
Daucus is a worldwide genus of herbaceous plants of the celery family Apiaceae of which the best-known species is the cultivated carrot. Daucus has about 75 species. The oldest carrot fossil is 1.3 Ma, and was found on the island of Madeira in the Atlantic Ocean.

Lepidium is a genus of plants in the mustard/cabbage family, Brassicaceae. The genus is widely distributed in the Americas, Africa, Asia, Europe, and Australia. It includes familiar species such as garden cress, maca, and dittander. General common names include peppercress, peppergrass, pepperweed, and pepperwort. Some species form tumbleweeds. The genus name Lepidium is a Greek word meaning 'small scale', which is thought to be derived from a folk medicine usage of the plant to treat leprosy, which cause small scales on the skin. Another meaning is related to the small scale-like fruit.

Hypoxis is a genus of flowering plants of the family Hypoxidaceae. The genus has an "almost cosmopolitan" distribution, occurring in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Australia. Europe lacks native species. Most species are in the Southern Hemisphere, especially in southern Africa. Common names for the genus include star-grass, star lily, yellow stars, African potato, and stars. The genus is the largest of the Hypoxidaceae and has its centre of variation in South Africa, where it occurs in open undisturbed grasslands. The name Hypoxis was taken over by Linnaeus in 1759 from a name coined by Paul Reneaulme in 1611 for a superficially similar species of Gagea and meaning "a little sour", referring to the taste of that plant's leaves.

Atriplex cinerea, commonly known as grey saltbush, coast saltbush, barilla or truganini, is a plant species in the family Amaranthaceae. It occurs in sheltered coastal areas and around salt lakes in the Australian states of Western Australia, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and New South Wales. The species is also known to be present in the Waimea inlet in New Zealand, although has historically been found in Boulder Bank, D'Urville Island, and Palliser Bay.

Stackhousia is a genus of annual and perennial plants in the family Celastraceae that are native to Australia, New Zealand, Malesia and Micronesia. The genus was first described by James Edward Smith in Transactions of the Linnean Society of London in 1798.

Hibiscus diversifolius, the swamp hibiscus, is a widespread species of hibiscus. It grows to between 1 and 2 metres in height, with prickly stems and yellow flowers with a maroon basal spot during spring summer.
Amphibolis antarctica is a species of flowering plant in the family Cymodoceaceae. It is referred to by the common names wire weed or sea nymph, and is a seagrass found in coastal waters of southern and western Australia.

Disphyma crassifolium subsp. clavellatum is the subspecies of Disphyma crassifolium that occurs in Australia and New Zealand. It is sometimes known by the common name rounded noon-flower

Brachyscome ciliaris, commonly known as variable daisy, is a small bushy perennial herb with a prominent flower, which occurs throughout most of temperate Australia

Bulbine semibarbata, commonly known as leek lily, native leek or wild onion, is a species of annual herb native to Australia.

Melilotus indicus, sometimes incorrectly written Melilotus indica, is a yellow-flowered herb native to northern Africa, Europe and Asia, but naturalized throughout the rest of the world.

Erodium cygnorum is a species of herb native to Australia.

Euchiton sphaericus, the star cudweed or tropical creeping cudweed, is a herb native to Australia, New Zealand, New Caledonia, Taiwan, Java, and Philippines. It has become naturalized in a few places in the United States.
Euphorbia tannensis is a species of herb or shrub native to Australia and some Pacific islands.

Parietaria debilis, commonly known as pellitory, small-flower pellitory, or native pellitory, is a herb native to Australia and New Zealand.
Plantago debilis is a species of herb native to Australia. Common names include shade plantain and weak plantain.
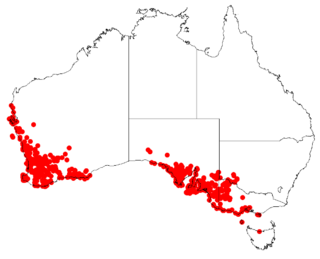
Podotheca angustifolia, commonly known as sticky longheads, is a species of herb native to Australia.
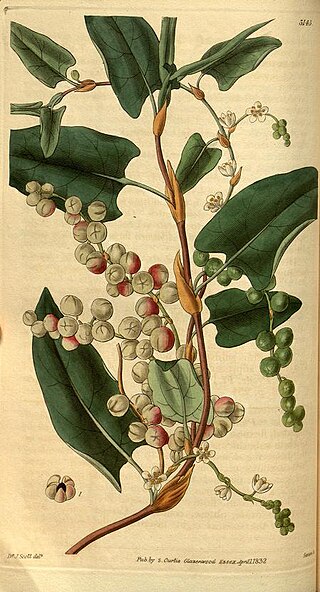
Muehlenbeckia adpressa, commonly known as climbing lignum, is a prostrate or climbing plant, native to Australia. It has thin red-brown stems up to 1 metre in length. The leaves are 1.5–6 centimetres (0.59–2.36 in) long and 1.5–3.5 centimetres (0.59–1.38 in) wide. It occurs in coastal areas of Western Australia, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and New South Wales.

Microlaena stipoides, synonym Ehrharta stipoides, is a species of grass. It occurs naturally in all states of Australia as well as in New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and the Philippines. It has also been introduced into Hawaii and Reunion Island and has been reported as invasive in both. Common names used include weeping grass, weeping rice grass and weeping meadow grass.

Gratiola peruviana, commonly known as austral brooklime, is a small perennial herb in the family Plantaginaceae. The species is native to South America and Australasia. It grows to between 10 and 30 centimetres high and has pink or white tubular flowers with red-purple stripes inside. These are followed by ovoid capsules that are up to 7mm long. The stem-clasping ovate leaves are arranged in opposite pairs and have shallowly toothed edges.

















