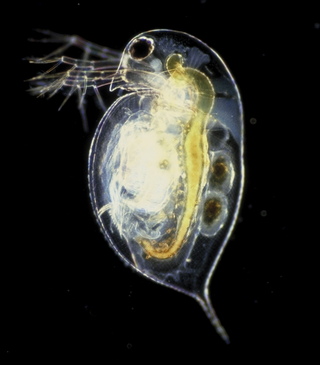
Daphnia is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, 0.2–6.0 mm (0.01–0.24 in) in length. Daphnia are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. Daphnia spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds.

The common gallinule is a bird in the family Rallidae. It was split from the common moorhen by the American Ornithologists' Union in July 2011. It lives around well-vegetated marshes, ponds, canals, and other wetlands in the Americas. The common gallinule is one of the most conspicuous rail species in North America, along with the American coot.

Francolins are birds in the tribe Gallini that traditionally have been placed in the genus Francolinus, but now commonly are divided into multiple genera.

The eastern wolf, also known as the timber wolf, Algonquin wolf and eastern timber wolf, is a canine of debated taxonomy native to the Great Lakes region and southeastern Canada. It is considered to be either a unique subspecies of gray wolf or red wolf or a separate species from both. Many studies have found the eastern wolf to be the product of ancient and recent genetic admixture between the gray wolf and the coyote, while other studies have found some or all populations of the eastern wolf, as well as coyotes, originally separated from a common ancestor with the wolf over 1 million years ago and that these populations of the eastern wolf may be the same species as or a closely related species to the red wolf of the Southeastern United States. Regardless of its status, it is regarded as unique and therefore worthy of conservation with Canada citing the population in eastern Canada as being the eastern wolf population subject to protection.

The hartebeest, also known as kongoni or kaama, is an African antelope. It is the only member of the genus Alcelaphus. Eight subspecies have been described, including two sometimes considered to be independent species. A large antelope, the hartebeest stands just over 1 m at the shoulder, and has a typical head-and-body length of 200 to 250 cm. The weight ranges from 100 to 200 kg. It has a particularly elongated forehead and oddly-shaped horns, a short neck, and pointed ears. Its legs, which often have black markings, are unusually long. The coat is generally short and shiny. Coat colour varies by the subspecies, from the sandy brown of the western hartebeest to the chocolate brown of the Swayne's hartebeest. Both sexes of all subspecies have horns, with those of females being more slender. Horns can reach lengths of 45–70 cm (18–28 in). Apart from its long face, the large chest and the sharply sloping back differentiate the hartebeest from other antelopes. A conspicuous hump over the shoulders is due to the long dorsal processes of the vertebrae in this region.

In biology, a species complex is a group of closely related organisms that are so similar in appearance and other features that the boundaries between them are often unclear. The taxa in the complex may be able to hybridize readily with each other, further blurring any distinctions. Terms that are sometimes used synonymously but have more precise meanings are cryptic species for two or more species hidden under one species name, sibling species for two species that are each other's closest relative, and species flock for a group of closely related species that live in the same habitat. As informal taxonomic ranks, species group, species aggregate, macrospecies, and superspecies are also in use.

Introgression, also known as introgressive hybridization, in genetics is the transfer of genetic material from one species into the gene pool of another by the repeated backcrossing of an interspecific hybrid with one of its parent species. Introgression is a long-term process, even when artificial; it may take many hybrid generations before significant backcrossing occurs. This process is distinct from most forms of gene flow in that it occurs between two populations of different species, rather than two populations of the same species.

The Indochinese box turtle, Vietnamese box turtle, or flowerback box turtle is a species of Asian box turtles from China, northern and central Vietnam, Laos, and possibly northeastern Cambodia. It is found in high altitude woodland where it tends to hide in the undergrowth. There is considerable confusion as to the taxonomy of this species with several subspecies being recognised by some authorities. and not by others. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as "critically endangered".

Desmarest's hutia or the Cuban hutia is a stout, furry, rat-like mammal found only on Cuba and nearby islands. Growing to about 60 cm (2 ft), it normally lives in pairs and feeds on leaves, fruit, bark and sometimes small animals. It is the largest living hutia, a group of rodents native to the Caribbean that are mostly endangered or extinct. Desmarest's hutia remains widespread throughout its range, though one subspecies native to the nearby Cayman Islands went extinct shortly after European colonization in the 1500s.

The Moluccan flycatcher or dark-grey flycatcher is a species of bird in the family Monarchidae. It is endemic to Indonesia.

The prehensile-tailed hutia is a small, furry, rat-like mammal found only in forests on Cuba. It is the only member of the genus Mysateles. It climbs and lives in trees where it eats only leaves, and it is threatened by habitat loss. The prehensile-tailed hutia is a member of the hutia subfamily (Capromyinae), a group of rodents native to the Caribbean that are mostly endangered or extinct.
Daphnia occidentalis is a species of crustacean in the family Daphniidae. It is endemic to Australia, and is the only species in the subgenus Australodaphnia.

The Capreolinae, Odocoileinae, or the New World deer are a subfamily of deer. Alternatively, they are known as the telemetacarpal deer, due to their bone structure being different from the plesiometacarpal deer subfamily Cervinae. The telemetacarpal deer maintain their distal lateral metacarpals, while the plesiometacarpal deer maintain only their proximal lateral metacarpals. The Capreolinae are believed to have originated in the Middle Miocene, between 7.7 and 11.5 million years ago, in Central Asia.

Neotamias is a genus of chipmunks within the tribe Marmotini of the squirrel family. It contains 23 species, which mostly occur in western North America. Along with Eutamias, this genus is often considered a subgenus of Tamias.
Carla Cáceres is a professor at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign known for her research in population, community and evolutionary ecology, focusing on the origins, maintenance, and functional significance of biodiversity within ecosystems. She is a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, the Ecological Society of America, and the Association for the Sciences of Limnology and Oceanography

Cabot's tern is a species of bird in subfamily Sterninae of the family Laridae, the gulls, terns, and skimmers. It is found in the eastern U.S. and Middle America, the Caribbean, Trinidad and Tobago, and in every mainland South American country except Bolivia and Paraguay.

Daphnia longispina is a planktonic crustacean of the family Daphniidae, a cladoceran freshwater water flea. It is native to Eurasia. D. longispina is similar in size and sometimes confused with the often sympatric D. pulex, but much smaller than D. magna. D. longispina is found in a wide range of standing freshwater bodies from small, ephemeral rock-pools to large lakes.
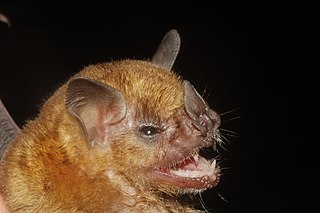
Sturnira honurensis is a species of bat found in Central America. Previously, it was considered a subspecies of the highland yellow-shouldered bat, but it has been considered distinct since 2010.
John Langdon Brooks (1920-2000) was an American evolutionary biologist, ecologist and limnologist.
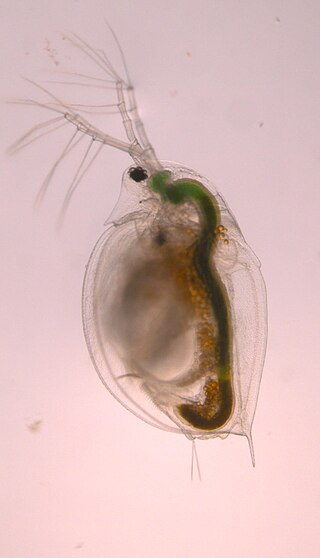
Daphnia pulicaria is a species of freshwater crustaceans found within the genus of Daphnia, which are often called "water fleas," and they are commonly used as model organisms for scientific research. Like other species of Daphnia, they reproduce via cyclic parthenogenesis. D. pulicaria are filter-feeders with a diet primarily consisting of algae, including Ankistrodesmus falcatus, and they can be found in deep lakes located in temperate climates. Furthermore, D. pulicaria are ecologically important herbivorous zooplankton, which help control algal populations and are a source of food for some fish. D. pulicaria are closely related to Daphnia pulex, and numerous studies have investigated the nature and strength of this relationship because these species can produce Daphnia pulex-pulicaria hybrids. In recent years, D. pulicaria along with other Daphnia species have been negatively affected by invasive predators, such as Bythotrephes longimanus.
















