
Apsopelix is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish that existed about 95-80 million years ago in the shallow waters of the Western Interior Seaway, Hudson Seaway, England, France, and Japan.
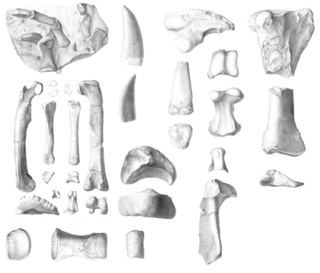
Erectopus is an extinct genus of basal allosauroid theropod from the Early Cretaceous La Penthiève Beds Formation of France and also possibly the Cernavodă Formation of southern Romania. The type species is E. superbus, which was initially known as a species of Megalosaurus.
Cooyoo is an extinct genus of ichthyodectid ray-finned fish known from the Lower Cretaceous. It contains a single species, C. australis, known from the Albian-aged Toolebuc and Allaru Formations of Queensland, Australia. C. australis was originally named by Arthur Smith Woodward as a species of Portheus in 1894, which was later amended to Xiphactinus.

Ichthyodectiformes is an extinct order of marine stem-teleost ray-finned fish. The order is named after the genus Ichthyodectes, established by Edward Drinker Cope in 1870. Ichthyodectiforms are usually considered to be some of the closest relatives of the teleost crown group.

Axelrodichthys is an extinct genus of mawsoniid coelacanth from the Cretaceous of Africa, North and South America, and Europe. Several species are known, the remains of which were discovered in the Lower Cretaceous (Aptian-Albian) of Brazil, North Africa, and possibly Mexico, as well as in the Upper Cretaceous of Morocco (Cenomanian), Madagascar and France. The Axelrodichthys of the Lower Cretaceous frequented both brackish and coastal marine waters while the most recent species lived exclusively in fresh waters. The French specimens are the last known fresh water coelacanths. Most of the species of this genus reached 1 metre to 2 metres in length. Axelrodichthys was named in 1986 by John G. Maisey in honor of the American ichthyologist Herbert R. Axelrod.

Pachythrissops is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish. It contains two species, P. laevis from the Purbeckian of England and P. propterus from the Tithonian of Germany. A third species, P. vectensis, has been reassigned to the elopiform genus Arratiaelops. Pachythrissops is often regarded as one of the most primitive members of the order Ichthyodectiformes; however, a phylogenetic analysis by Cavin et al. (2013) placed it and the related genus Ascalabothrissops outside the group.

Bananogmius is an extinct genus of marine ray-finned fish that was found in what is now North America and Europe during the Late Cretaceous, from the Cenomanian to the Santonian. It lived in the Western Interior Seaway, which split North America in two during the Late Cretaceous, as well as the proto-North Sea of Europe.
Asiatoceratodus is an extinct genus of lungfish which lived during the Middle-Late Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous periods in what is now Asia (Kyrgyzstan), Africa and South America.

Chirocentrites is an extinct genus of marine ray-finned fish in the order Ichthyodectiformes. It contains a single species, C. coroninii, from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) of Slovenia. A potential specimen is also known from the Albian-aged Pietraroja Plattenkalk of southern Italy, but it has been suggested that this specimen actually represents Cladocyclus.

Calamopleurus is a prehistoric genus of marine holostean ray-finned fish from the Early Cretaceous of South America and northern Africa. It was a relative of the modern bowfin, with both belonging to the family Amiidae.

Araripichthys is an extinct genus of marine ray-finned fish that lived from the Aptian to Coniacian stages of the Cretaceous period. The genus is named after the Araripe Basin, where it was found in the Crato and Santana Formations. Other fossils of the genus have been found at Goulmima in Morocco, the Tlayua Formation of Mexico and the Apón Formation of Venezuela.

Aethalionopsis is an extinct genus of prehistoric freshwater bony fish from the Early Cretaceous of western Europe. Formerly classified as a species of the elopiform Anaethalion, it is now known to be a relative of the modern milkfish (Chanos) in order Gonorhynchiformes. It was previously placed as a basal member of the suborder Chanoidei, but is now more often placed as a basal member of the subfamily Chaninae of the family Chanidae, placing it closer to the extant Chanos.

Anaethalion is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine and freshwater ray-finned fish related to modern tarpons and ladyfish. It is known from the Late Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous of Europe and northeasterrn Asia, roughly encompassing the Tethys Ocean.
Clupavus is an extinct genus of marine ray-finned fish that lived during the middle of the Cretaceous period. It is known from North Africa, Europe, Brazil, and possibly North America.

Crossognathiformes is an extinct order of ray-finned fish that lived from the Late Jurassic to the Eocene. Its phylogenetic placement is disputed; some authors have recovered it as part of the teleost stem group, while others place it in a basal position within crown group Teleostei. Other placements have found it to be polyphyletic, with Varasichthyidae being stem-group teleosts whereas the other, "true" crossognathiforms are crown-group teleosts within Teleocephala.
The Aoufous Formation is a geological formation that contains some of the vertebrate assemblage of the Kem Kem Group, of Late Cretaceous date. It underlies the Ifezouane Formation and overlies the Akrabou Formation.

Pseudocorax is an extinct genus of mackerel sharks that lived during the Late Cretaceous. It contains six valid species that have been found in Europe, the Middle East, North Africa, and North America. It was formerly assigned to the family Anacoracidae, but is now placed in its own family Pseudocoracidae along with Galeocorax. The former species "P." australis and "P." primulus have been reidentified as species of Echinorhinus and Squalicorax, respectively.

Concavotectum is an extinct genus of freshwater plethodid ray-finned fish that lived during the Cenomanian in Morocco and possibly Egypt. It was discovered and named in 2008 and is known from a single well preserved hand-sized skull and a few isolated vertebrae discovered in the Kem Kem Group. The type species, C. moroccensis, was named in 2008 and described in 2010.

Paraisurus is an extinct genus of mackerel sharks that lived during the Cretaceous. It contains four valid species, which have been found in Europe, Asia, North America, and Australia. A fifth species, P. amudarjensis, is now considered a synonym of P. compressus. While this genus is mostly known from isolated teeth, an associated dentition of P. compressus was found in the Weno Formation of Texas. It went extinct around the Albian-Cenomanian boundary, as a supposed Coniacian occurrence of "P. sp." is likely a misidentified pseudoscapanorhynchid.
The Sainte-Barbe Clays Formation is a geological formation in Belgium. It is found in localised areas of the northern margin of the Mons Basin, alongside the equivalently aged Hautrage and Baudour Clay Formations. It is Upper Barremian-Lower Aptian in age. It predominantly consists of laminated clay, with some lignite. It is well known for the "Iguanodon sinkhole" locality near Bernissart where many specimens of Iguanodon bernissartensis were described by Louis Dollo in the late 19th century.
















