenia.

Juvenile nephronophthisis is the juvenile form of nephronophthisis that causes end stage kidney disease around the age of 13; infantile nephronophthisis and adolescent nephronophthisis cause ESKD around the ages of 1 and 19, respectively.

COACH syndrome, also known as Joubert syndrome with hepatic defect, is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disease. The name is an acronym of the defining signs: cerebellar vermis aplasia, oligophrenia, congenital ataxia, coloboma and hepatic fibrosis. The condition is associated with moderate intellectual disability. It falls under the category of a Joubart Syndrome-related disorder (JSRD).
Portosystemic shunts are a type of vascular abnormality that causes blood to be emptied into the circulation, without passing through the liver. This prevents the liver from detoxifying the blood. The condition may be either congenital or acquired.














